When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may earn an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it works .
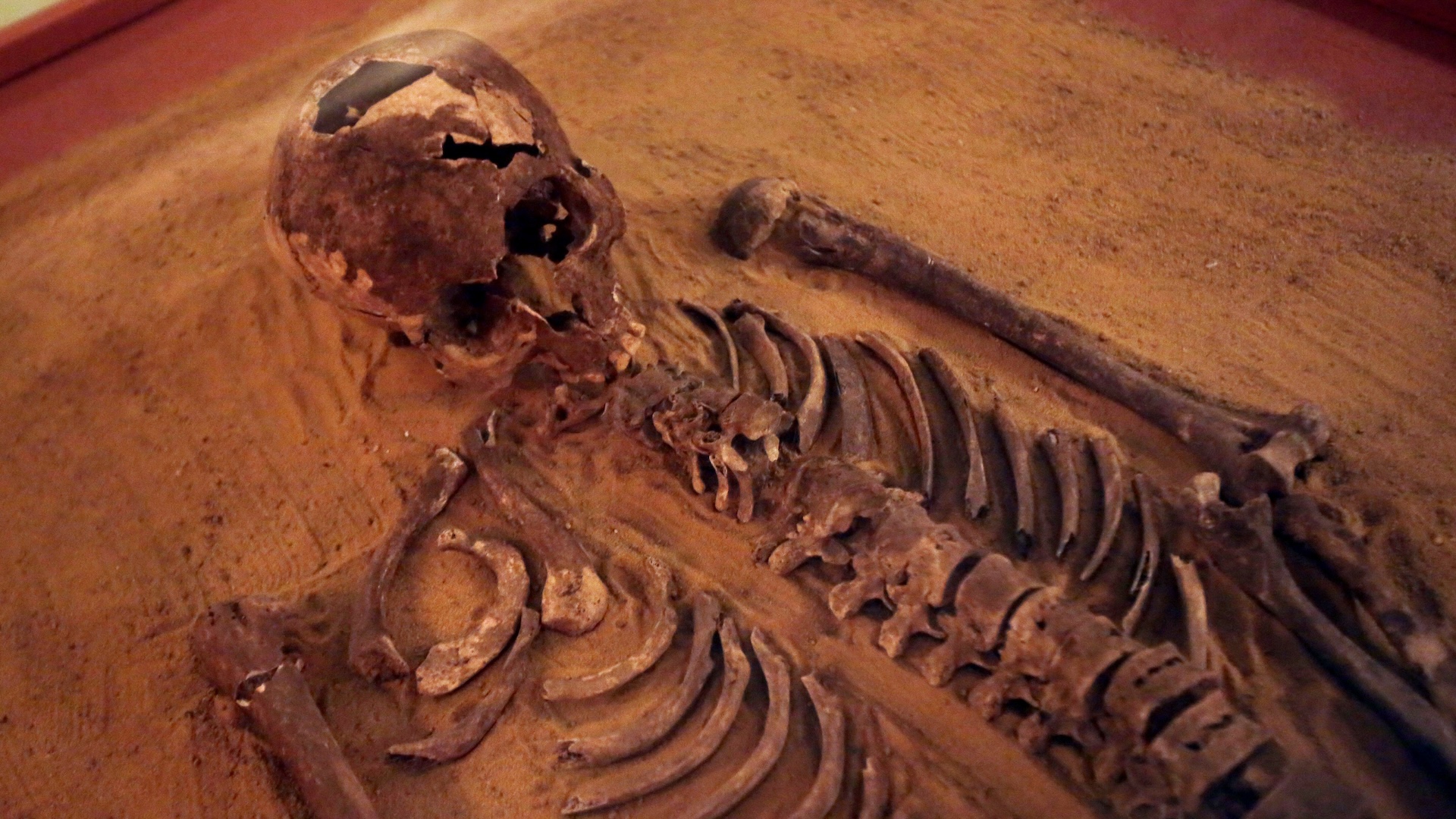
In a first , scientist have used ancient proteins to determine the sex of an primitive human relative that live up to 3.5 million long time ago , a new study reports .
An international team of scientists examine a set of protein called the proteome . They collect this material from the tooth enamel of anAustralopithecus africanusindividual whose remains were get in a South African cave decades ago . The method they used , called paleoproteomics , has never successfully go on such an old hominin ( modern humans along with their ancient relatives and ancestor ) , the researchers say in a study publish in theSouth African Journal of Scienceon Friday ( Feb. 7 ) .
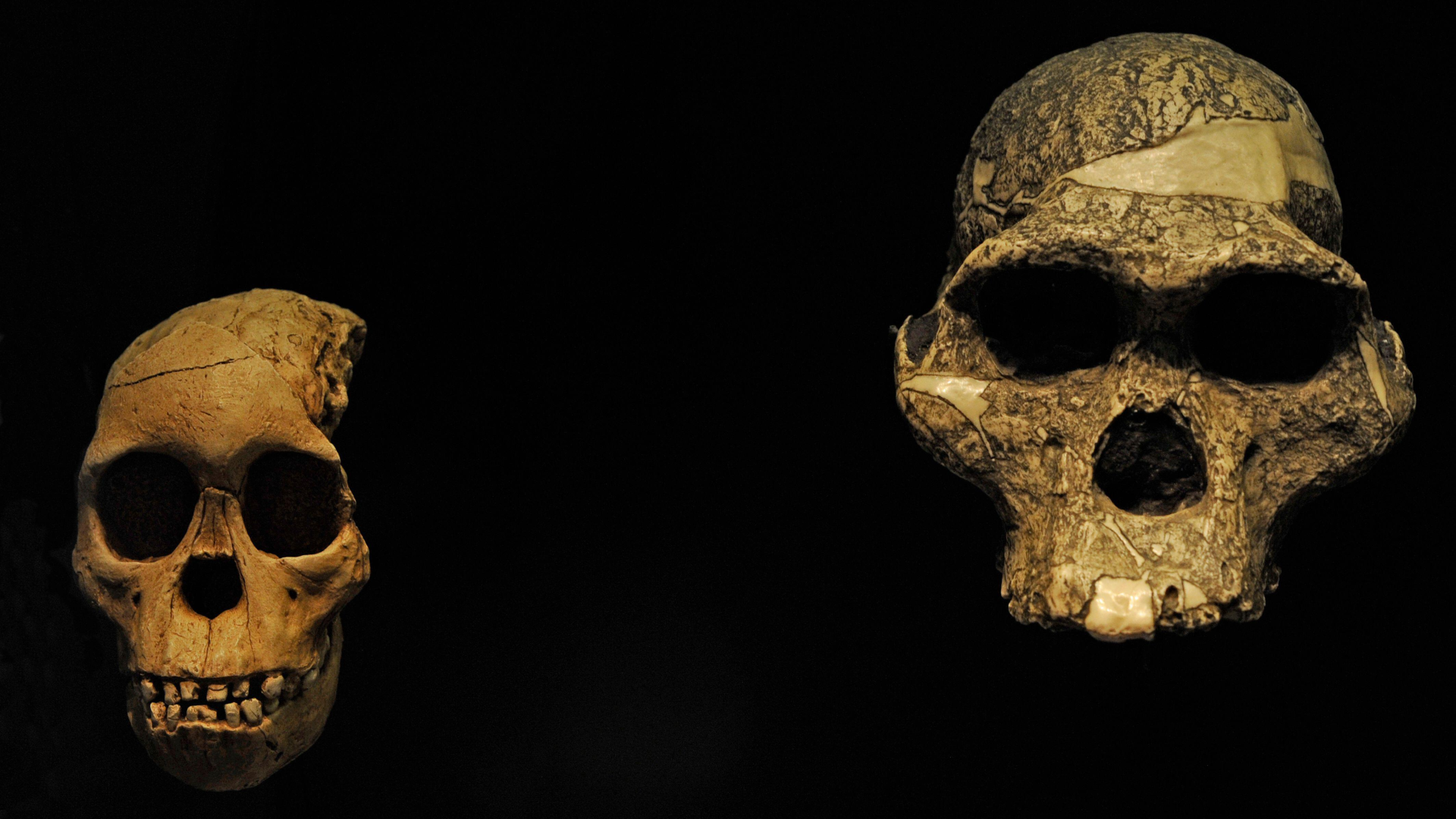
Skulls of a young (left) and an adult (right)Australopithecus africanus
" To my noesis , among the in public shared hominin enamel proteomes , A. africanusis the oldest hominin to be submit to palaeoproteomic analysis , " sketch lead authorPalesa Madupe , a postdoctoral researcher in the Section for Geogenetics at the University of Copenhagen , told Live Science in an email .
Paleoproteomics , the subject field of ancient proteins trapped in tooth enamel , was developed about 30 geezerhood ago . Because proteins can bear on longer thanDNA , paleoproteomics is used to study the inherited building blocking of creatures that are trillion of years old , such as an80 million - year - oldBrachylophosaurus . Only latterly , however , have paleoanthropologists been able-bodied to take out these proteins from our dodo ancestors .
Madupe and her team have been working to recoup trace of protein from hominin fossils in South Africa ’s Cradle of Humankind , where at least six hominin species lived , includingA. africanus(3.5 million to 2.0 million years ago ) andHomo naledi(335,000 to 236,000 year ago ) . Paleoproteomics , they wrote in the study , can help researchers well translate how the unlike species vary . This would include determining the sexual urge of these somebody , which is not always straight render the fragmental nature of ossified skeletal system .

