When you buy through links on our internet site , we may garner an affiliate committee . Here ’s how it works .
Scientists are tracking a massive plumage of toxic gas moving across northern Europe that was spat out by theongoing volcanic eruptionin Iceland . The gas swarm is unbelievable to cause any serious wellness problem . However , it could impact the ozone hole above theArctic , experts warn .
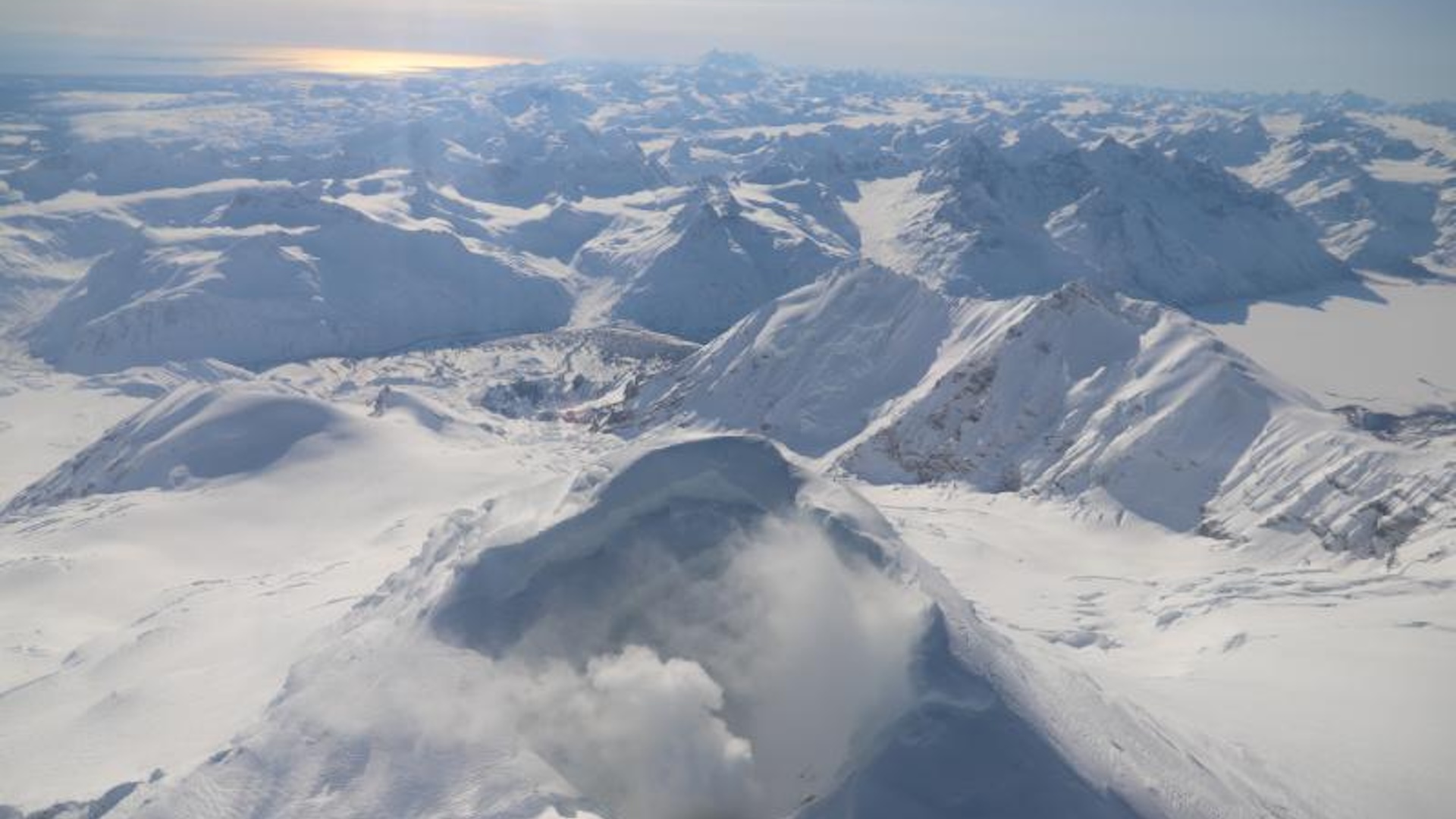
On March 16 , an cloak-and-dagger vent in Icealnd ’s Reykjanes Peninsula blew its top for the quaternary meter in as many months , opening up the bombastic fissure of the current eruption round and unleashing a monumental lava flow that narrowly missed the evacuated townspeople of Grindavík . There were ab initio fear that the lava current could accomplish the sea and unleash a feather of hydrochloric back breaker , which would have been " liveliness - threatening " to anyone cheeseparing to the coastline , Live Science previously report . However , the lava never attain the shore .
