When you buy through link on our land site , we may garner an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it ferment .
uranologist have used the James Webb and Hubble space telescopes to affirm one of the most perturbing brain-teaser in all of physical science — that the universe come out to be expanding at bafflingly dissimilar speed depending on where we appear .
This trouble , known as the Hubble Tension , has the potential drop to spay or even upend cosmogeny altogether . In 2019 , mensuration by theHubble Space Telescopeconfirmed the puzzle was veridical ; in 2023 , even more precise measurements from theJames Webb Space Telescope(JWST ) cemented the discrepancy .
Illustration of the expansion of the Universe.
Now , a triple - confirmation by both scope working together appears to have put the possibility of any measurement mistake to bed for upright . The study , published February 6 in theAstrophysical Journal Letters , suggests that there may be something seriously incorrect with our savvy of the universe .
refer : After 2 class in distance , the James Webb telescope has break up cosmology . Can it be fix ?
" With measurement error negate , what stay is the material and exciting possible action we have misunderstood the cosmos , " lead study authorAdam Riess , professor of physics and astronomy at Johns Hopkins University , said in a statement .
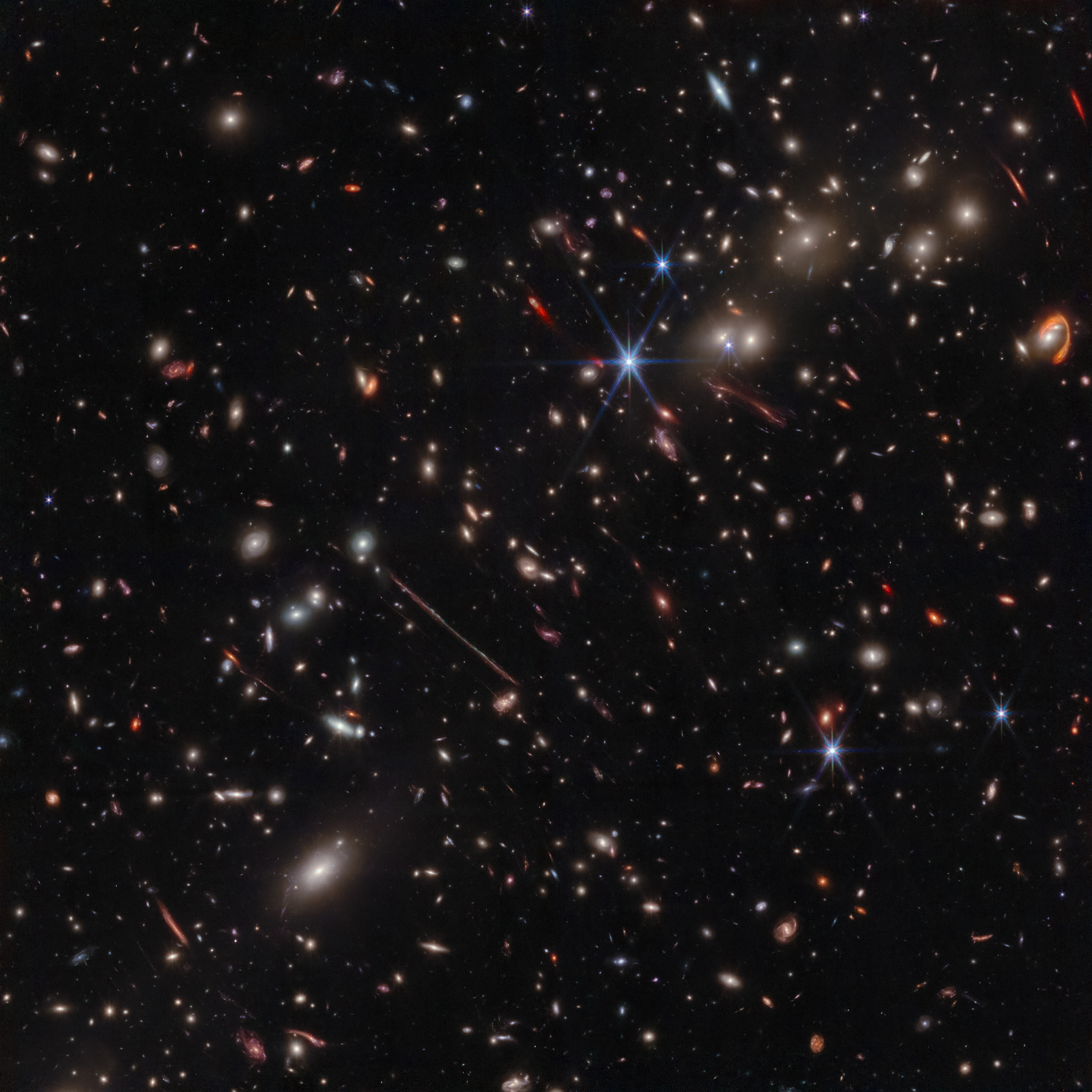

