When you purchase through link on our site , we may gain an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it puzzle out .
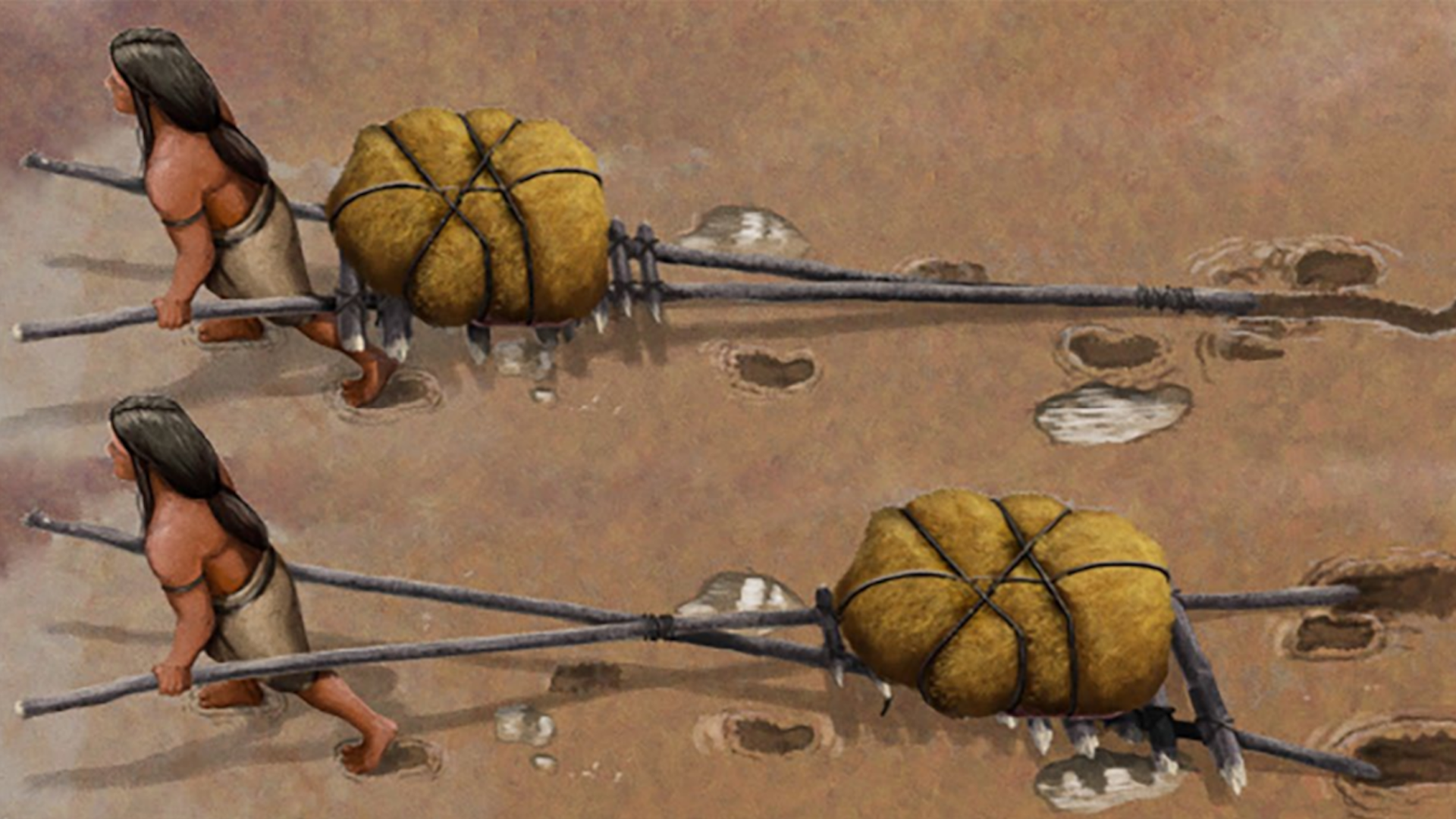
Ancient humans may have butchered and eaten a giant armadillo - like creature around 20,000 age ago in what is now Argentina , a new study finds .
