When you buy through tie on our site , we may garner an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it mold .
Astronomers using theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) may have identify the smallest star in the hump universe — or at least , the smallest known target that began forming like a star , before fizzling out as a so - called brown dwarf .
" One basic head you ’ll determine in every uranology textbook is , what are the smallest stars?,“Kevin Luhman , an astronomer at Pennsylvania State University and go generator of a new paper on the foreign object , say in astatement . " That ’s what we ’re stress to answer . "
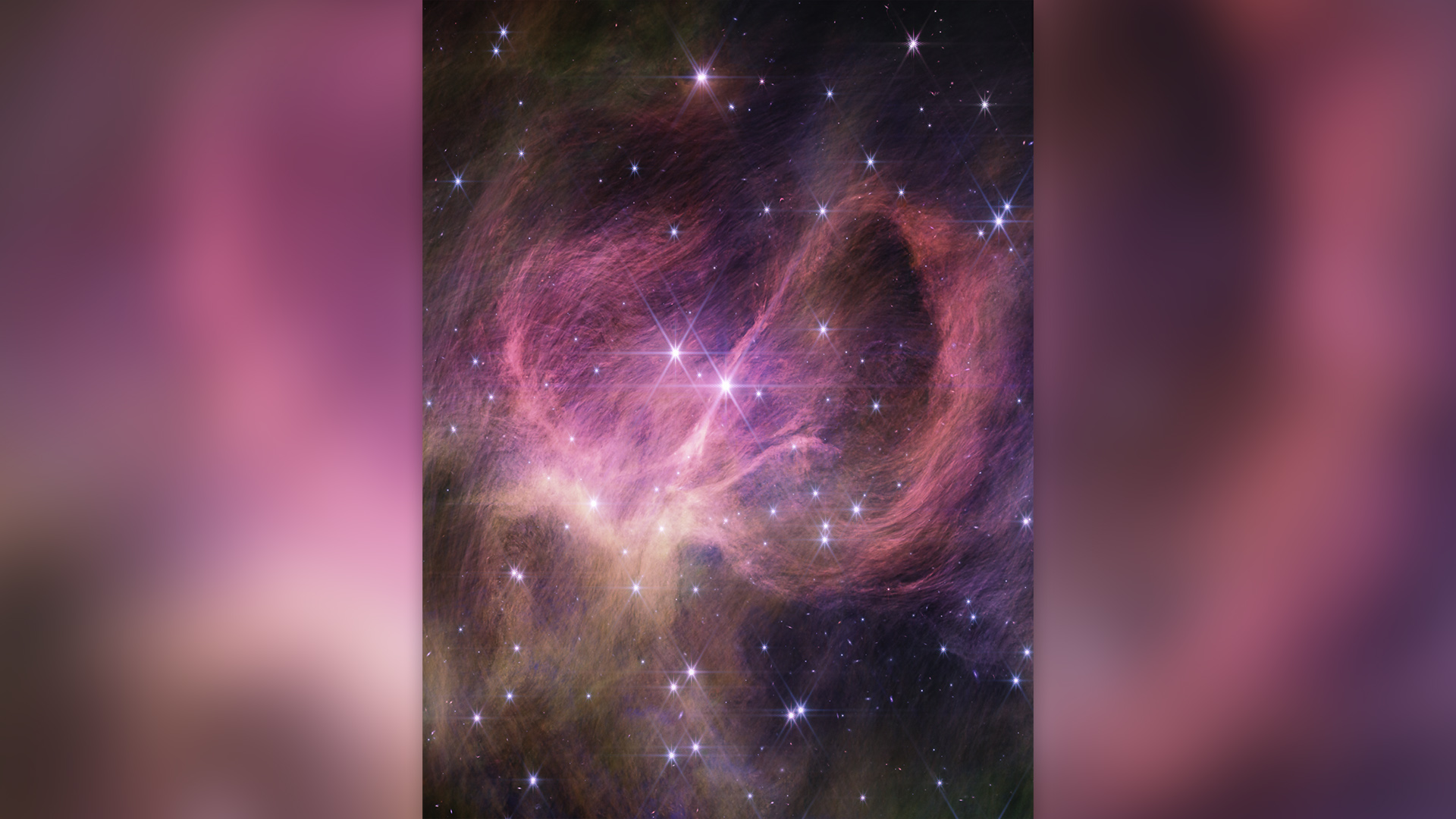