JWST’s infrared cameras allow it to look at the universe in more precise detail than any telescope before it.
Reiss , Saul Perlmutter and Brian P. Schmidtwon the 2011 Nobel Prize in physicsfor their 1998 discovery ofdark energy , the mysterious force behind the universe of discourse ’s speed up expansion .
Currently , there are two " gold - banner " methods for figuring out the Hubble invariable , a time value that report the enlargement pace of the universe . The first involve concentrate over tiny fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background signal ( CMB ) — an ancient keepsake of the universe ’s first luminosity produced just 380,000 years after theBig Bang .
Between 2009 and 2013 , astronomers map out this microwave oven fuzz using theEuropean Space Agency ’s Planck satellite to infer a Hubble invariable of roughly 46,200 mph per million light - years , or about 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec ( km / s / Mpc ) .

The 2nd method uses pulsating stars call Cepheid variable . Cepheid stars are dying , and their outer layers of He gas grow and shrivel up as they suck and unloosen the star ’s radioactivity , making them sporadically flitter like distant signal lamp .
As Cepheids get brilliant , they pulse more slowly , cave in stargazer a means to measure their absolute luminousness . By comparing this luminousness to their observe brightness , astronomers can chain Cepheids into a " cosmic distance ravel " to peer ever deeperinto the universe ’s past . With this ladder in place , astronomers can find a exact turn for its enlargement from how the Cepheids ' illumination has been stretched out , or red - tilt .
Related : Mysterious ' unparticles ' may be pushing the macrocosm asunder , newfangled theoretic discipline suggests

But this is where the mystery begins . According to Cepheid variable measurement demand by Riess and his colleagues , the universe ’s elaboration charge per unit is around 74 kilometer / s / Mpc : an impossibly high value when equate to Planck ’s measurements . Cosmology had been hurtle into chartless territory .
" We would n’t call it a tenseness or job , but rather a crisis,“David Gross , aNobel Prize - gain astronomer , say at a 2019 league at the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics ( KITP ) in California .
Initially , some scientists retrieve that the disparity could be a result of a measuring error triggered by the blending of Cepheids with other stars in Hubble ’s aperture . But in 2023 , the investigator used the more accurateJWSTto confirm that , for the first few " rungs " of the cosmic ladder , their Hubble measurements were ripe . Nevertheless , the theory of crowding further back in the macrocosm ’s past rest .

— ' It could be profound ' : How astronomer Wendy Freedman is trying to desexualize the universe
— James Webb scope discover old black hole in the universe of discourse
— 8 stunning James Webb Space Telescope discoveries made in 2023

To resolve this issue , Riess and his colleagues build on their premature measurements , observing 1,000 more Cepheid stars in five host Galax urceolata as remote as 130 million light - year from Earth . After comparing their data to Hubble ’s , the uranologist affirm their past mensuration of the Hubble constant .
" We ’ve now spanned the whole range of what Hubble observe , and we can rule out a measurement error as the suit of the Hubble Tension with very high confidence , " Riess said . " Combining Webb and Hubble give us the best of both worlds . We detect that the Hubble measurements remain reliable as we climb far along the cosmic distance run . "
In other row : the latent hostility at the heart of cosmology is here to stay .












