When you purchase through tie-in on our site , we may realize an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
TheJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) would be capable to spy the star sign of our civilization on Earth if it was spying on us from another star scheme in theMilky Way , a novel study shows . The determination raises Hope that the nation - of - the - art spacecraft could detect alien civilization as it stares out toward distant world in our galaxy .
Since launch in recent 2021 , JWST has been preponderantly peering out into thedeepest reaches of the cosmosin search of clues about how the early universe formed . But one of the telescope ’s secondary objectives is to take apart the ambiance of nearby exoplanets , or planet beyond thesolar system , to look for gases produced by biological life , known as biosignatures , and chemical produce by advanced foreign civilizations , known as technosignatures .

A new study suggests that the James Webb Space Telescope could detect Earth’s human civilization from across the galaxy
Related : Are stranger genuine ?
But despite being the most advanced scope currently in surgical operation , it is still indecipherable how well JWST will be able to spot the tell - tale signs of sound life . To answer this head , researchers resolve to test whether the space scope could successfully notice level-headed life from the only planet in the universe that is known to be both habitable and presently inhabited — Earth .
In the new study , uploaded to the pre - print serverarXivon Aug. 28 , researcher consider a spectrum of Earth ’s air and deliberately decreased the quality of the data to mimic how it would attend to an observer dozens of light - years away . The team then used a computing gadget model , which replicated JWST ’s sensor capabilities , to see if the spacecraft could detect the cardinal biosignatures and technosignatures from the dataset , such as methane and oxygen , acquire by biological life , and nitrogen dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons ( CFCs ) , which are produced by humans .
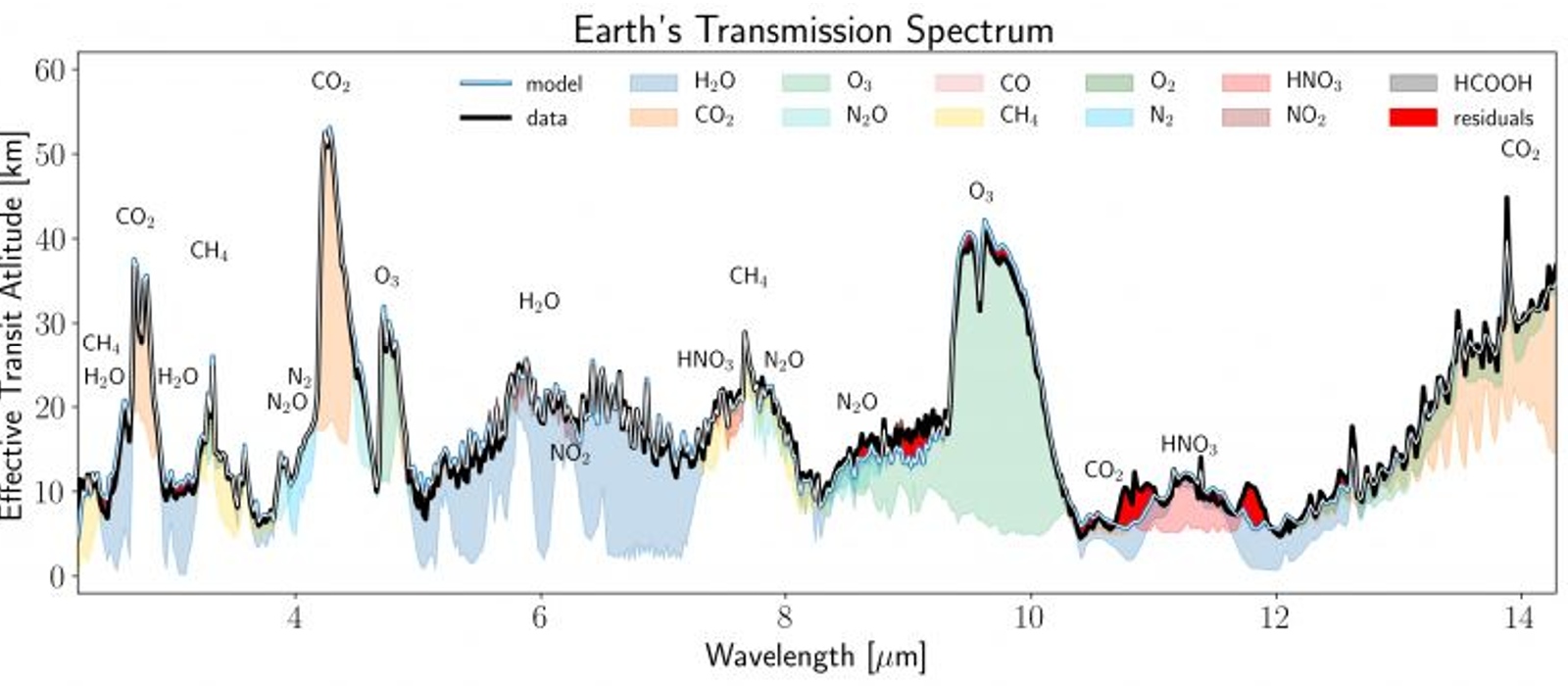
This graph shows the raw atmospheric data used in the new study. Specific biosignatures and technosignatures are highlighted in different colors.
The outcome , which have not yet been peer - refresh , show that JWST could in all likelihood detect all the key marker of non - healthy and intelligent life in our major planet ’s atmosphere .
Related : There may be hundreds of gazillion of habitable satellite in the Milky Way , raw subject suggest
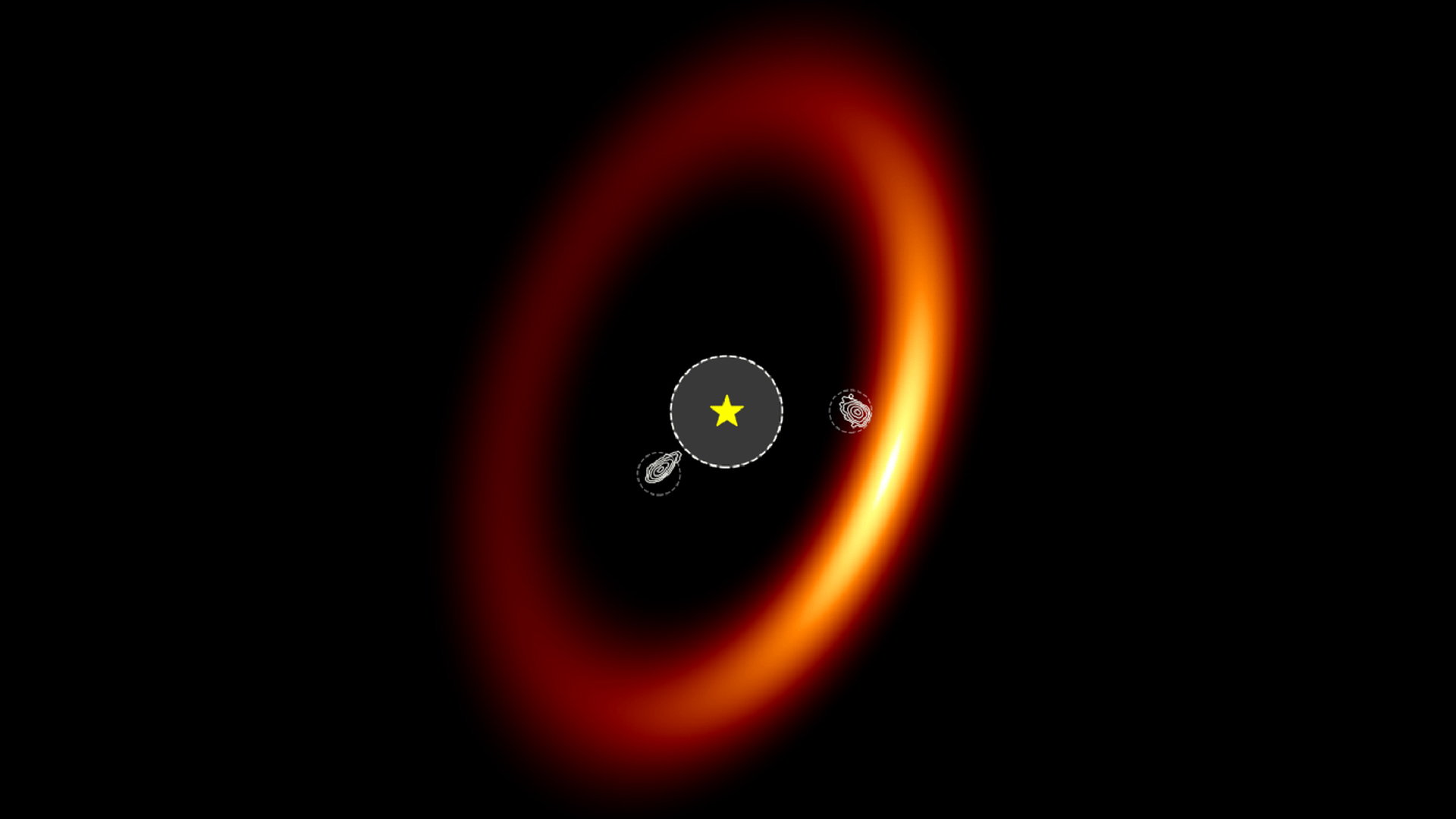
The researchers noted that the quality of the modify dataset is just about equivalent to JWST observations of planets from TRAPPIST-1 — a star system containing seven exoplanets that orbit a red midget star around 40 light - class from Earth . This suggests the telescope should be able to find life or alien civilisation on exoplanets within 40 sluttish - years of Earth . But the team believes JWST could possibly notice signs of extraterrestrial living up to 50 clear - years from Earth .

An artist’s interpretation of what the TRAPPIST-1 system might look like.
Only around 20 exoplanets have been officially discovered within a 50 - light - year radius of Earth , but based on the number of suspect star in this part of place , expert omen that there may actually be as many as 4,000 exoplanets within JWST ’s compass , according toProject EDEN , an international astronomical collaborationism dedicate to finding potentially habitable planet close to Earth .