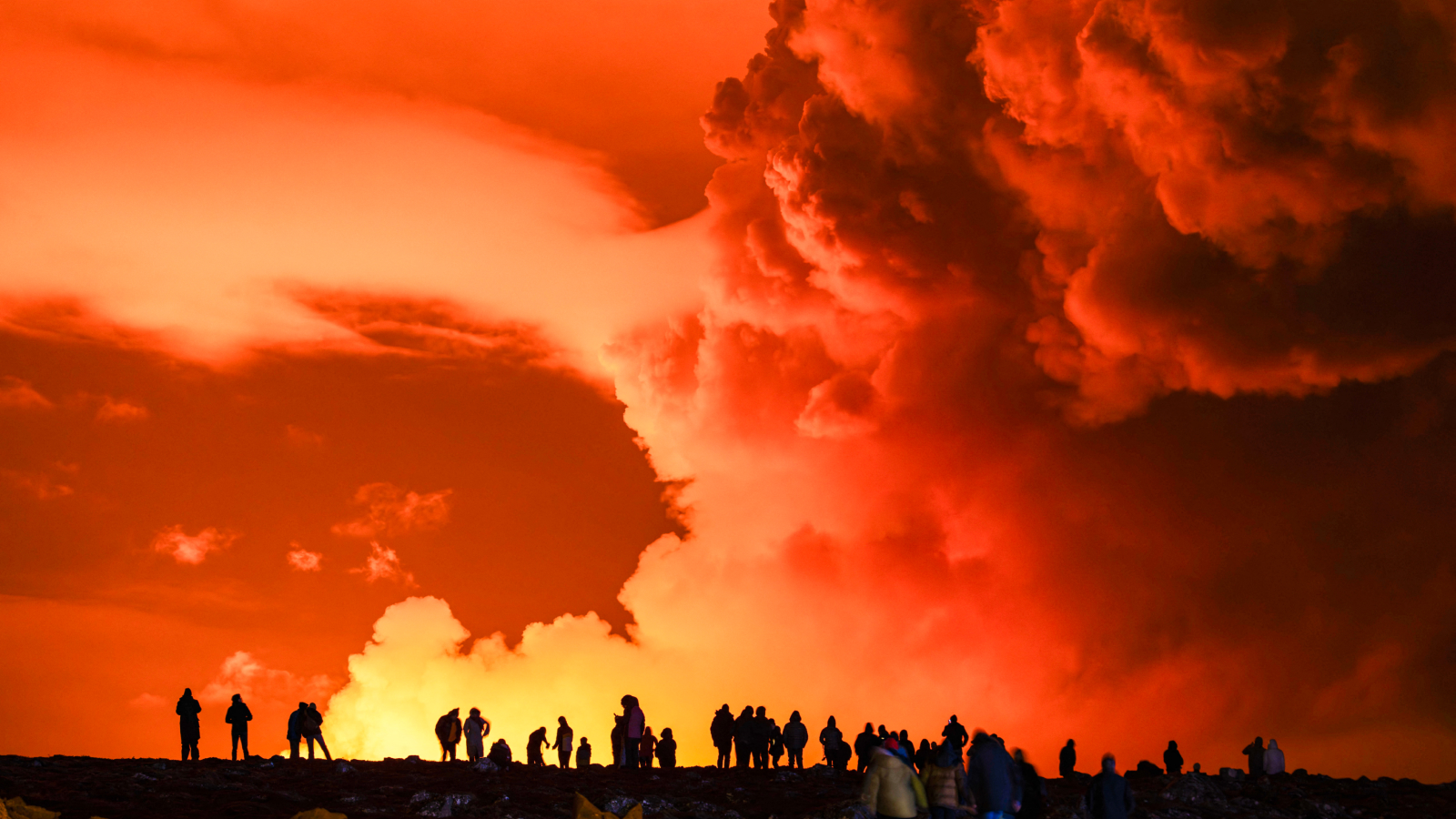

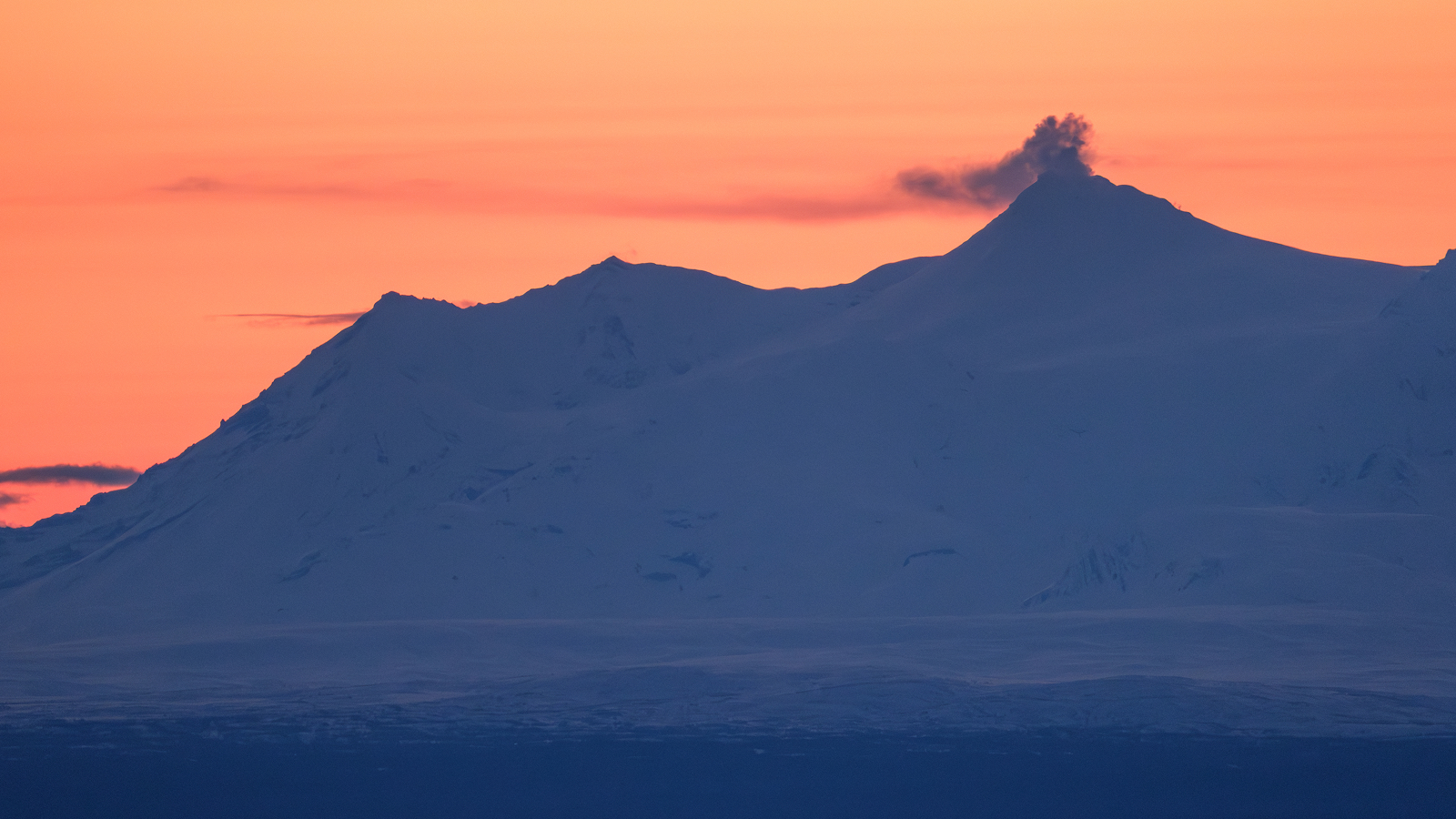
Volcano enthusiasts watch as the volcano on Iceland’s Reykjanes Peninsula pumped out high levels of sulfur dioxide on March 17.
