When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
Antioxidantsare nature ’s weapon against harmful corpuscle called " free radicals , " which are incessantly created by the dead body as cell do their task . These precarious molecules can damage our cells and cause disease such as Cancer the Crab as we maturate .
Some antioxidants are made by the body , while others — like beta - provitamin A from carrot , lycopene from tomatoes and polyphenols from grapevine — come from a individual ’s diet . All are retrieve to preclude and set the cell damage , or " oxidative tenseness , " because of free base .

Supplements can make it easy to consume high quantities of antioxidants, sometimes with detrimental effects.
But given all their benefits , is it potential to have too many antioxidant ?
Research showsthat people whose diets are full of antioxidant - rich fruit , veggie and legumes tend to have a lower risk of cardiovascular disease , cancer and early decease from any movement . So it ’s easygoing to suppose that upping your antioxidant intake — by taking supplements , for instance — would be beneficial . But compared with food , supplements make it gentle to outmatch the recommend dose of antioxidants , which can actually be harmful .
relate : Does vitamin cytosine help with colds ?
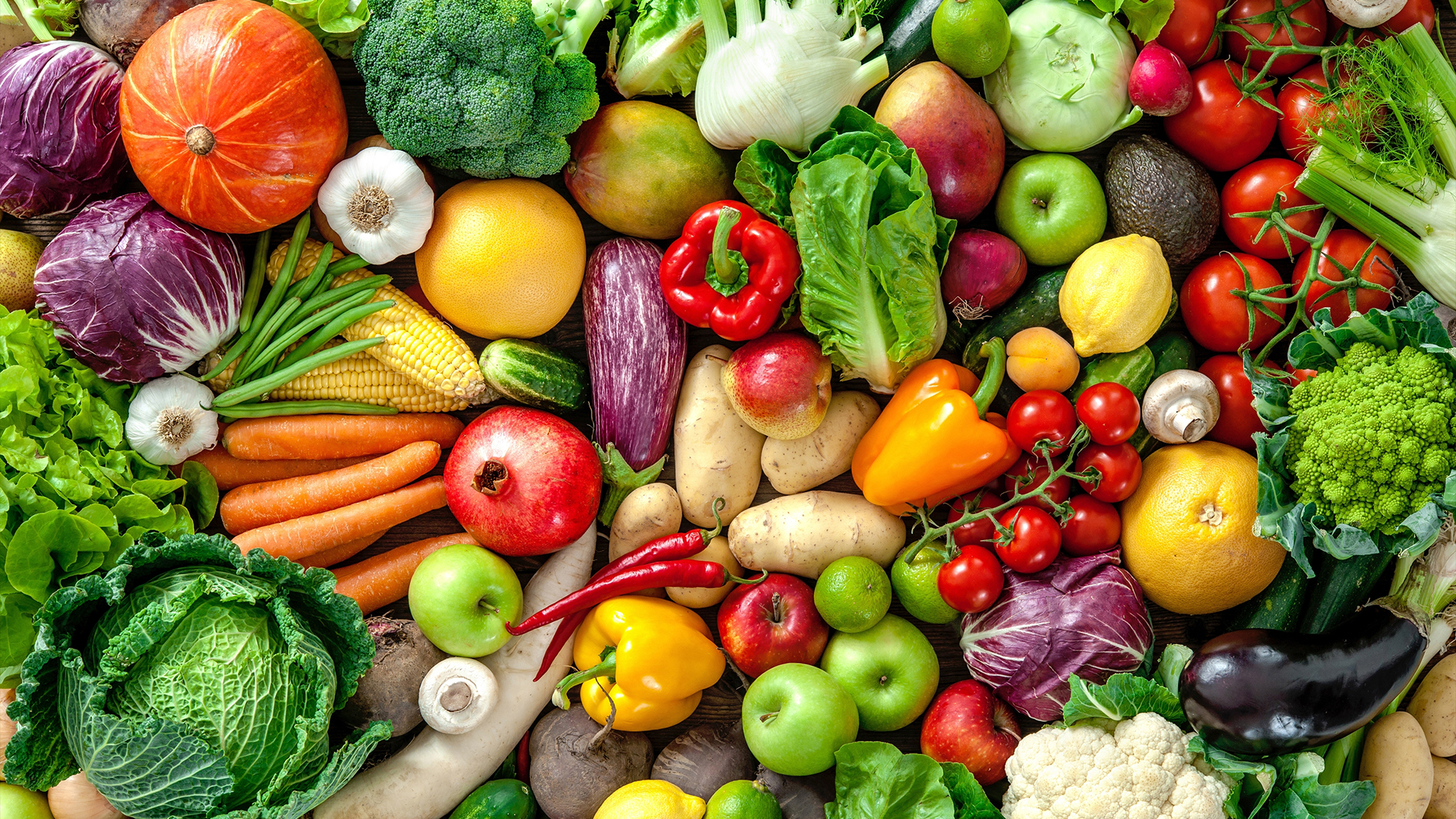

