When you purchase through links on our site , we may bring in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
In this adapted excerpt from " Infinite Life : The Story of Eggs , Evolution , and Life on Earth , " ( Pegasus Books , 2024 ) authorJules Howardexamines the invasiveness of the placenta — how far it permeates into the wall of the uterus and the maternal tissue — in mammals after the dinosaur - kill asteroid struck .
Although it has not been preserve in the fogy record , the diverseness of placentae among innovative - daytime mammals intimate that , about 10 or 20 million class after the final stage - Cretaceous , at around the metre that the animals of theMessel Pitwere live , the mammal placenta was changing . rude selection was tweaking this electric organ .
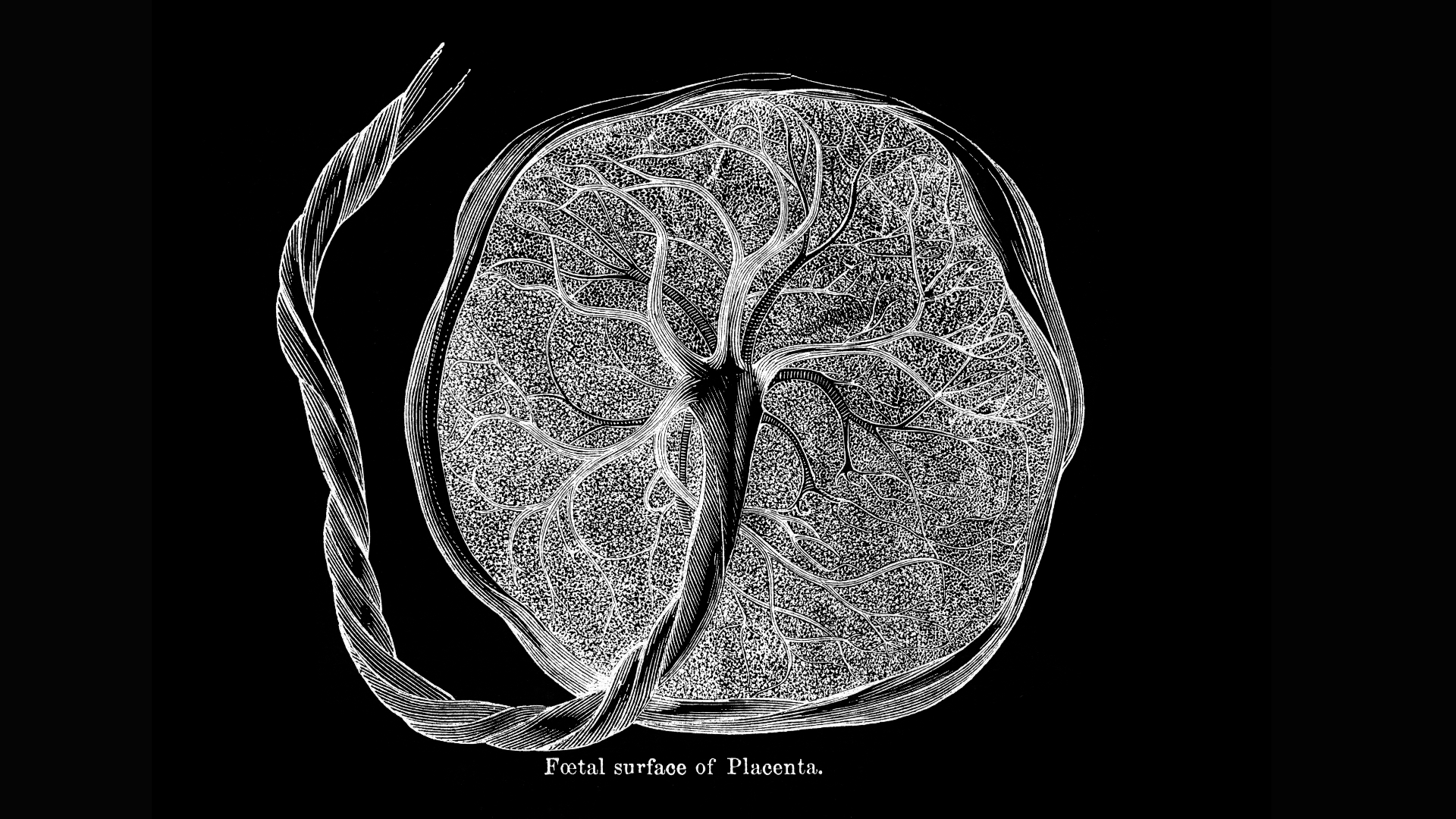
The relationship between human mother and child, connected via the placenta, has become, evolutionarily, strained in our species.
In many case , it was take the individual placentae well able to extract as much vigour from the paternal host as potential . Yet , amazingly , in some line of descent the placenta appeared to take a step back , becoming less , rather than more , invasive . Looking at data across 60 mammal species , a trend becomes apparent .
plot the invasiveness of each placenta ( judged partly by how many blood- assemblage , finger - same projections the placenta has ) against important life - history item , such as how long a species accept to mature and how many offspring each year a species might produce , the least invading mammal placenta are those associated with a more rapid footstep of life .
mintage that live tight and die young , in other row , seem to terminate up evolving a less invasive placenta .