But the eruption did turn sulfur dioxide — a colourless , toxic gas that can be passing unsafe in high concentration .
On March 17 , the vent was spit out around 110 pounds ( 50 kilo ) of sulfur dioxide every second , according to a translated financial statement from theIcelandic Met Office . Workers at the nearby Svartsengi office plant were empty from the facility due to high level of the accelerator , Icelandic news siteRÚV reported , and local anaesthetic were temporarily warned to remain at bottom , agree toIceland ’s Civil Protection .
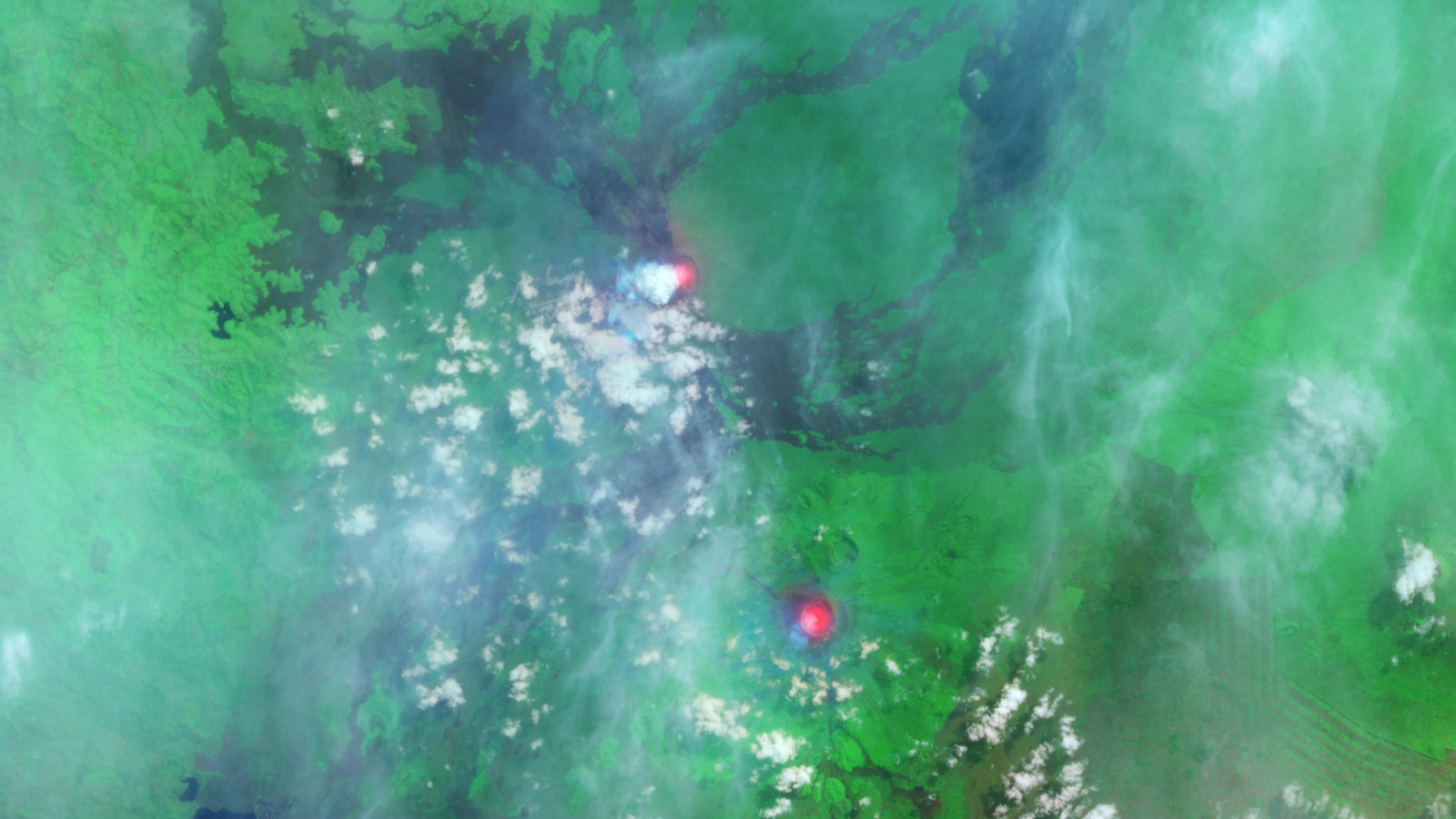
Sulfur dioxide emissions have diminished significantly since March 18 , but new data from the Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service ( CAMS ) — part of the European Union ’s Copernicus program , which tracks atmospheric condition and mood change using artificial satellite data — shows that the initial fountain of gas form a 3 - mile - tall ( 5 kilometers ) concentrate column that has since blown toward other nation in northerly Europe .
