When you buy through link on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Modern observation made by theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) have further cement one of the most bizarre observation in all of cathartic — that the universe expanded at dissimilar amphetamine across varying degree of its lifetime .
The conundrum , referred to as the Hubble tenseness , has fuel a disputation among stargazer that could alter or even upend the field wholly .

A dense cluster of bright stars, each with six large and two small diffraction spikes, due to the telescope’s optics.
In 2019 , measure by theHubble Space Telescopeconfirmed the job was real . Then in 2023 and 2024 , even more exact measuring from JWSTappeared to corroborate the discrepancy .
Now , further measurements have used the enceinte sample of JWST data collected over its first two years in space to further cement the problem . The Modern physics that could do the mystery remains ill-defined but , as the researchers outline in a newspaper publisher bring out Dec. 9 in theThe Astrophysical Journal , the tenseness is not going anywhere .
" The more oeuvre we do the more it is patent that the causal agent is something much more interesting than a telescope defect . Rather it is likely a lineament in the cosmos , " lead work author and Nobel laureateAdam Riess , professor of natural philosophy and uranology at Johns Hopkins University , state Live Science . " [ The ] next steps are many . More data on many front end and new estimate are needed . "
Related : After 2 years in blank space , the James Webb scope has broken cosmology . Can it be fixed ?
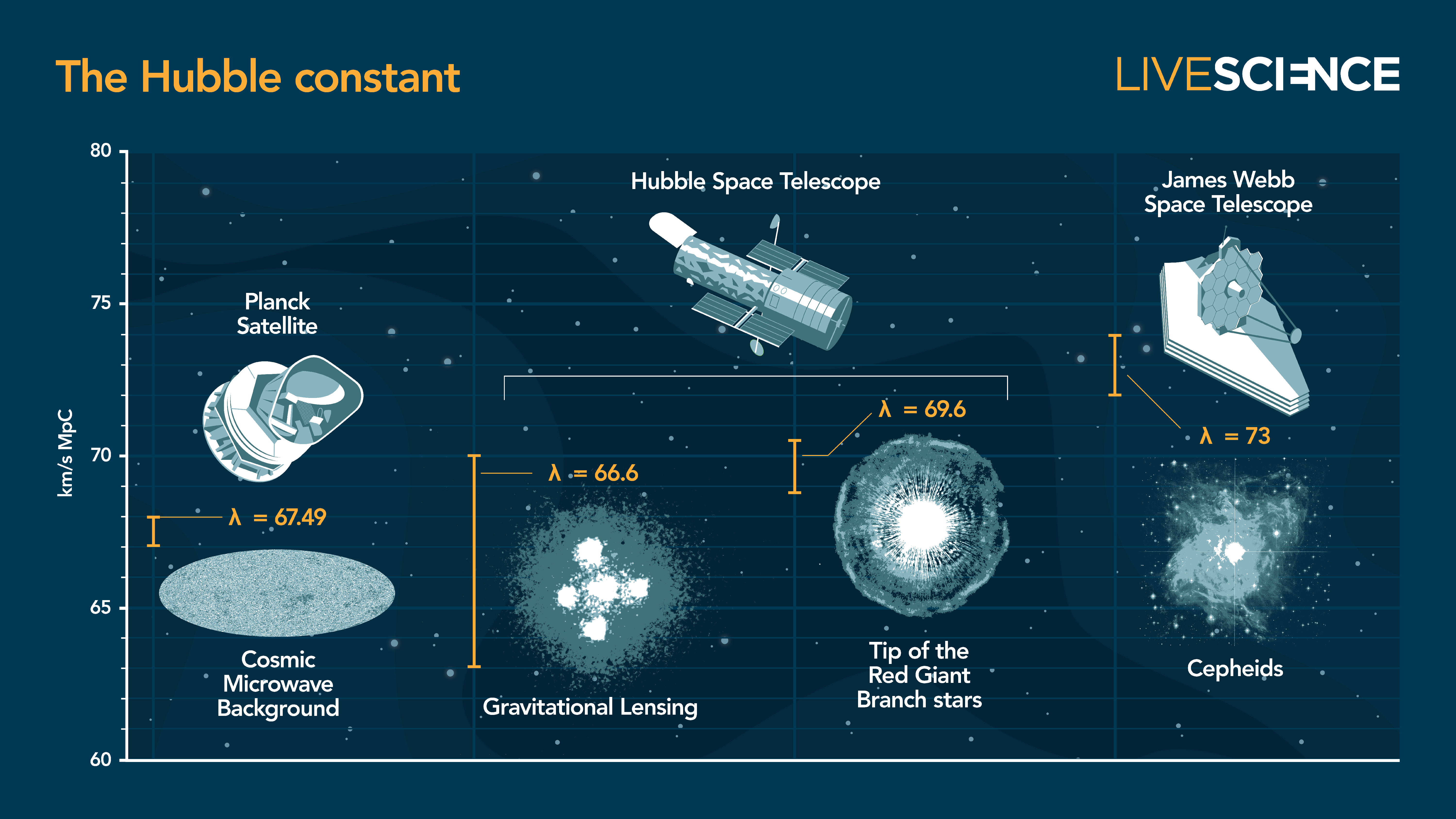
There are two gold - standard methods for picture out the Hubble constant quantity , the note value that quantifies the speed of the universe ’s enlargement . The first is taken by measuring tiny fluctuations in the cosmic microwave screen background — an ancient snapshot of the universe ’s first lightness produced just 380,000 years after theBig Bang .
Aftermapping out this microwave oven hissusing theEuropean Space Agency’sPlanck orbiter , cosmologist inferred a Hubble constant of roughly 46,200 mph per million clean - years , or roughly 67 klick per 2d per megaparsec ( km / s / Mpc ) . This , alongsideother measurements of the former universe , aligned with theoretical prediction .

