When you purchase through links on our site , we may gain an affiliate delegation . Here ’s how it solve .
For the first clock time , scientists have growncerebral organoids — three - dimensional , lab - grown " minibrains " — from human fetal brain tissue .
The new organoids grow to the size of a cereal of rice and bear many case of cells that ego - organise into complex 3D structure . The investigator also triggered the growth of brain tumors within the minibrains and tested the tumors ' response to be Cancer the Crab drugs .
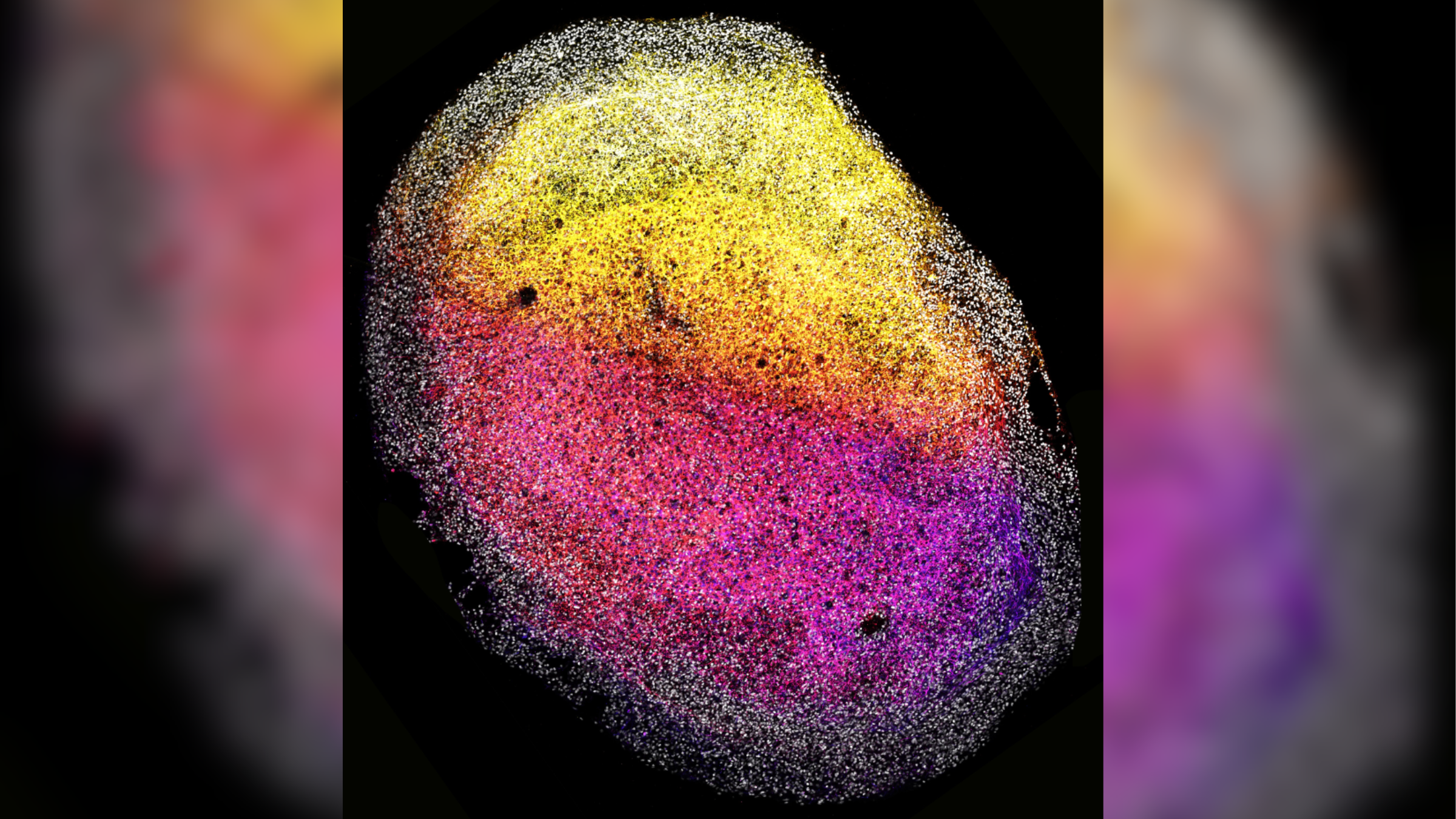
This image shows one of the human fetal tissue-derived minibrains, with stem cells (gray) surrounding nerve cells (color-coded from pink to yellow, depending on their depth relative to the outside of the minibrain).
Minibrains mimic key face of the development and function of full - sizehuman mastermind . They have previously been develop from humanstem cellsbut never directly from already formed brain tissue paper , so the new organoids unfold up exciting possibilities , the authors of the raw subject area , published Monday ( Jan. 8) in the journalCell , aver in astatement .
" Until now , we were able-bodied to gain organoids from most human organs , but not from the Einstein — it ’s really exciting that we ’ve now been able to jump that hurdle as well,“Dr . Hans Clevers , co - senior work author and professor of medicine at Utrecht University in the Netherlands , said in the affirmation .
The minibrains could complement existing stem - cellphone - derived organoids and facilitate new , unique ways to study brain health and disease , the researchers said . While stem cell must be inveigle into resembling unlike part of the nous , tissue pull straight from the brain can precisely capture its tissues at specific developmental stage , the author wrote in the report . And while shank cells must often be provided " scaffold " to grow upon , brain tissues can make their own , they added .
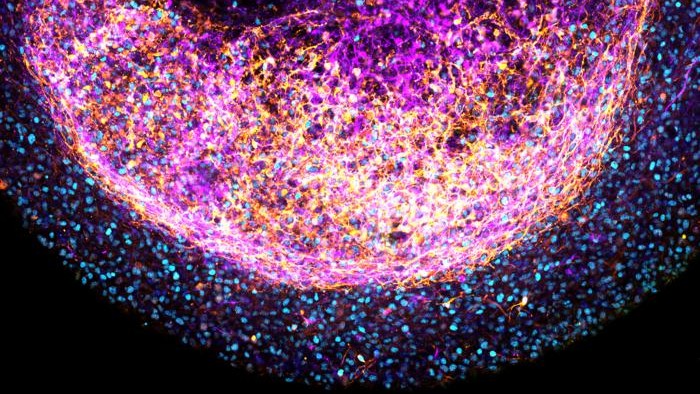
This close-up image shows one of the tissue-derived minibrains, with stem cells in blue and nerve cells color-coded from pink to yellow depending on how far they were from the outer surface of the minibrain.
Related : Lab - grown minibrains will be used as ' biologic computer hardware ' to make young biocomputers , scientists purport
Thus , " these new foetal tissue - derived organoids can offer novel insights into what shapes the different region of the mastermind , and what create cellular diversity , " first survey authorDelilah Hendriks , an connected radical leader from the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology in The Netherlands , said in the statement .
Scientists have antecedently organise minibrains usingpluripotent stem cells — primitive cells that have the potency to become any type of cell if supplied with a specific cocktail of chemical . These minibrains are utilitarian for studying development and associated disorderliness . However , minibrains educe directly from brain tissue paper may provide fresh insights into the behaviour and feature of cells that are specific to the mastermind , the discipline source write in the paper .

