When you purchase through connexion on our site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
For the first time , scientists have observed solo corpuscle floating freely and interacting in space . The uncovering helps to confirm some of the most canonic rationale ofquantum mechanicsthat were first predicted more than a century ago but were never like a shot aver .
single atoms are notoriously hard to keep due to their quantum nature . Researchers can not , for example , know both an corpuscle ’s place and its velocity at the same clock time , due to quantum weirdness . But using certain optical maser techniques , they have capturedimages of cloud of mote .

An illustration of atoms floating freely in the air.
" It ’s like seeing a cloud in the sky , but not the single water corpuscle that make up the cloud,“Martin Zwierlein , a physicist at MIT and Colorado - author of the young research , said in astatement .
The new method kick the bucket one step further , allowing scientist to becharm images of " free - orbit " speck in free blank space . First , Zwierlein and his colleagues corralled a swarm of sodium atoms in a slack trap at ultracold temperatures . Then , they shot a wicket of laser light through the cloud to temporarily block the atom in place . A second , fluorescent laser then illuminated the single atoms ' position .
Related : There may be a ' obscure mirror ' creation within ours where atoms go to form , fresh study suggests
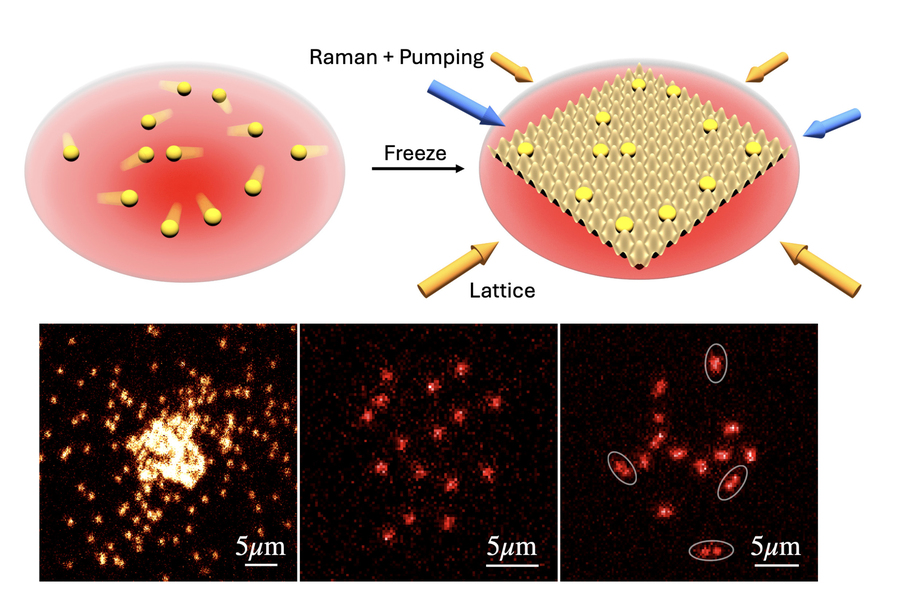
Top: Two illustrations show how atoms in an atom trap (red) are suddenly frozen in place via an optical lattice. Bottom: Three microscope images show (left to right) bosonic 23Na forming a Bose-Einstein condensate; a single spin state in a weakly interacting 6Li Fermi mixture; and both spin states of a strongly interacting Fermi mixture, directly revealing pair formation.
The observed corpuscle belong to a group called bosons . These particles share the same quantum mechanical country and , as a result , behave like a undulation , bunch together . This conception was firstproposed by Gallic physicist Louis de Brogliein 1924 and has afterward become known as a " de Broglie waving . "
Sure enough , the boson Zwierlein and his team observe display de Broglie undulation behavior . The researchers also captured effigy of atomic number 3 fermion — a type of particle that repels similar particles rather than bunching together .
— physicist make hottest Schrödinger ’s cat ever in quantum technology breakthrough

— Scientists exact to find ' first observational evidence supporting cosmic string theory , ' which could finally reveal the nature of dark energy
— ' Einstein ’s equality need to be elaborate ' : Tweaks to cosmopolitan relativity could finally explicate what lies at the inwardness of a black hole
The results were published May 5 in the journalPhysical Review Letters . Two other group reported using a alike technique to observe pairs of boson and fermion in the same emergence of the journal .

" We are able to see undivided atoms in these interesting clouds of atoms and what they are doing in relation to each other , which is beautiful , " Zwierlein said .
In the future , the team plans to employ the new technique — called " atom - answer microscopy " — to investigate other quantum mechanical phenomena . For exemplar , they may use it to try observing the " quantum Hall effect , " in which electrons synchronise up under the influence of a strong magnetic field .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be incite to get into your display name .