The 2d method lock at closer distances and in the universe ’s later animation using pulsating stars calledCepheid variables . Cepheid stars are tardily die , and their outer layers of helium gas grow and quail as they absorb and exhaust the star ’s radiation , prepare them sporadically flicker like distant signal lamp .
As Cepheids get bright , they pulse more slowly , enabling stargazer to measure the champion ' intrinsic brightness . By comparing this brightness level to their maintain brightness level , astronomers can chain Cepheids into a " cosmic distance ravel " to peer ever deeperinto the universe ’s past .
With this ladder in stead , and after anchoring the Cepheids ' brightnesses to explosions from Type Ia supernovae , astronomer can find a precise number for the universe ’s expansion velocity from how the flick stars ' brightness level has been stretched out , or redshifted . The Hubble invariable returned by this method is around 73 kilometer / s / Mpc : a value far outside of the wrongdoing reach of the Planck measurements .

Related:‘It could be profound ' : How astronomer Wendy Freedman is trying to fix the universe
Astronomers have offered various explanation for the cause of this disagreement , with some seek to tease out thepossibility of systematic errorwithin the results . Meanwhile , Riess and his squad have been cement the tautness withincreasingly preciseand wider - encompassing studies .
This new study is yet another link in this mountain chain . continue around a third of the sample size of the 2019 Hubble study , the fresh analysis used JWST to quantify the sample ’s Cepheid distances to within 2 % truth — a large advance on Hubble ’s precision of 8 - 9 % .

— ' It could be profound ' : How stargazer Wendy Freedman is attempt to fix the existence
— James Webb telescope discovers former black hole in the universe
— 8 sensational James Webb Space Telescope find made in 2023

Cross - checking these results with other distance - appraise stars such as carbon rich stars and bright red giants return a note value of 72.6 km / s / Mpc , make it nearly identical to Hubble ’s original measurement .
Exactly what could be causing the strange mismatch is unreadable ( " I wish I knew , " Riess told Live Science ) . But supposition is prevailing among astronomers .
One opening is " something missing in our savvy of the early universe , such as a young component of matter — earlydark energy[the deep phenomenon push back cosmic enlargement ] — that gave the universe an unexpected rush after the big bang,“Marc Kamionkowski , a cosmologist at Johns Hopkins University who help calculate the Hubble invariable and who was not involve in the bailiwick , enounce in a statement . " And there are other idea , like laughable saturnine matter dimension , exotic particle , changing electron mass , or aboriginal charismatic field that may do the whoremonger . Theorists have permission to get pretty creative . "












