When you buy through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it turn .
In a first - of - its - kind discovery , theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) has detected piddle in the internal region of a magnetic disk of planet - forming natural gas and dust ring an infant star .
The detection is substantial because the water supply , along with other molecules needed to form worlds like Earth , were found close to several monolithic , youthful star that generate uttermost ultraviolet radiation radiation sickness . Such uttermost environment were previously thought to be unfit for the formation of rocky planets , but this fresh find suggest that terra firma - like planet may be capable of organize in a wide-eyed range of cosmic environments than once thought .
An illustration of a protoplanetary disk of planet-forming gas and dust around an infant star.
The finding could also help scientists better understand how the planets of thesolar systemformed around 4.5 billion year ago . The research also represents the first solution from JWST ’s eXtreme Ultraviolet Environments ( XUE ) program , which place to characterize the environments and chemical science of huge spinning phonograph record of debris , gas and stone that fence in star in their youth and eventually spawn planets , asteroidsand comets .
" The JWST is the only telescope with the spatial resolution and sensitivity to study major planet - forming disks in monolithic star - forming area , " team leaderMaría Claudia Ramírez - Tannus , a scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany , said in astatement .
Ramírez - Tannus and her fellow detailed the discovery in a paper published Nov. 30 inThe Astrophysical Journal Letters .
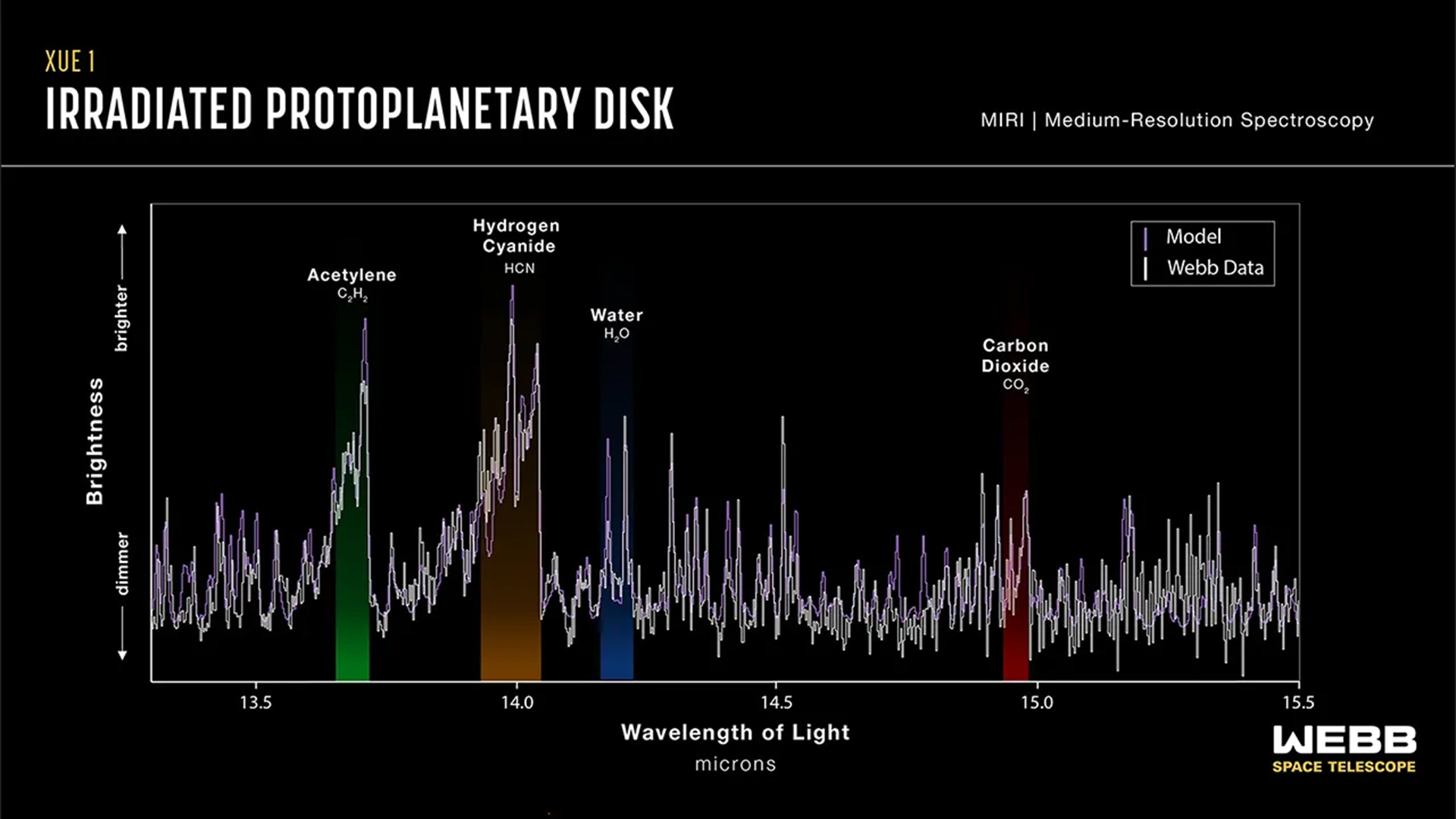
The spectrum of light from the protoplanetary disk, with water in its inner region highlighted in blue.