To make the newfangled minibrains , the researchers took samples of brain tissue from deceased fetus around the gestational eld of 12 to 15 weeks old , which had been provided by anonymous donor . They separately maturate small samples of each of the tissue paper on small plates using specific food and growth factors . Each sample was continuously shaken as it grew , to insure that all the cells within them were uncover to these chemicals , and they were not provided any physical staging to raise upon .
Around four to eight days subsequently , the research worker noticed the organisation of " multiple organized 3D structures " that later on matured into organoids with a " tissue - like visual aspect . "
The resulting minibrains contained many types of cells , including neural base mobile phone known asouter radiate glia . The foetal tissue paper also produced their ownextracellular matrixproteins , which do as scaffolding and supported their 3D organization . This may enable scientist to further take how theenvironment of cellsinfluences their development .

Minibrains develop from sure mind tissues , such as the forebrain , retain geomorphologic characteristic specific to that part of the organ , and they responded to specific signalize molecules that are involve in genius developing .
In this initial experiment , the minibrains were grow for six calendar month . Notably , the researchers were able to grow multiple minibrains from a single tissue sample . Organoids are emerging as anew way to try out the safety and effectiveness of drugs , so this ability to bring forth many organoids from one sample could someday be useful for conducting repeat experiments of new therapies for disease .
— Spherical ' minibrains ' to be grown on the International Space Station

— Rat brain injuries ' plug ' with lab - grow human minibrains in world - first experiment
— Lab - made mini brains grow their own sets of ' middle '
Going forward , the authors want to create more complex versions of the minibrains and potentially formulate them from fetal tissues at different stages of maturation , as well as pathological tissue that could capture brain defects colligate with infant mortality .

Likeother models of the human nous , " dedicated ethical frameworks " and " active word with donor and the scientific community " are needed before any further experiments are lead using these organoids , the source wrote in the paper . For instance , researchers must cautiously consider the ethic of transplant human genius tissue paper into other species , such as rodents , as has been done withstem - cellular telephone derived organoids .
Ever marvel whysome the great unwashed build up muscle more easily than othersorwhy freckles come out in the sun ? direct us your questions about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question resolve on the internet site !