Human brains are about twice the size as chimp brains at birth.
Brain size is another marking that tracks closely with how invasive a placenta evolves to be . Not just how orotund the wit is in relation to the body , but also how quickly the genius arise before birth . Both factors correlate with specially invasive placenta . How it works is unproblematic : The bigger a mammalian ’s brain evolves to be , the greater selective force play is placed on the placenta to acquire free energy for the increase of the fertilized egg , which , by nature , get the phylogeny of an ever - hungrier placenta .
Mammals are , as a group , more smart as a whip than other similar sized organisms , but this was n’t always as key a feature of our kind . It seemed to happen gradually , after thedemise of dinosaursand as the Cenozoic Era ( 66 million years ago to the present ) begin to work up . scientist had originally thought that this relative growth in brain size was simply a by-product of the phylogeny of larger body size of it in mammals , but recently ( using three - dimensional manakin of fossilized mammal skulls ) this assumption has been more rigorously test .
At first , it seems , in the 10 million age after the epoch - ending meteorite , mammal body size of it increased and , relatively , so too did brain sizing . But then , clearly seeable at fogy sites like Messel , brainiac size in certain lineages increase at a higher than expected rate compared to body size . Mammal brains , in some line of descent , were yield a metaphorical shot in the arm . So why ? If they be both mother and fetus more to bring on , particularly in the embryo stage , what ’s so good about big mind ?
The placenta has developed techniques to get as much as the fetus needs from the mother.
The researchers who first made this reflection about brainiac sizes in mammals , comparing three - dimensional models of fossilised skull , think that this drift occurred because of competition . At first — without dinosaur and other large land animals — plants , insects and other resources were easy to glean and competition between mortal was low . In this environment , energy - sapping brainiac were costly and unnecessary .
But after , when mammals diversified and established themselves — when there was more competition for recess , for food and resources — smarter individual were comparatively more successful in some species . In term of the transmittance of genes , large brains start to pay out and , in some lineages , bigger and unspoilt brains started to germinate . In some mammalian groups today , such as dolphin , rodents and particularly order Primates ( monkeys and aper ) , the ratio of Einstein size to body size has continue to increase with clip . In humans , perhaps the wiliest of all primates , the style keep on with cool .
There is no denying the selection pressure at work here : freehanded brains really are inordinately expensive for bodies to build . And human brains truly disagree from the brain of our near relatives , the chimpanzees ( Pan troglodytes ) . At birth , for case , a chimp ’s psyche is 130 cubic centimeters ( 8 three-dimensional in ) and then three-bagger in size in the be three years .

Compare that to the human brain . At birth , the human brain is more than twice the size of a chimpanzee ’s and , in six age , it quadruples in size . Although our brain take up just 2 % of our total body weight unit , this harmonium consumes between 20 % and 25 % of our rest energy budget . The human mind costs something like 420 calorie a day to run , four time more than the chimpanzee ’s head .
This is why the family relationship between human mother and tiddler , connected via the placenta , has become , evolutionarily , so forced in our species . More forced , it seems , than in any other mammal .
Liam Drew , generator of the authoritative " I , Mammal " ( Bloomsbury Sigma , 2018 ) head out just how twisted this relationship becomes . For starters there ’s pre-eclampsia , when the mother ’s body go through a life history - threatening upsurge in blood insistency as the human foetus increase the charge per unit of pedigree flow through the placenta .