However , this does n’t guarantee that JWST would be able-bodied to discover life on other planets .
discover biosignatures and technosignatures on other domain " may prove challenging to translate without contextual knowledge about the habitable environment , " the research worker wrote . In this study , the team already knew which markers to look for , but on an exoplanet with dissimilar conditions and alternating potential life-time forms or technologies those life - signatures may not be as obvious , they add .

— James Webb telescope reveals the cosmos may have far fewer alive ignominious holes than we guess
— James Webb scope detects the earliest strand in the ' cosmic web ' ever see
— ' Wrinkle in space - time ' enables James Webb to seize stunning figure of most distant principal ever detected

JWST has already made some interesting discoveries about exoplanets near Earth . The telescopespotted urine on the Neptune - size exoplanet GJ 1214b , which is around 40 promiscuous - years from Earth , and come up that TRAPPIST-1b , the second - closest exoplanet to the star in the TRAPPIST-1 system , likely has no air at alldue to its extreme heat energy . The spacecraft also glimpse agigantic dust storm in the atmosphere of VHS 1256 b , a " super - Jupiter " exoplanet 40 light - old age from Earth .
Closer to home , JWST has also detectedgiant geysers spout out of Saturn ’s moon Enceladus , which could contain the chemical ingredients require for sprightliness . And further out into the creation , the space vehicle has alsoglimpsed potentially life-time - give carbon compounds in an baby star systemmore than 1,000 light - years from Earth .