Related : James Webb telescope bring out ' glasshouse ' of 500,000 mavin in the chaotic warmheartedness of the Milky Way
James Webb Space Telescope is studying a cosmic lobster
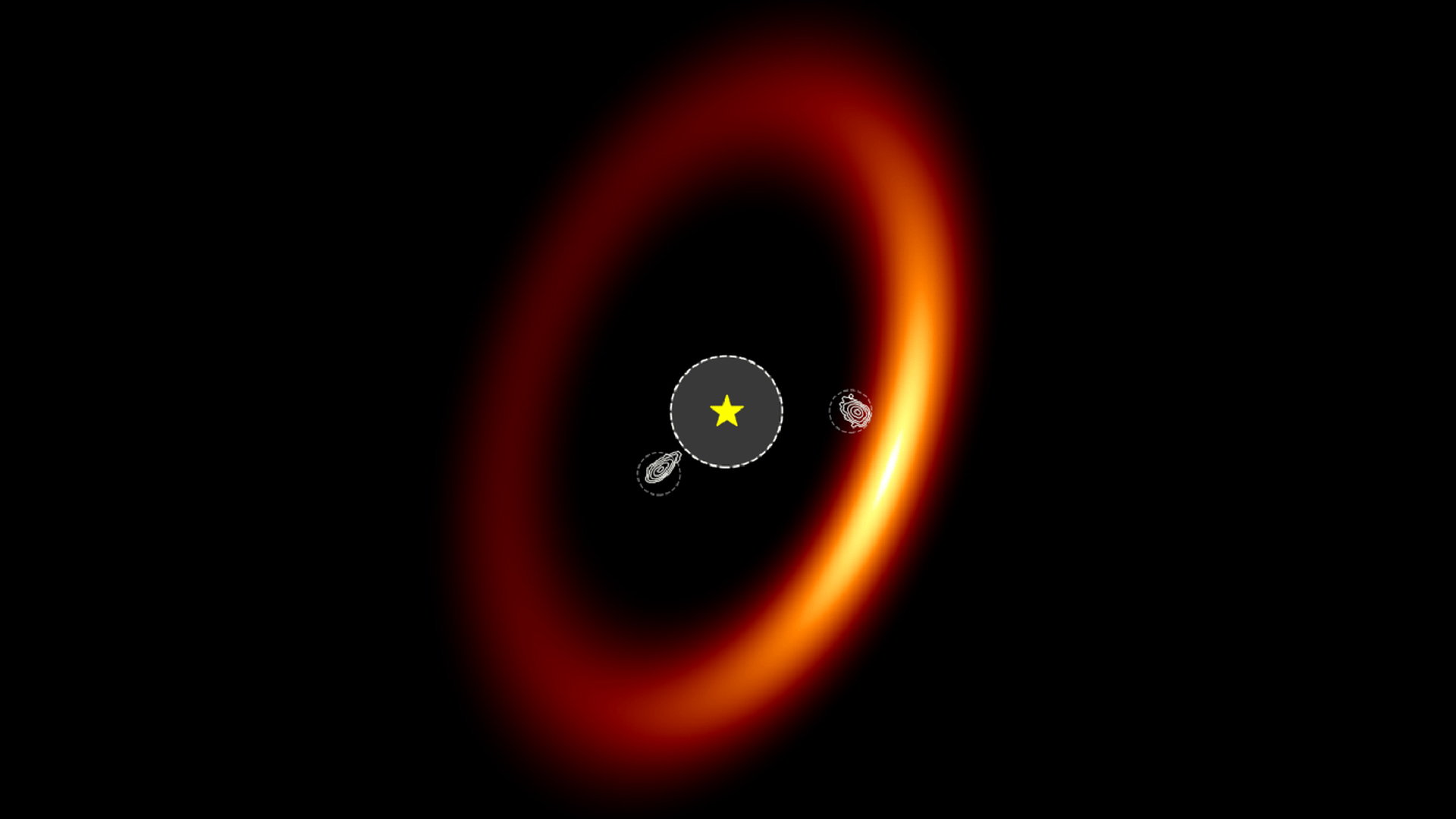
The first resultant from the XUE campaign get along from observations of a protoplanetary phonograph record designated XUE 1 , which is located in the principal cluster Pismis 24 .
XUE 1 is just one of 15 protoplanetary magnetic disk in NGC 6357 — also get laid as the " Lobster Nebula " and settle around 5,500 light years from Earth — being studied as part of the XUE program .
The Lobster Nebula is one of the untried and closest region of intense star birth to Earth . It also hosts some of the most massive stars in theMilky Way , which are hotter than star topology likethe sunand thus give out more ultraviolet visible radiation . This actinotherapy help take in the gas and dust that birthed these young , massive stars , meaning these protoplanetary disc ca n’t survive long around these red star ; they unremarkably last only 1 million years or so .
The team expected these observations to show that XUE 1 is constantly peril to gamey levels of ultraviolet radiotherapy , but they were surprised to detect that the protoplanetary disk is also packed with small , part crystalline silicate dust that could serve as the construction block for rocky planet . In addition to this silicate dust and water , the investigator found traces of molecules such as carbon monoxide , carbon dioxide , hydrogen nitril and acetylene .
" We were surprised and unrestrained because this is the first clip that these molecules have been detected under these extreme atmospheric condition , " sketch Colorado - author Lars Cuijpers , a investigator at Radboud University in the Netherlands , said in the statement .
— James Webb scope let on carbon paper compounds important to lifespan in star system 1,000 low-cal - days from Earth

— mammoth ' hole ' in the Sunday wider than 60 earth is spewing superfast solar wind powerful at us
— Mercury may have a ' potentially inhabitable ' area below its surface , salty glacier propose
Because the conditions found in the XUE 1 protoplanetary magnetic disk near massive stars are similar to the conditions found in other wiz - forming regions confining to Earth that are live with low - deal stars , the squad ’s finding support the idea that it ’s common for rocky planets across the Milky Way to work around star of differing masses and in a broader range of environment than scientists had previously thought .

" XUE 1 shows us that the conditions to form rocky planet are there , so the next step is to check how coarse that is , " Ramírez - Tannus said . " We will observe other disks in the same part to define the frequency with which these conditions can be observed . "