Put simply , it want to be bathed in as much life - giving line as potential . And there ’s gestational diabetes , due to the fetus ' attack to co - opt enate control of ancestry sugars — predictably , it desire more than the female parent is able-bodied to give .
Preeclampsiaaffects about 5 % of human females channel a unmarried baby to term . total more offspring into the mixing , twins or trine say , each of whom will often have their own placenta , and preeclampsia rate increase to one in three pregnancies . This makes childbirth a risky activity for human females .
There are other tricks that the placenta has evolved to get what it needs for the fertilized egg . Staggeringly , we now know that the placenta uses a peculiar protein ( squall PP13 ) to stir up the tissue paper around tiny veins in the uterus , causing the mother ’s resistant system to invest heavily in resistant defenses . It ’s a definitive beguilement technique evolved by the placenta : If the mother ’s immune system is firefighting elsewhere , it is less likely to focus its tending on combat the placenta ’s active uterine encroachments .

What lead from all of this , saysCat Bohannon , author of " Eve : The Real Origin of Our Species " ( Knopf , 2023 ) is a " nine - month dead end " : " cleaning lady ’s eubstance are particularly adapted to the rigour of pregnancy not simply so we can get pregnant but so we can survive it , " she writes .
The highly invading human placenta , influenced by our enormous psyche and ( probably to a less extent ) our boring - and - steady life history , also explicate another quirkiness of our metal money , the phenomenon of menstruation . This version is fleetingly rare among mammals , found only in some high priest , bats and elephant shrew . In human being , menstrual hemorrhage is particularly open and , by now , after reading the old paragraph , you may probably guess why .
— Ancient relation of ' support fossil ' Pisces reveals that geologic activeness supercharges evolution

— Fossils of os - crushing and pith - slashing Tasmanian tiger antecedent discovered in Australia
— Human origins connect to ancient jawless blood - sucking Pisces
Having an extra - thick-skulled uterine liner avail the female survive the potentially hostile tentacle - alike villi of the placenta , should pregnancy occur . The lining of the womb in our species has become so slurred that we can not possibly reabsorb it every few twenty-four hour period or weeks , as other mammal do . It is more efficient , in our coinage at least and a smattering of others , to cast the uterine arming and grow it afresh each cycle quick for the next possible implantation .

And so , human evolution has hap both due to , and in spitefulness of , the placenta . Every gestation , unthinkingly , must voyage a careful path through it . Every menstruum is testament to it . It is partly why menopause exists , to give individual an escape from the energetic cost assort with its imposition . This life - history phenomenon only exists in a small figure of apes and some giant and dolphin .
In many years of writing about the insides and outside of fauna , I confess I have never written of a stranger organ or a weirder evolutionary contract bridge . I find myself quietly saluting the placenta that fight for me in my earliest moments , while simultaneously feeling apologetic to the enatic emcee in which I grew . This is a creation - changing adaptation , in more path than one .
Excerpted from " Infinite Life : The Story of Eggs , Evolution , and Life on Earth " by Jules Howard . Published by Pegasus Books , Sept. 3 , , 2024 .

Infinite living : The Revolutionary Story of Eggs , Evolution , and lifespan on Earth—$21.27 on Amazon
Infinite biography : The Revolutionary Story of Eggs , Evolution , and Life on Earth , offers a totally raw perspective on the brute kingdom , and , indeed , life on Earth . By try egg from their earliest histories to the very latest fossilized discoveries — embrace the unnumerable changes and mutations of ball from the development of yolk , to the intemperate eggshells of lost dinosaurs , to the animals that have evolved to at the same time give birth to egg and live vernal — Howard break untold stories of enceinte diverseness and majesty to throw away light on the huge impact that nut science has on our life .
In uncommon evolutionary event , weird platypus cousin evolved from live in water to living on dry land

Evolution itself can acquire , new study argue
What are neural processing units ( NPUs ) and why are they so important to modern computation ?