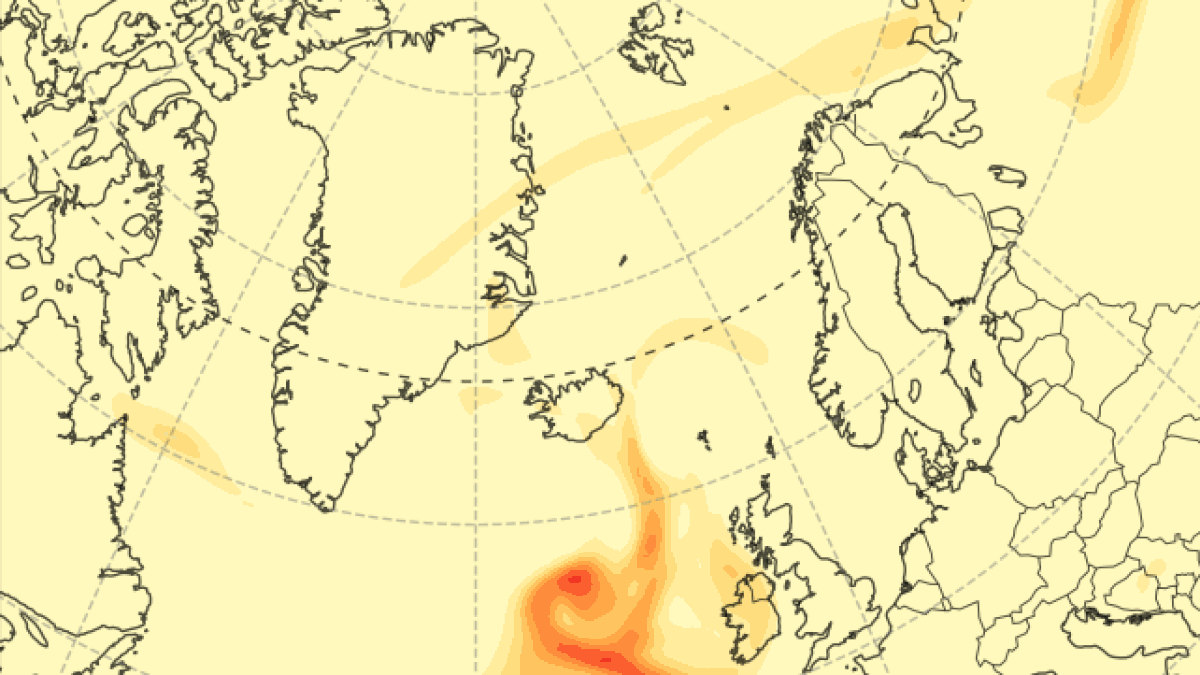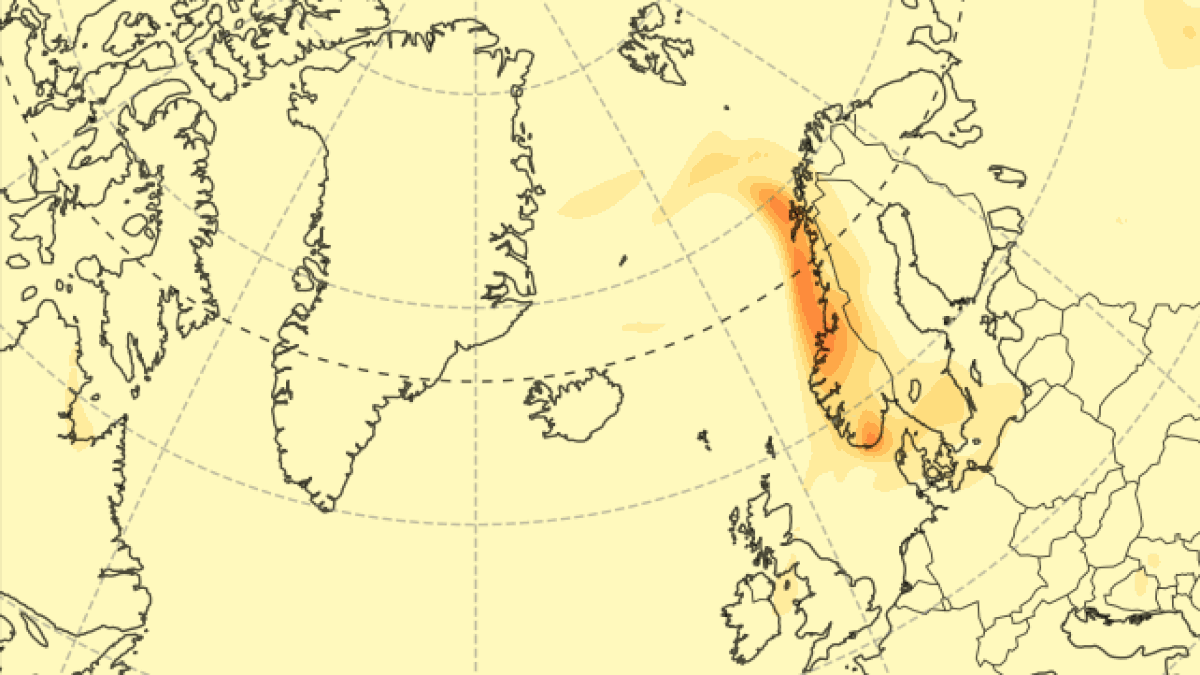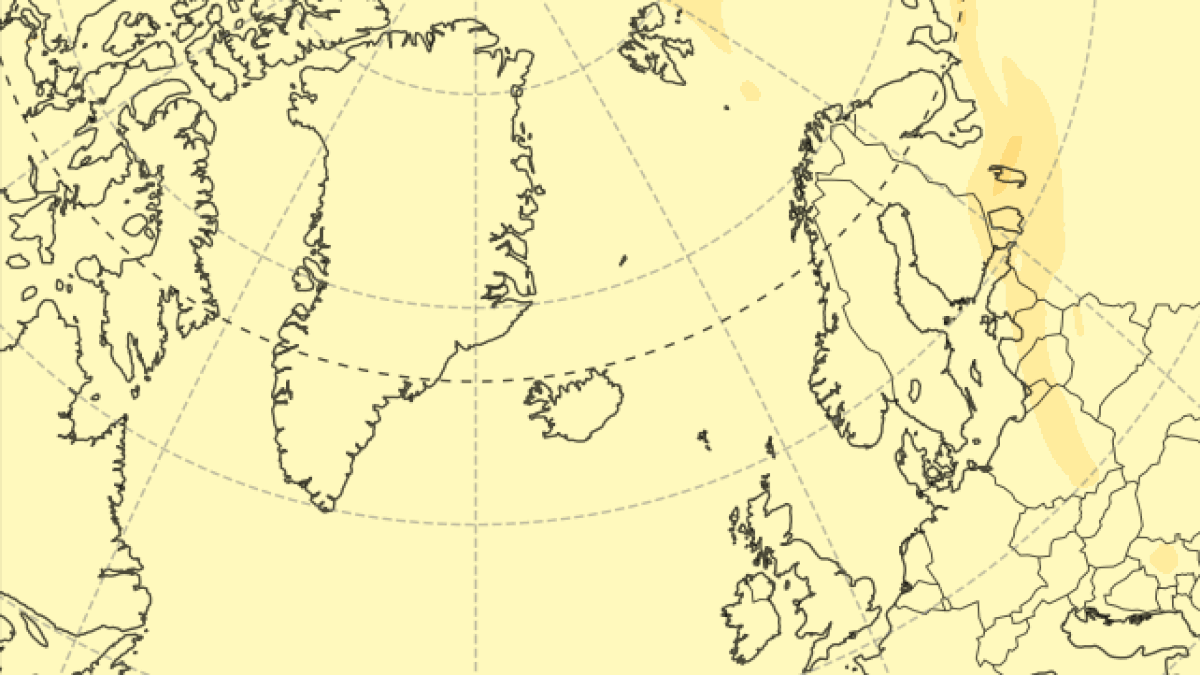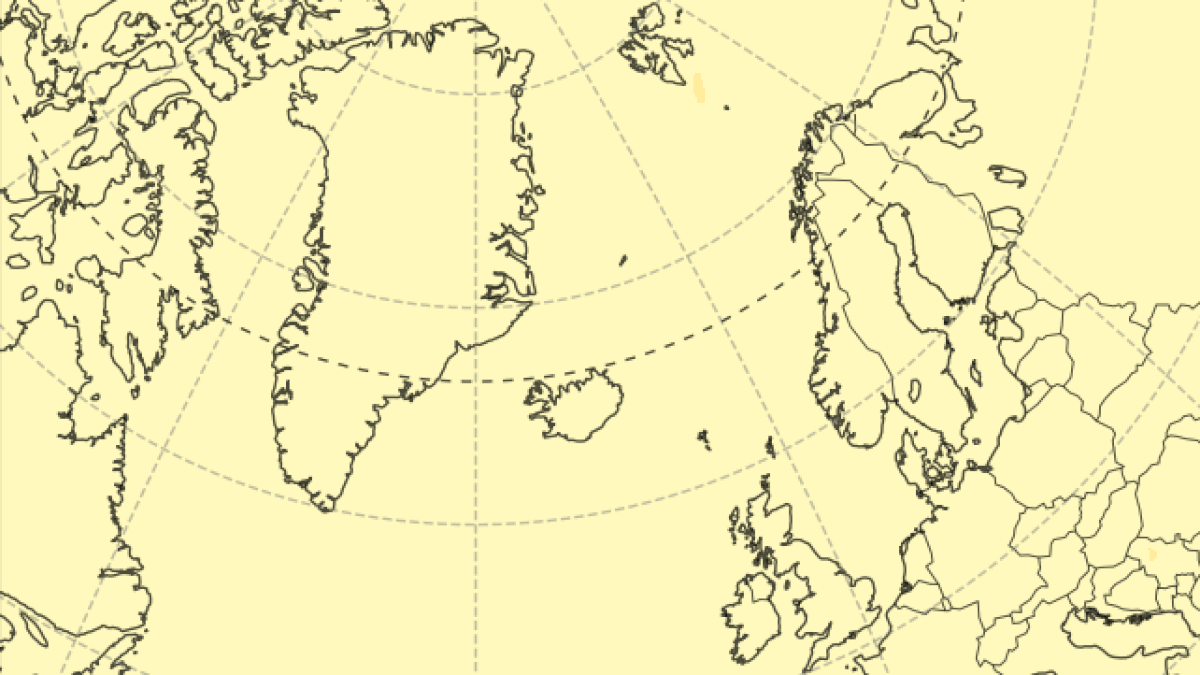
The toxic plume is forecast to move over the U.K. and Scandinavia over the coming days.
link up : Heat explosion from Iceland ’s late eruptions in eerie NASA satellite image
The gas plume has already passed above the U.K. and is presently approach Scandinavia , where it will start out to break up before record Russia .
CAMS will continue to track the feather " although we do n’t wait there to be any impact on surface air quality or climate , " senior CAMS scientistMark Parringtonsaid in a statement e-mail to live on Science .