An image of the central portion of the star cluster IC 348 from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
Using the JWST , Luhman and his team spot the tiny proto - star in a star cluster named IC 348 , which is located 1,000 light - yr from Earth . The object is likely to be a brown gnome , a character of celestial object that blurs the line between planet and star . The researcherspublishedtheir findings on Dec. 13 in theAstronomical Journal .
Brown dwarfsare not quite wizard , but they come close . Essentially , they are stars that failed to ignite , realise them the unflattering moniker " failed stars . " Brown dwarf are not massive enough to get typical hydrogenfusionin their cores . However , they do have enough hoi polloi to utter light and heat from fusing a specialised character of H , called heavy hydrogen . Deuterium is a static form of hydrogen with an added neutron , whereas normal hydrogen only has a proton in its nucleus .
Related : What ’s the large planet in the cosmos ?
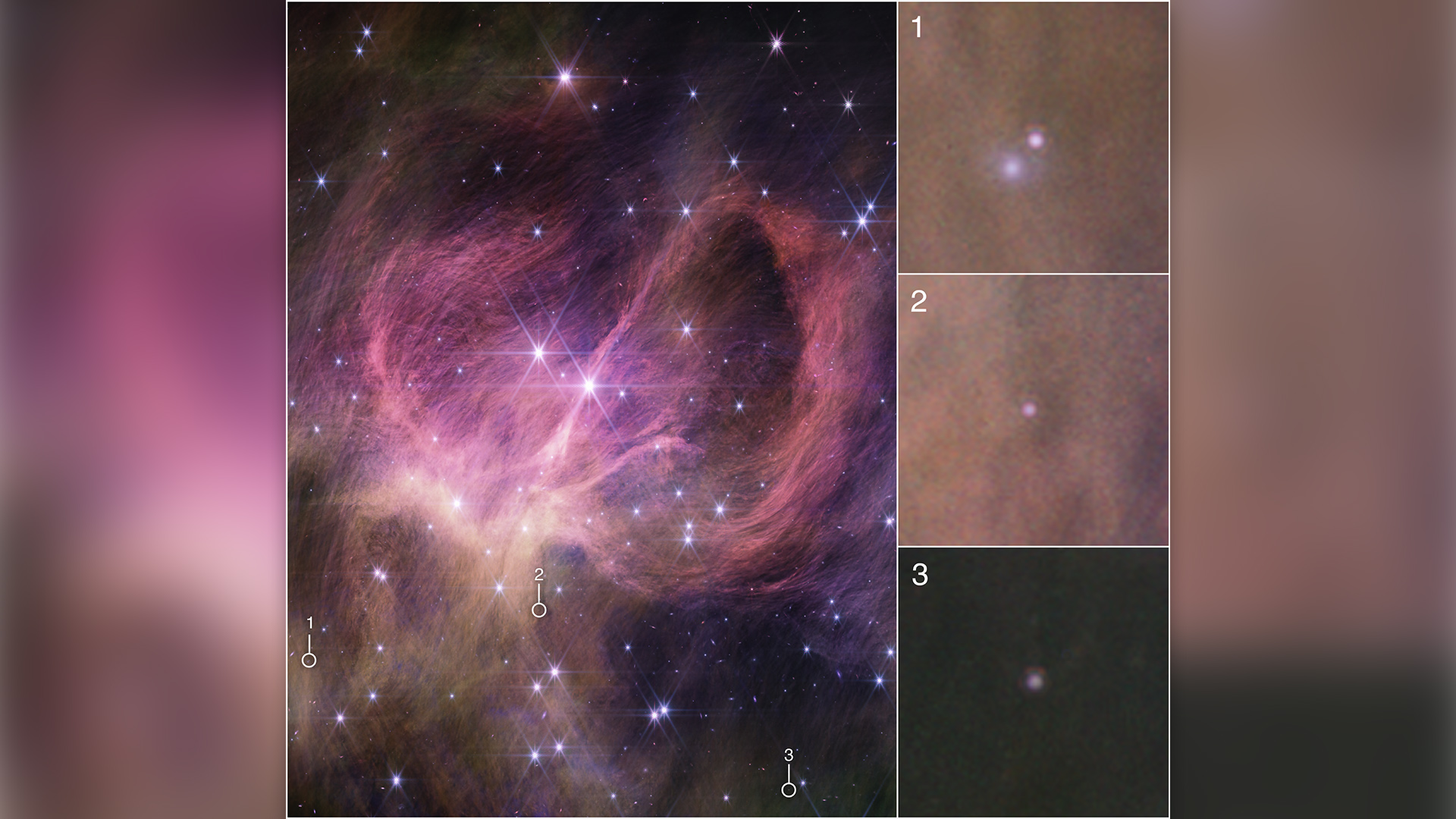

This image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope shows the central portion of the star cluster IC 348, including three brown dwarfs that are less than eight times the mass of Jupiter, which are circled in the main image and shown in the pullouts at right. The smallest weighs just three to four times Jupiter, challenging theories for star formation.
Most star are incredibly dense compared to even the biggest major planet ; our own sunshine is about 1,000 times the mountain ofJupiter , the gravid satellite in oursolar organization , but its diameter is only 10 times that of Jupiter , according toNASA . In equivalence , a large brown dwarf could pack about 80 Jupiters deep down . But this particular brownish nanus is only three or four time more massive than Jupiter — easily making it the smallest " star , " or star - like object , ever discover . It is also very young ; the star topology cluster that it belong to to is just 5 million eld former .
In addition to being minuscule , the brown midget and its neighbors appear to have an intriguing atom floating around in their atmospheres , the team found . The researchers detect a spectral signature from an unidentified hydrocarbon , a corpuscle that take some of the rude fixings for life as we have it away it . NASA ’s Cassini probe observe the same molecular signature in the atmosphere of Saturn ’s moon Titan , but this is the first prison term it has been seen outside of the solar organization .
— Bizarre unexampled cosmic aim is the most magnetized star in the universe

— Bizarre ' failed star ' the sizing of Jupiter is 2,000 degrees hotter than the Lord’s Day
— first evidence of atomic nuclear fission in asterisk hints at component ' never produced on Earth '
" Models for brown dwarf atmospheres do n’t predict its being , " field of study co - authorCatarina Alves de Oliveira , an astronomer at theEuropean Space Agency , said in the statement . " We ’re wait at object with younger long time and low masses than we ever have before , and we ’re image something unexampled and unexpected . "

have together , these observations could help investigator paint a clearer picture of how headliner form — and how they give out . The researcher go for that future work will reveal even pocket-size leading object , as well as any lilliputian true stars that may be cover nearby .