When you purchase through link on our site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Left unbridled , the space around our planet could get so cluttered with dust that we might not be able to use some orbits anymore , agree to the latestEuropean Space Agency(ESA ) paper on the blank environs .
Thereport , published April 1 , state that although new standards to curb place dust are becoming more widely adopted , they are n’t enough to keep the junk currently in orbit from collide with itself — make dangerous detritus cloud in a runaway outgrowth know as " Kessler syndrome . "

Kessler syndrome will ‘threaten our future in space’ without active cleanup, a new report finds.
" Even if we created no Modern outer space debris , it would not be enough to prevent a runaway series of collision and fragmentations , " ESA order in astatement . " The actual number of space debris objects larger than 1 centimeter in size – large enough to be capable of cause ruinous damage – is estimated to be over 1.2 million , with over 50,000 objects of those larger than 10 cm . "
Impact by a 1 cm diameter object ( about the size of a pea ) could disable crucial planet system , fit in to ESA , while anything big could potentially puncture theInternational Space Station(ISS ) . " Anything heavy than 10 cm could shatter a satellite or spacecraft into pieces , " the agency’sstatementsaid , after a petite fragment only a few one-thousandth of a millimetre across left a 7 mm chip in the ISS ’s glass windows in 2016 .
Related : Space junk : How broken artificial satellite are creating a scraps crisis in the sky
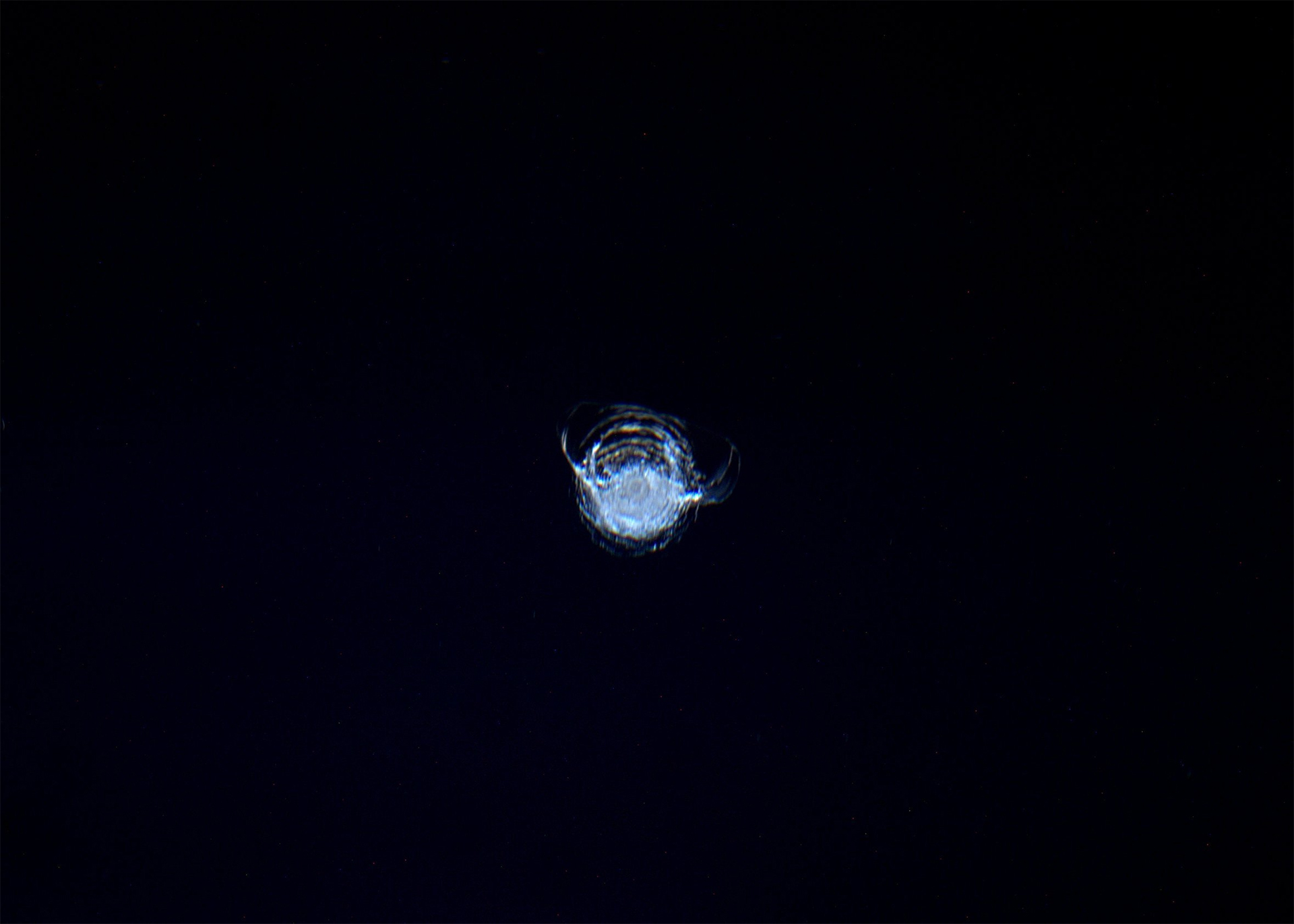

A 7-millimeter diameter chip in one of the glass windows making up the International Space Station’s Cupola, caused by the impact of a tiny piece of space debris estimated to be less than a few thousandths of a millimeter wide.
The ESA report also discussed how late changes in space traffic are making the existing debris problem worse , paint a picture three major factors — dealings mass , spacecraft type and the act of commercial hustler — that should be considered when planning sustainable place operation .
The figure of launches taking place is higher now than it has ever been , and many of the spacecraft being plunge are smaller systems deploy as large constellations of spacecraft . In other words , there is a lot more likely dust being add up to electron orbit — at a prison term when there ’s already too much junk orbit Earth as it is .
Space dust does n’t stick around forever — some of it burn up in our atmosphere , and some of it crash back down to Earth . However , the debris currently leaving orbit is n’t enough to match the debris being added , even though " integral artificial satellite or rocket organic structure are now re - inscribe the Earth standard atmosphere on average more than three times a Clarence Day , " according to ESA .

— Falling metal space junk is changing Earth ’s upper atmosphere in ways we do n’t fully understand
— ISS dodges its 39th piece of potentially risky space junk . expert say it wo n’t be the last .
— How do petite pieces of blank space junk cause incredible damage ?
quad detritus makes more of itself by breaking aside into increasingly smaller pieces with every collision . There is n’t much in quad to slow down fragments hurtling around our satellite — they mostly keep go until they jar with something , or until their orbital cavity decays ( gets stuffy to Earth due to energy loss ) enough for the atmosphere to burn them up .
It ’s a poisonous bicycle : the more debris there is , the more chances there are for a hit to go on , and the more collision there are , the more debris is created .
To cut new detritus , the ESA is now recommending spacecraft be contrive to burn up within five years of the end of their lifetime , five times shorter than the late recommendation of 25 geezerhood . For the debris already circling the planet , the ESA read active remotion is the next step — before the problem escalates out of control condition . ESA’sClearSpace-1 commission , planned to launch in 2028 , will be the first mission to attempt to capture and take out a defunct satellite from eye socket , demonstrating combat-ready rubble remotion for the first time .

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to insert your showing name .