People who eat a diet full of antioxidant-rich fruits, vegetables and legumes have a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases, cancer and deaths from all causes.
Side effects of mellow antioxidant doses crop from balmy to very serious . On the milder goal , high amounts of genus Beta - provitamin A are known toturn the skin yellow or orange , which is visually prominent but not harmful , per se . Excessivevitamin Cintake can lead todigestive return , like diarrhea , sickness and abdominal spasm .
More gravely , gamey Lucy in the sky with diamonds of beta - provitamin A mayincrease the risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular diseasein individuals already at gamy risk for these disease , such as current and former smoking car and people who have been exposed to asbestos . There ’s also evidence fromstudies of animals and human tissuesuggesting that antioxidant can encourage the growth and cattle ranch of some cancers .
In addition , in high spirits - dosevitamin Esupplements have been shown tointeract with certain medicinal drug , such as acetylsalicylic acid , warfarin , tamoxifen and cyclosporine A. They ’ve also been splice to anincreased risk of exposure of former deathin citizenry with continuing disease .

These studies evoke that , yes , having exuberant amounts of antioxidants can be bad for you — but why ? One reason is that low amounts of gratuitous root word can actually be helpful .
" There is lots of evidence indicating that free radicals have beneficial role in physiologic processes,“Ismail Laher , a professor of pharmacological medicine at the University of British Columbia , told Live Science in an email . At low engrossment , free radicalshelp mobile phone acquire and are part of the body ’s defense mechanism against disease . They are also postulate in themetabolism , or breakdown , of drugs and enter in cell - to - cell communication .
However , " If too many antioxidant are consume , these normal and essential process can be disrupt , resulting in unsuitable effects,“James Kehrer , a prof emeritus and James Dean at the University of Alberta Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences and an adjunct professor at the University of New Mexico College of Pharmacy , said in an electronic mail to Live Science .

How can we check that not to overdose on antioxidants ? Skip the supplements , and adhere to a healthy dieting , Kehrer advocate .
" When someone rust a balanced diet that admit sufficient fruit and vegetable , the right amount of antioxidants will be consumed , " Kehrer said . " dietetical supplements are rarely , if ever , require , except in the longsighted - full term absence of an appropriate dieting , or in some types of disease . " For instance , you may be advocate supplements if you haveataxia with isolated vitamin E deficiency(AVED ) , a rare inherited neurodegenerative disorder .
Exercise is also important , Laher mention . The body is capable of bring forth its own antioxidants , andexercise increase this built - in antioxidant productionin the muscles , heart and liver .

If you are turn over an antioxidant add-on , discuss it with a health guardianship professional . It ’s essential to be mindful of the supplementation ’s doses and how they align with your daily dietary intake , because overconsumption may lead to toxicity . It ’s also crucial to recognise if a supplement could interact with a medication you take .
When it comes to antioxidants , it ’s crucial to believe a concept called " hormesis , " which is when a low Cupid’s itch of a inwardness has a good effect but a high dose has a toxic upshot . Or , as Kehrer put it , " If a little is good , more is NOT better . "
— What are superfoods ?

— 10 antioxidant plentiful foods to let in in your diet
— What do antioxidant do for your skin ?
This article is for informational purpose only and is not intend to pop the question aesculapian advice .

Ever wonder whysome people work up muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckles number out in the Lord’s Day ? station us your questions about how the human soundbox mold tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question answered on the website !