When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
On Nov. 19 , theInternational Space Station(ISS)dodged a potentially dangerous piece of space junkleft in orbit from a planet that broke up in 2015 .
The maneuver , which demand the ISS farm its common celestial orbit of about 250 miles ( 440 kilometers ) above Earth ’s aerofoil , was the first of its form in 2024 . Without it , NASA officials saidthe flying objective could have come within a perilously close 2.5 Roman mile ( 4 km ) of the space station .
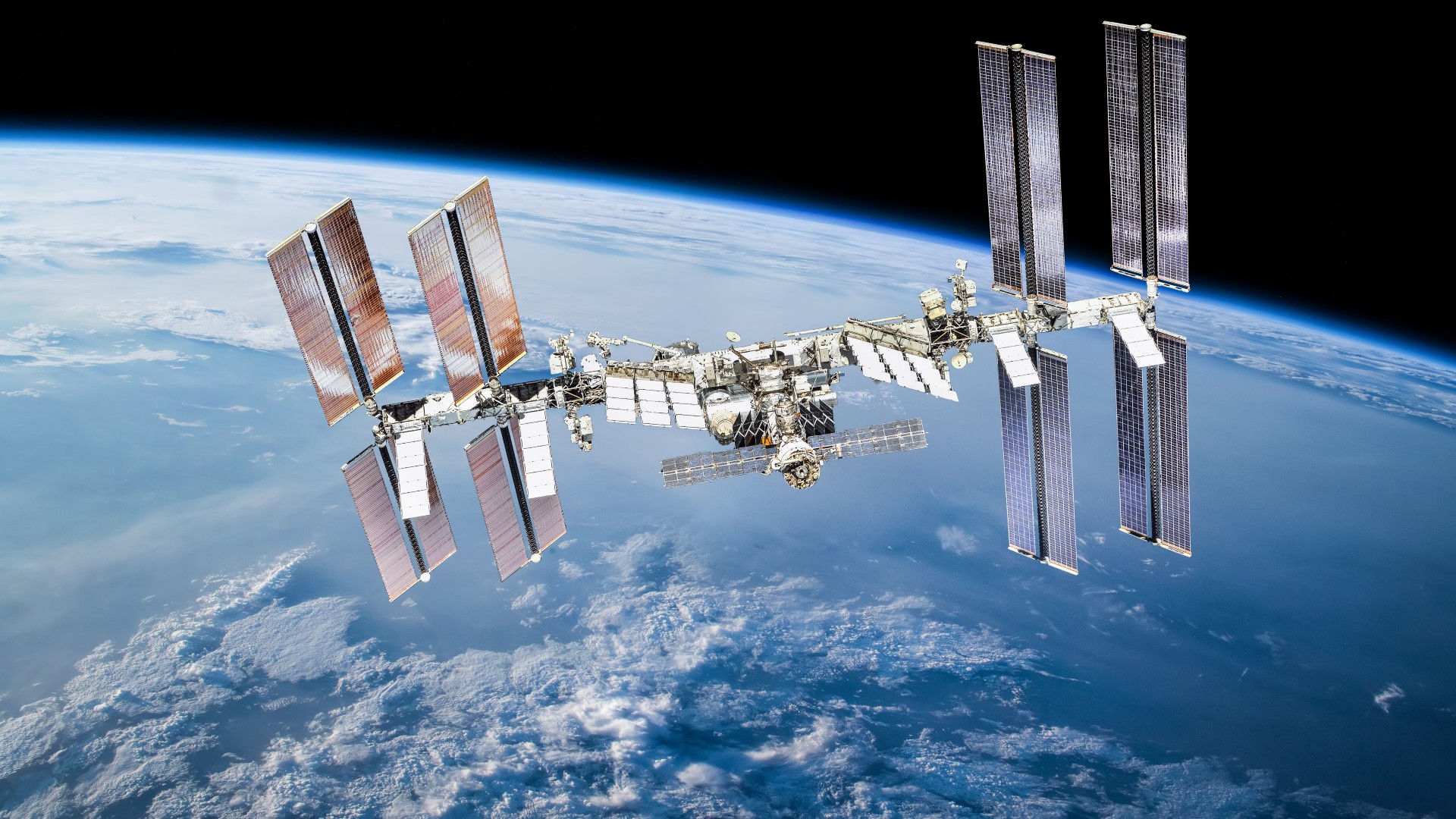

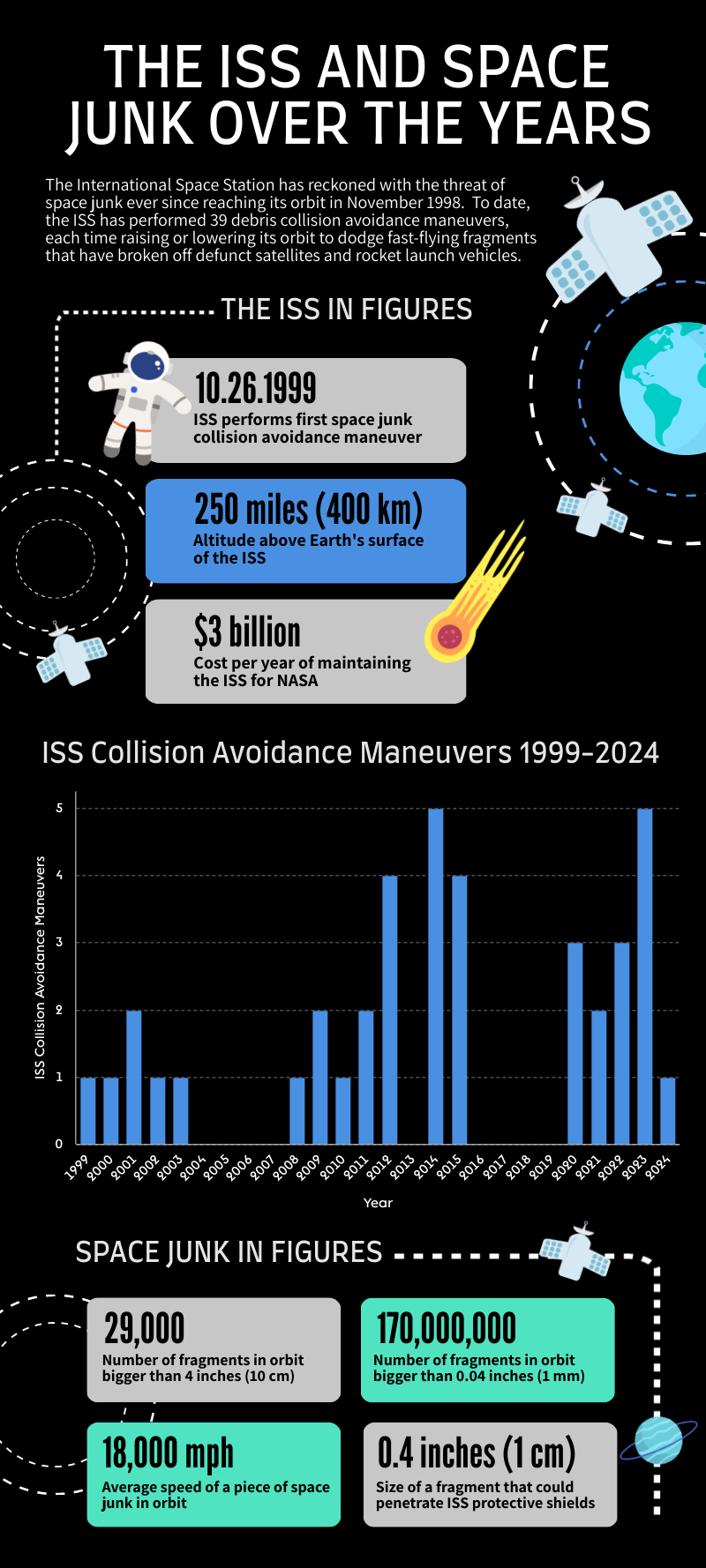
On Nov. 19, the ISS dodged a fragment of space junk in the 39th collision avoidance maneuver since the space station launched in November 1998.