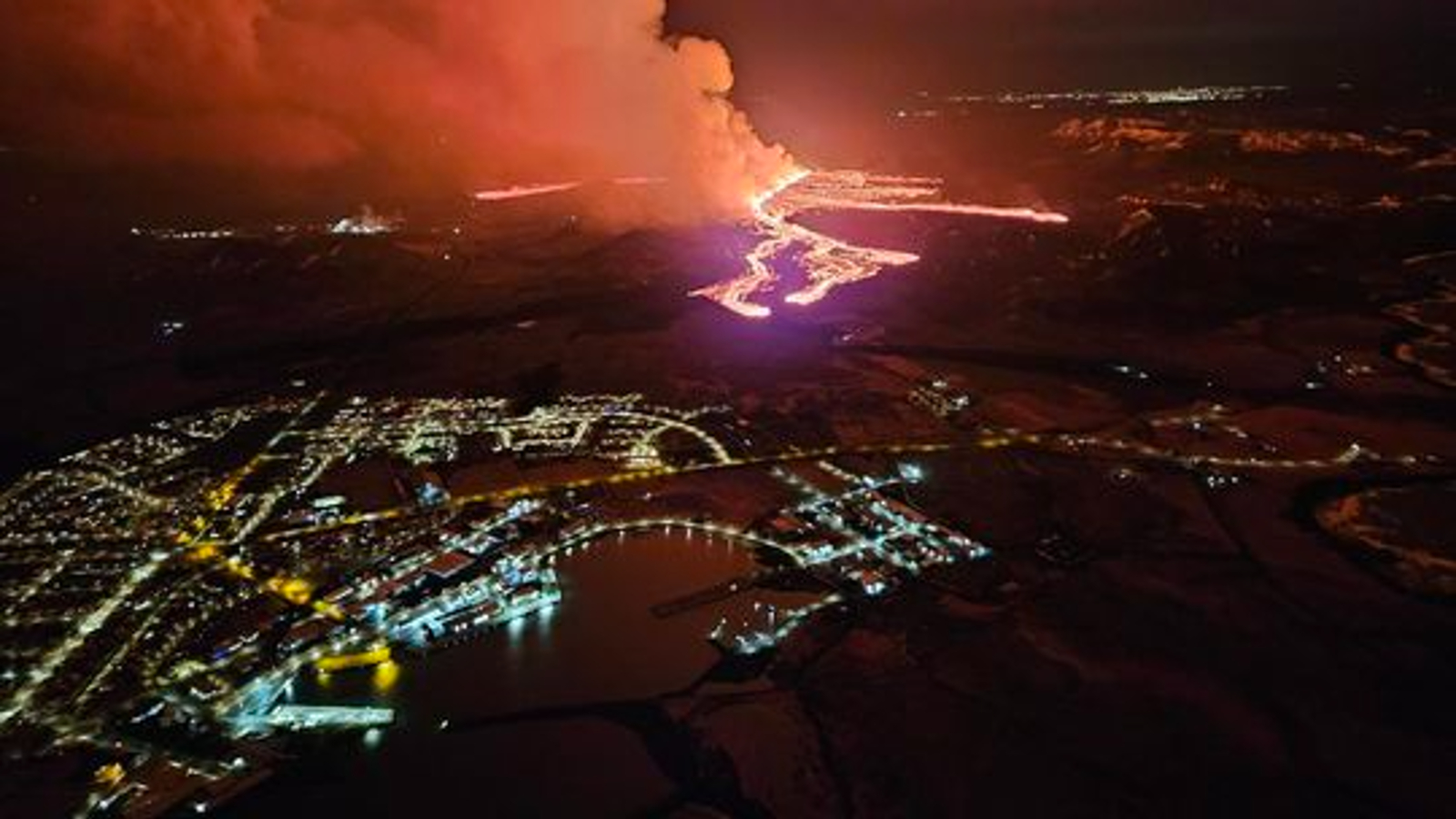

The lava plume from the most recent eruption narrowly missed Grindavík.
However , tracking sulfur dioxide emissions is still important because the natural gas can react with atmospheric ozone atom , depleting the amount of this protective meaning in the ozone layer , which harbour Earth ’s surface from the sun ’s harmful ultraviolet irradiation .
In October 2023 , scientists partially assign thenear - record - largest ozone pickle above Antarcticato the 2022 clap of an submersed volcano in Tonga , whichreleased high layer of water vapour into the atmospherethat may have eat ozone levels .
— Lava bleeds from Iceland vent into the frozen landscape painting in unbelievable satellite effigy

— Iceland vent could flare up again ' without warning '
— Breathtaking photos show wall of lava erupting from Iceland vent
Experts predict that the recent extravasation in Icelandcould be the first of a fresh centuries - retentive geological period of activityin the neighborhood . As a result , the amount of S dioxide being pumped toward the Arctic could also arise over the next few days , which could go to turgid northerly ozone yap in the future .

" The shock of the volcanic eruptions in Iceland in the atmosphere have not yet been so severe , but it is relevant to keep monitoring the evolution of the situation , " CAMS directorLaurence Rouilsaid in the financial statement .