The discovery of the slaughter pearl stand a growing torso of evidence that people spread throughout the Americas much earlier than previously put on .
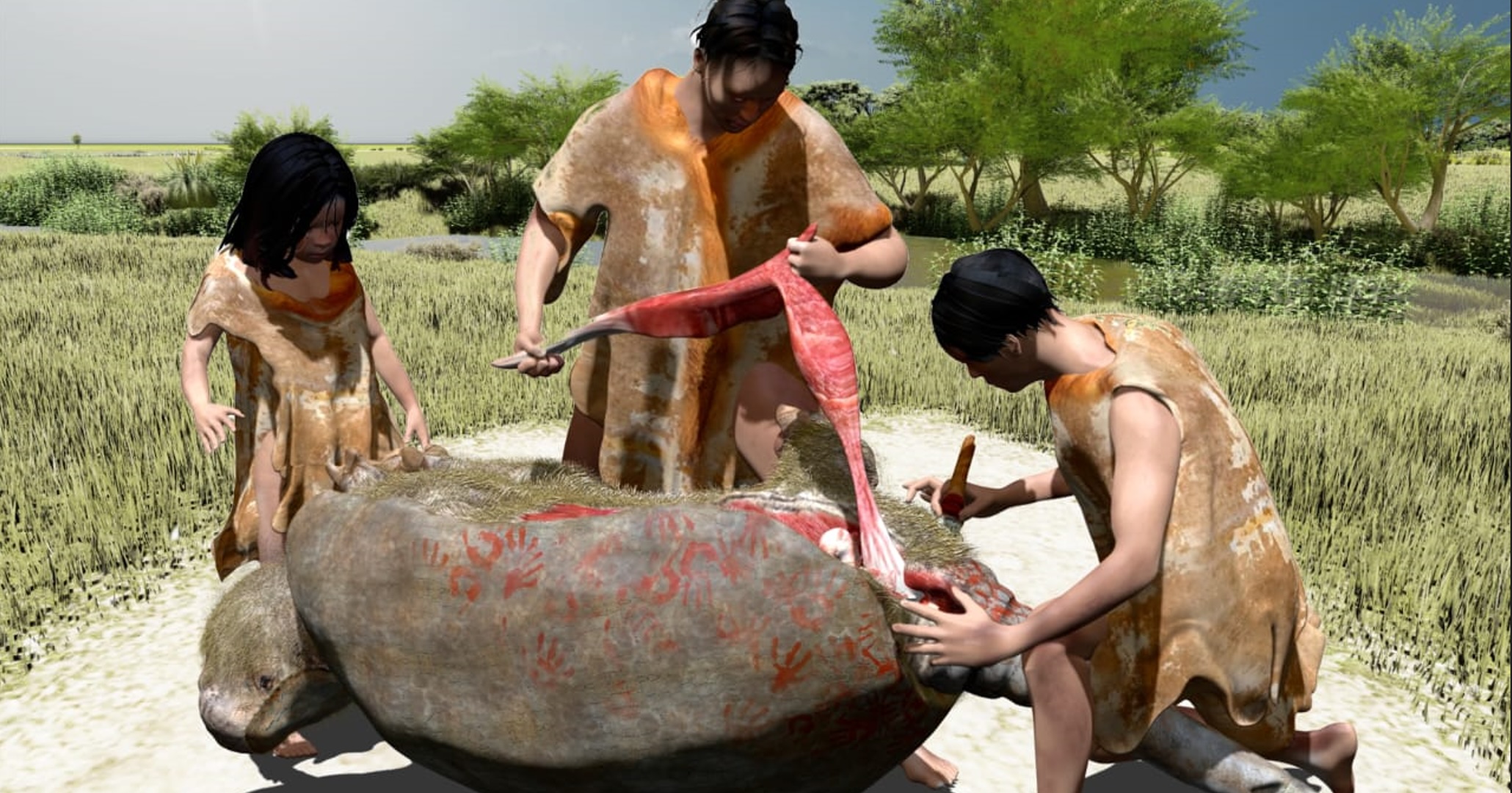

An artist’s interpretation of how ice age humans may have butchered a glyptodont about 20,000 years ago in what is now Argentina.