outer space junkrefers to any fragment of homo - made machinery that remains in Earth ’s orbit after dish out its intended purpose . This twelvemonth ’s single scheme maneuver — technically call a Pre - determined Debris Avoidance Maneuver — mark a significant drop from the five similar maneuvers the ISS was force to perform in 2023 . It ’s also fewer thanthose performed in 2020 through 2022 , when the ISS change its orbit at least doubly per year to foreclose collisions with outer space detritus .
Astronauts aboard the ISS were favourable that so few piece of debris add up close enough to require maneuvers this year , but that credibly wo n’t last , saidHugh Lewis , a professor of astronautics and a space junk modeling expert at the University of Southampton in the U.K. " For all we know , next calendar week there will be three maneuvers , " Lewis told Live Science .
connect : Sci - fi - prompt tractor beams are substantial and could solve a major space junk trouble
Graph showing ISS collision avoidance maneuvers (red histogram) in relation to solar activity (black dots) and tracked ISS-orbit-crossing objects (blue circles) as of September 2022.
NASArecords show the tardy tactical maneuver is the 39th time the ISS has evade space junk since the first part of the ISS launched in November 1998 , and the risk of collisions is increasing every year due to farm amounts ofspace junk clogging up the sky .
The ISS receive warnings , or " conjunction messages , " about incoming place junk from the U.S. Space Force , although that responsibility may soon change hands , Lewis said . A fragment is count potentially speculative if experts forecast it will infix a pizza pie - box - shaped area that extends 2.5 by 30 by 30 miles ( 4 by 50 by 50 klick ) around the ISS . " Anything that function into that box , then that triggers the next form , " Lewis order , " and they keep going through that cognitive operation until they ’ve identified if there is a real risk . "
The brink to act on perceived risk of infection is much lower for the ISS than for other ballistic capsule because there are man on panel , Lewis enounce . " They ’re calculate at events typically that will be higher [ peril ] than 1 in 10,000 , " he said .
Graph showing ISS collision avoidance maneuvers (red histogram) in relation to solar activity (black dots) and tracked ISS-orbit-crossing objects (blue circles) as of September 2022.
It’s raining satellites
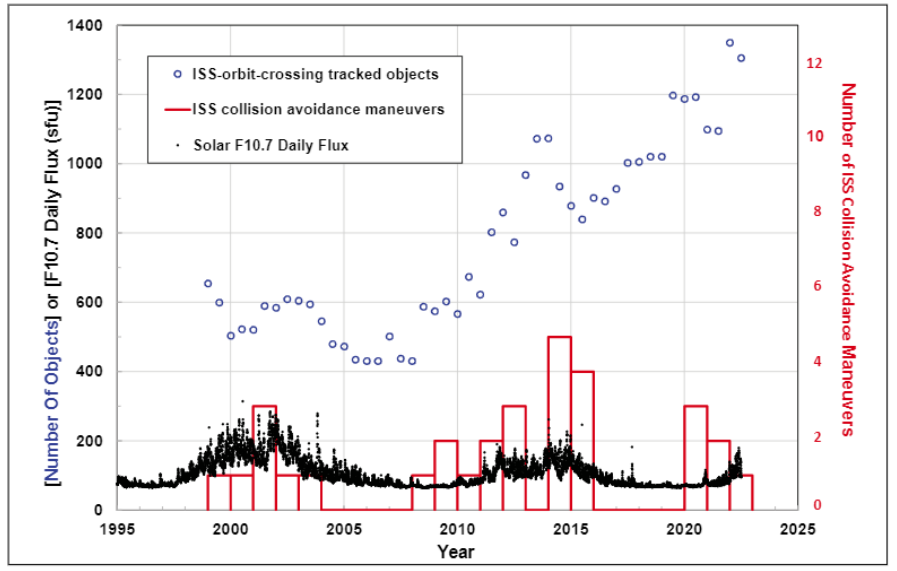
How often place junk approaches the ISS depends on several factor , including the Sunday ’s activity and " fragmentation events , " when satellites go against up in orbit , Lewis state .