link : Famous Taung Child dodo from South Africa is 2.58 million years old , fresh field finds
Using a minimally invasive technique , the researchers express over 100 peptide — unforesightful chains of aminic superman that are built into protein — from the tooth of oneA. africanusindividual found in theSterkfontein limestone cavesin South Africa . Several of these peptides were unique to amelogenin , a protein that is key in normal tooth development . Because male and female build this protein slightly otherwise , the researchers could assure theA. africanustooth was from a manful individual .
— South African fogy may rewrite history of human evolution

— From ' Lucy ' to the ' Hobbits ' : The most illustrious fossil of human congeneric
— 1.4 million - yr - onetime jaw that was ' a moment eldritch for Homo ' call on out to be from never - before - seen human congener
The study was published as part of a limited outcome of theSouth African Journal of Sciencein honour of the hundredth day of remembrance of the " Taung Child . " The famous child ’s tiny skull was unintentionally happen upon by quarry workers who were blast a limestone cliff in South Africa . In a groundbreaking study published in the journalNatureon Feb. 7 , 1925 , Australian anthropologist Raymond Dart boldly suggested thatA. africanuswas a human relative , making it the first ancient hominin ever chance upon in Africa .

Although the new study shew that proteins can be recovered from hominin fossils up to 3 million years old in South Africa , Madupe wants to apply the technique to a wider range of a function of regions and climate around the humanity .
" These are all incredibly exciting discovery that are poised to revolutionise our understanding of human organic evolution , " the researchers write .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your video display name .