During the LatePleistocene epoch(129,000 to 11,700 years ago ) , ice sheets and glaciers covered much of the planet , particularly during the Last Glacial Maximum , a period around 26,000 to 20,000 years ago when the ice years was at its height . While archaeologists previously think that thefirst Americansarrived by travel along aland bridgeconnecting Siberia with Alaska 13,000 year ago , archaeological sites discover in North and South America in the last ten point to human beings arriving in the region much earlier .
In a newfangled study write Wednesday ( July 17 ) in the journalPLOS One , researchers revealed they found turn off marks on the fogy cadaver of a glyptodont known asNeosclerocalyptus — a gargantuan , extinct armadillo relative . These marked bones , found in the Pampean region of Argentina , may be among the early model of humans interacting with megafauna in South America .
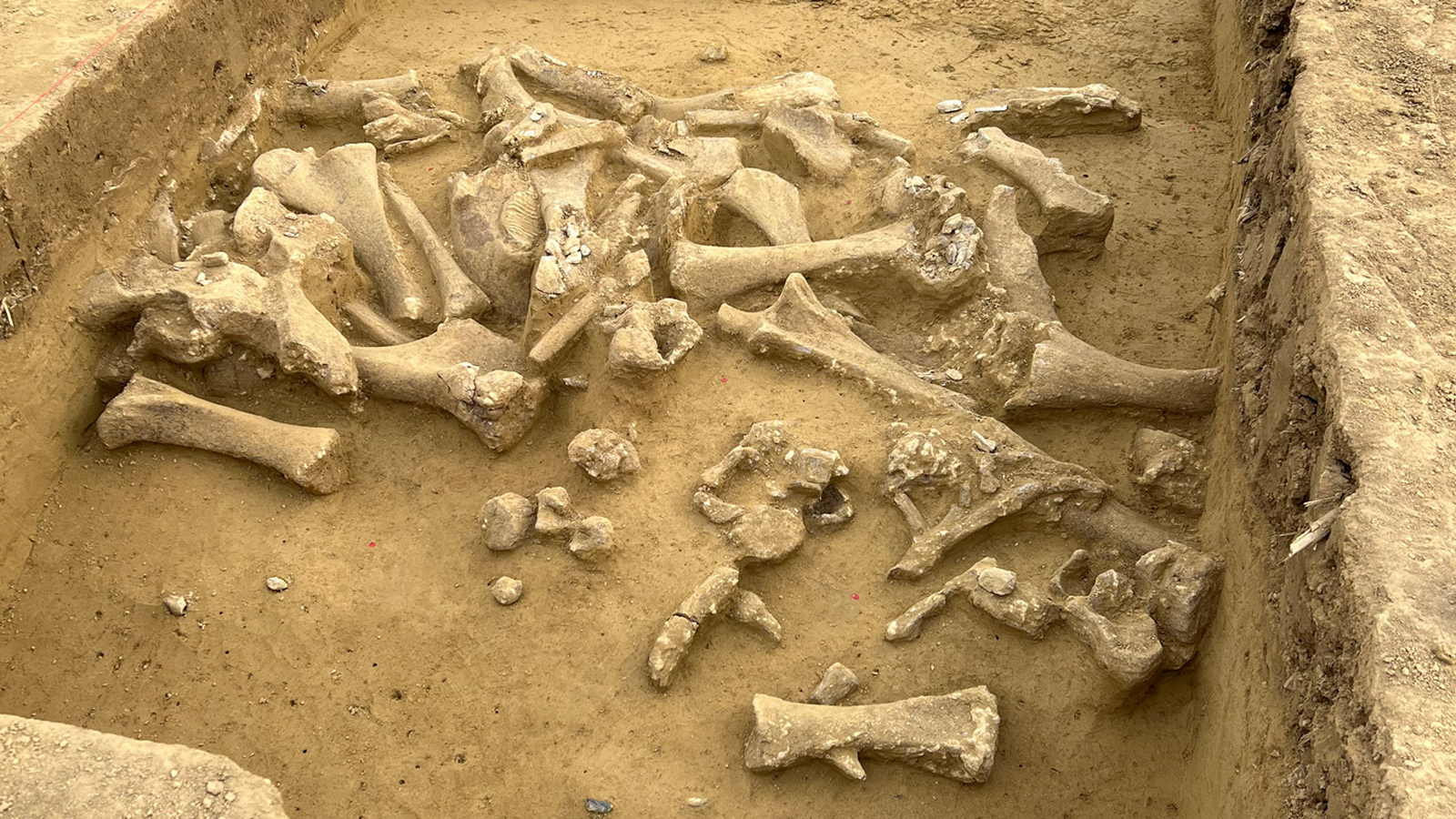
The incomplete animal systema skeletale , found along the bank of the Reconquista River on the outskirt of Buenos Aires , included parts of the pelvis and tail as well as a portion of the carapace — bony home that covered the top of the animate being ’s soundbox . The researchers atomic number 6 - date a fragment of pelvic osseous tissue to 21,090 to 20,811 years ago , which was logical with the geological dates of the deposit in which the animal was found .
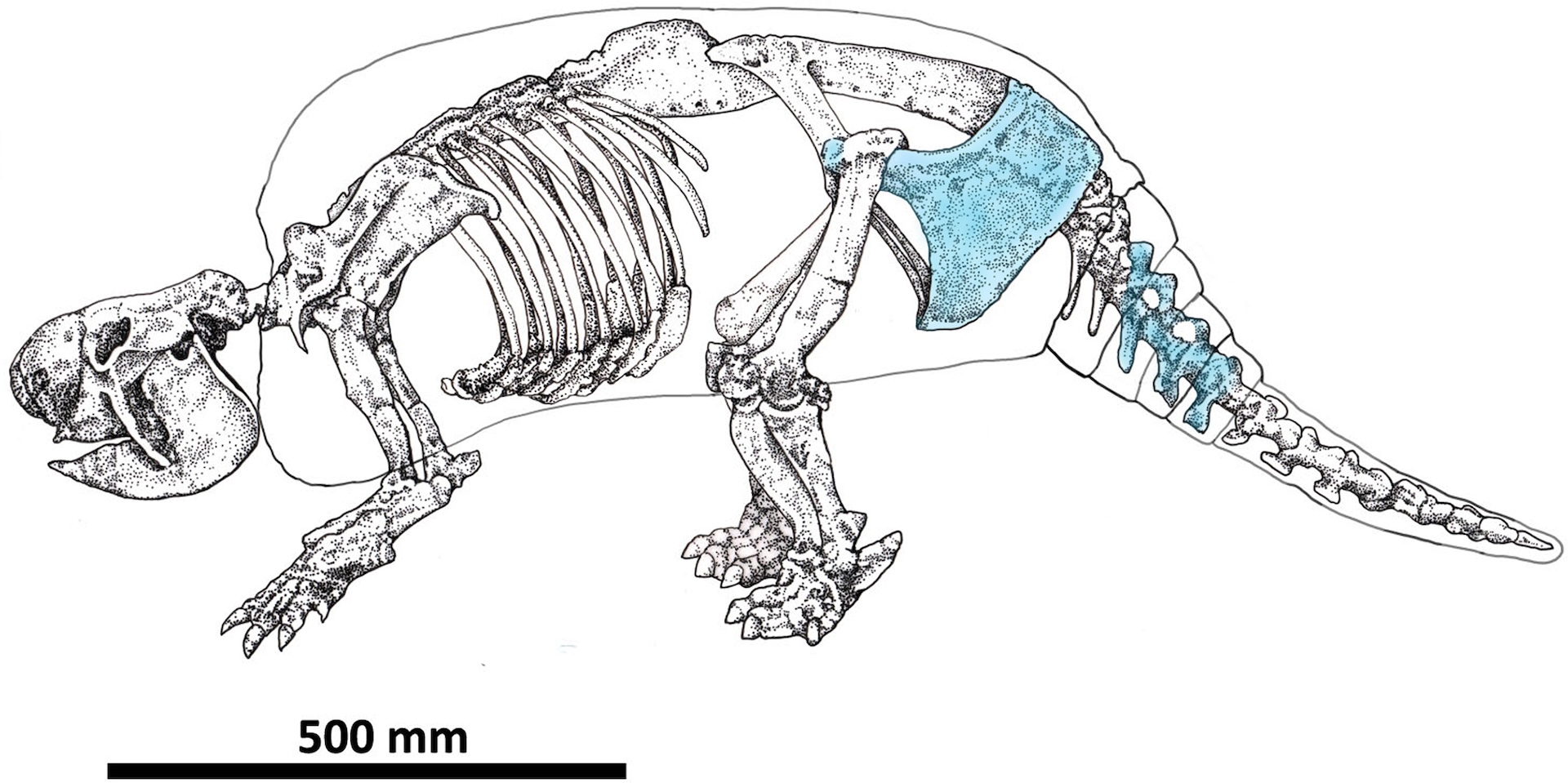
An illustration of aNeosclerocalyptusskeleton that show the cut-marked skeletal elements in light blue.