Solar bodily function — includingcoronal mass projection , flares and in high spirits - speed winds — follows an 11 - yr cycle and peaks duringsolar level best , whichresearchers say is now underway . At solar level best , the sun emit a immense amount of vitality that gets absorbed by Earth ’s standard atmosphere and causes it to expand . This , in turn , increase the pull military group on objects in arena up to 1,200 miles ( 2,000 kilometre ) above Earth ’s surface , intend they get pulled toward the planet at a faster rate than in flow outside solar upper limit .
The effect of solar activity on space junk is a bit like falling rain , Lewis said . " The rain gets harder , if you like , during a solar upper limit , " so pieces of rubble are more likely to cross the broken ISS orbit , he tell . " You ’d expect to see more maneuvers during the solar maximum . "
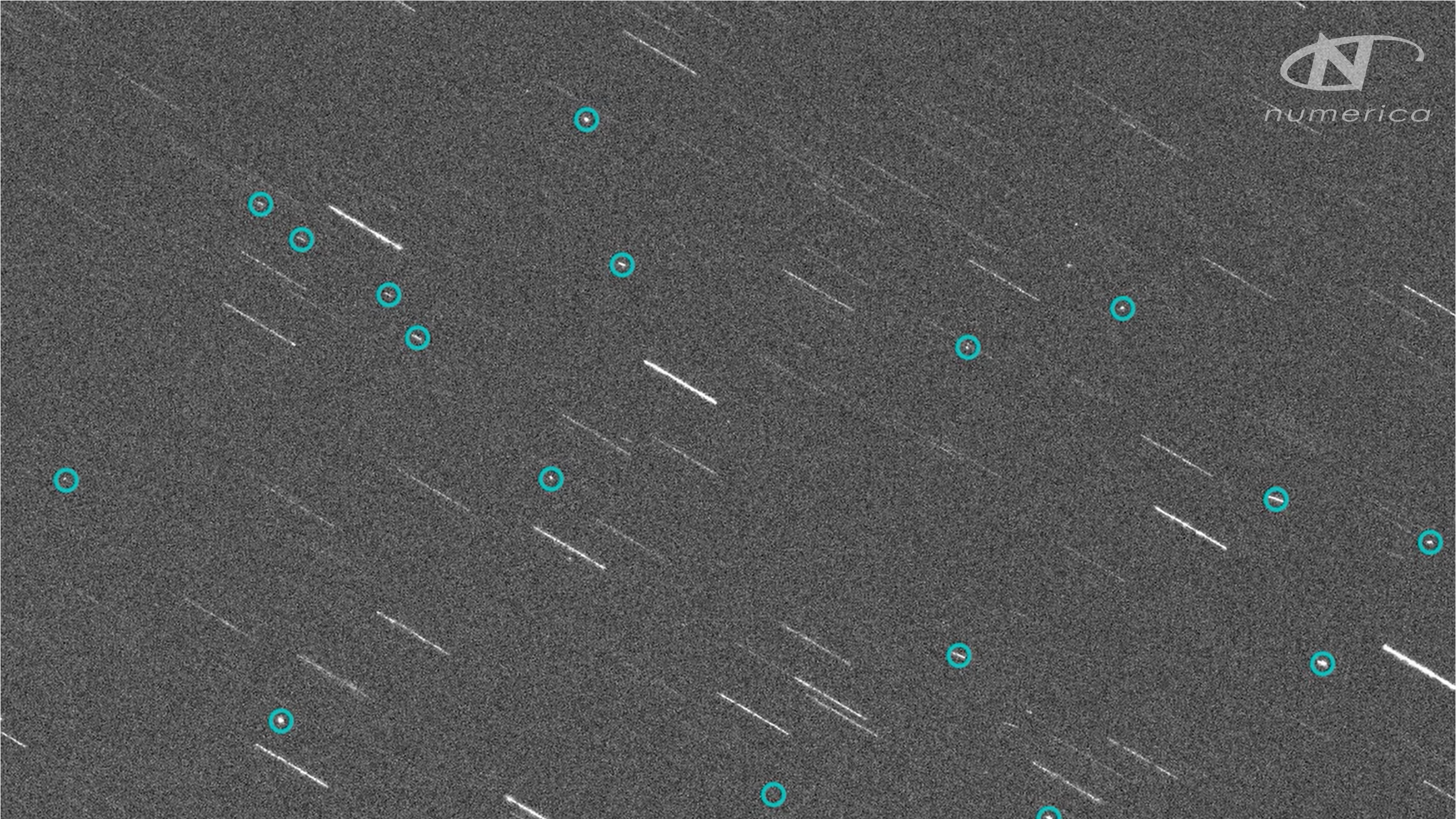
Telescope image showing a cloud of space junk after the destruction of a Russian satellite, Cosmos-1408, by a Russian anti-satellite weapon on Nov. 15, 2021. Space junk fragments are circled in light blue.
Yet the sun’sfast - growing activitythroughout 2024 does not seem to have had a major impact on collision risk with the ISS .
Anti-satellite tests