come to : How did humans first reach the Americas ?
To find out whether the cutting marker were human - made , the researchers photographed and created 3D scans of the animal bone . Some of the marker had a atomic number 23 - shaped cross - surgical incision , which the squad believe is highly suggestive of stone pecker slaughter patsy . In total , the researchers counted 32 cutting marks across the animate being ’s bones . Using a variety of statistical techniques to assort and liken the mark quantitatively , they conclude that the pattern could not have been random — the cuts were made by humans using tools .
The team rule out other possible causes of the marks , including carnivores — whose tooth marks are usually U - shape — and raw weathering of the bone after the decease of the animal , as there was significant evidence that the brute ’s body was buried quickly after destruction , preventing degradation from weather or scavenger .

The location of trimmed marks in different area of the body reveals a butchering sequence , the research worker concluded , and implies that ancient humans acquired — and presumably ate — a large amount of meat from the muscles of the pelvis and tail of the giant armadillo .
" It is possible that citizenry targeted glyptodonts because of their size ( ~300 kilos [ 660 pounds ] ) and the prominent muscularity pack they possess , " sketch co - authorMiguel Delgado , a paleoanthropologist at the National University of La Plata in Argentina , told Live Science in an email .
In addition to revealing the interactions between humans and megafauna , the results of this study " push back the chronological frame of both human presence and human- megafauna interaction nearly 6,000 days in the beginning than put down for other sites in southern South America , " the generator write in their study .

Loren Davis , an archaeologist at Oregon State University who was not involved in the study , say Live Science in an e-mail that the generator ' advanced access to this inquiry is laudable but require more study , particularly as no human - made tools were constitute at the site .
— gem tools and camel tooth suggest people were in the Pacific Northwest more than 18,000 years ago
— human were in South America at least 25,000 old age ago , gargantuan sloth bone pendant reveal
— What ’s the former grounds of humans in the Americas ?
" Establishing the grade to which human actions of butchery are alike to and dissimilar from the breadth of natural processes that change pearl is needed to support their claim for human bearing at this website ~21,000 years ago , " Davis say .
The researchers noted the " demand to establish a stronger radio link between fossil bones with cut marks and the archeological criminal record , " but they hope to do this presently .

" While we have n’t found any peter yet , it ’s worth notice that we ’ve only excavated a small portion of the site , and there may be more evidence , such as lithic peter , " Delgado enunciate .