The impact of solar activity on the ISS is somewhat predictable , but less - foreseeable factors also affect blank junk hit risks . Anti - satellite ( ASAT ) tests , when area deliberately destroy satellites in area , are especially relate because they create a huge amount of debris that can linger for foresightful period , Lewis said .
In 2022 , the U.S. and other countriespledged not to conduct ASAT tests , butChina , Russia and India have not adopted the answer . NASA records show that aRussian antisatellite trial on Nov. 15 , 2021 , is responsible for almost half — four out of nine — of all ISS hit turning away maneuvers carried out in the past three years . The satellite in question , Cosmos-1408 , was a long - dead Soviet spacecraft launched in 1982 .
Another antisatellite test on a Formosan conditions satellite called Fengyun-1C in 2007 is responsible for at least four hit turning away maneuvers since then . China frivol away down the satellite at a height of 500 miles ( 800 klick ) above Earth ’s surface , which is much higher than the 300 - mile - high ( 480 kilometer ) orbit of Cosmos-1408 and explains why theISS had to swerve around Fengyun-1C debrisas latterly as August 2023 , Lewis aver .
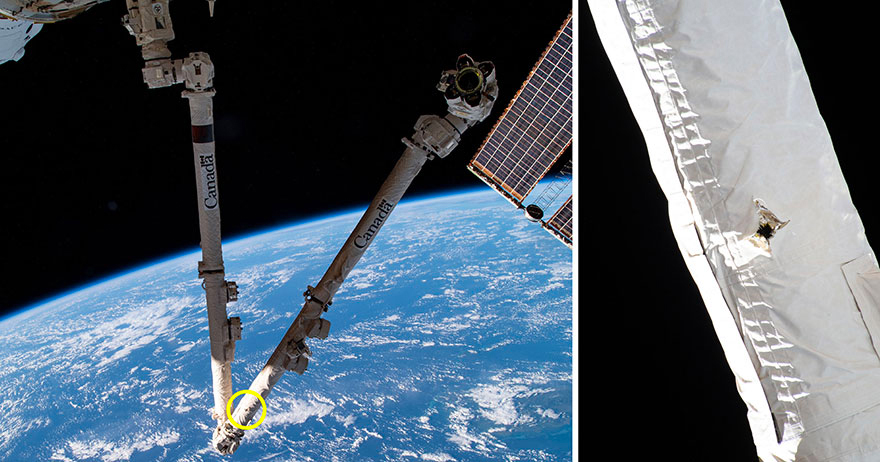

An inspection in May 2021 revealed that space junk had smacked into a robotic arm on the ISS, punching a hole in the cladding. The hole did not affect operations.
Space dust orbiting Earth at in high spirits altitude experiences much weaker drag than space dust in low orbits , meaning it lasts longer in orbit beforecrashing down through the atmosphere , Lewis said . The ISS is still at risk of infection from Fengyun-1C fragments as a result of the conditions satellite ’s high orbit , he aver . But " Cosmos-1408 was scummy , so the shard would n’t have endure as long . "
Clouds of junk
While the ISS has performed only one collision avoidance maneuver so far this year , a rarified event ask a cloud of distance detritus alsoforced astronauts to take shelterin a spacecraft docked to the blank post in June . The incident took place after a defunct Russian satellite broke aside in arena , sending more than 100 shard fly dangerously confining to the ISS .
In the case of such urgent events , there is no time to exchange the ISS ' orbit . " Those things have to be planned , " Lewis say . " You ca n’t just do them by flick a electric switch . "
The spaceman resumed normal mathematical process shortly thereafter , and there was no damage to the place station — but upshot like these have the potential to ruin the ISS , Lewis allege .

" The fragments are typically of a size that will go through any shielding on the distance place , and the infinite station is a pressurized scheme in a vacuum , " he said . " If you want an doctrine of analogy , blow up a balloon and stick a pin in it ; it ’s exactly the same process . "
The ISS is not the only space vehicle that start the endangerment of destruction by blank junk . Due to the f number at which objects traveling in arena , any operating satellite could become disused if it were to cross way of life with a fragment from a long - forgotten rocket . The middling piece of space junk reaches speeds of 18,000 mph ( 29,000 km / h ) , or almost seven times profligate than a bullet , consort to NASA .
Even a chip of paintcan induce irreparable damage at these speeds , and a 4 - inch ( 10 centimeter ) physical object trigger " a ruinous fragmentation of a typical artificial satellite , " concord to theEuropean Space Agency . Around 29,000 objects of this sizing or bombastic currently orbit Earth , but those form only a fraction of the more than 170 million piece — or 9,900 tons ( 9,000 metric tons ) — of debris estimated to be out there .

SpaceX’sStarlinksatellites illustrate the weighing machine of the problem , Lewis said . Between June 2023 and June 2024 , Starlink ’s fleet of 5,500 planet made near 75,000 play in aggregate to forbid collisions with quad junk . " The figure of conjunction messages that they would have received from the U.S. Space Force would have been in the millions , " Lewis tell .
Looking ahead
NASAplans to retire the ISS in 2031 , but until then , the outer space station will go forward to host experiment on behalf of NASA scientist and private contractors . And while it does so , the floating laboratory will belike have to perform many more quad junk dodging maneuvers , Lewis said .
— Japan capture first image of blank debris from orbit , and it ’s spookily arresting
— Boeing - made satellite shatters in electron orbit , and nobody eff why

— ' Lightning - like energy bursts ' could be used to track the 99 % of blank junk that ca n’t be come across from Earth
The trouble with space detritus is that it multiply : The more blank space debris there is in electron orbit , the great the risk of collisions becomes and the faster the mass of detritus maturate . Therefore , the best mitigation strategy is to remove satellites that have reached the end of their missions , Lewis tell .
" That has an enormous effect on the future population , because you ’re transfer objects from orbit , so they ca n’t be collision threats , " he say . ( The ISSwill be deorbitedat the end of its foreign mission . )

Most space agency and companies recognise the need for responsible demeanour in orbital cavity , Lewis say , and regulations aim to ensure that all actors are held to in high spirits standard . " go along a clean surroundings helps their bottom line of products , because they do n’t have to make as many maneuver , [ and ] they would n’t lose satellites in collisions , " Lewis said . " There is a purpose to those regularisation . "