When you buy through links on our web site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
When Charles Darwin developed histheory of evolutionin the mid-19th century , he figured this fundamental process took position very slowly over geologic timescales , get gazillion of years .
But is this correct , or can evolution befall more apace ? How fast can evolution work ?

Evidence shows that meat-eating theropod dinosaurs evolved into birds, but how fast does evolution normally take?
First , get ’s define phylogenesis , which is the process by which a species ' gene or forcible appearing changes bit by bit over time . The driving force is lifelike pick , in which individuals with more good trait survive and procreate , station those traits to the next generation . Over many generations , this is recognise as adaptive evolution .
Combined , natural choice and adaptive evolution take into account a " specie to give chase changes in its surroundings , " saidTimothée Bonnet , an evolutionary biologist at the French National Center for Scientific Research and La Rochelle University .
In the famous exercise of Darwin ’s finches on the Galápagos Islands , dissimilar speciesevolved different beak form and sizeswithin a few decade to specialise in feeding on different eccentric of nuts and insect . This determination made waves following the publication of the Pulitzer Prize - winning playscript , " The snout of the Finch : A Story of Evolution in Our Time " ( Knopf , 1994 ) .
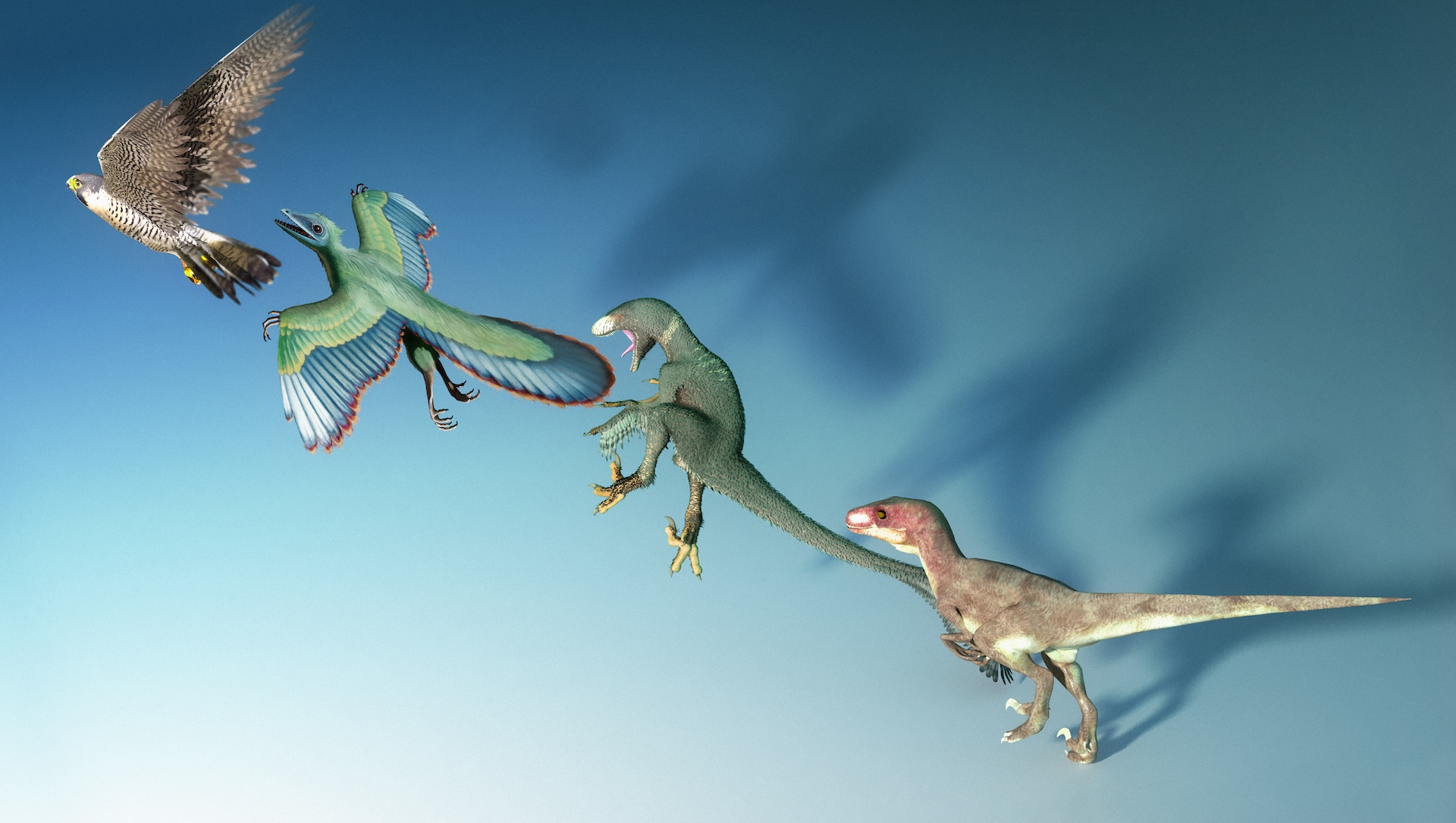

Evidence shows that meat-eating theropod dinosaurs evolved into birds, but how fast does evolution normally take?
Related : Which animate being are most likely to survive climate change ?
Then , there ’s a third element : speciation . This is when one species branches off into two discrete species over fourth dimension . Bonnet said this happens much more lento than adaptive evolution .
By the early to mid-20th hundred , scientists realized that evolution can happen much more quickly than Darwin ever thought by using the theory of born selection to makecrops morepalatable inas few as seven yearsand domesticate dogsover a few generation . " We made evolution pass , " Bonnet told Live Science . " We could see that the alteration happening at this scale of a few generation ( can ) be quite dramatic . "

This contrived selection accelerate development , but how tight can the process work of course ?
To find out , Bonnet and an international team of research worker psychoanalyze decennary ofgenetic data for 19 bird and mammal coinage . They found that the rate of adaptive phylogeny wastwo to four times fasterthan former idea . More specifically , each generation increased its selection and facts of life by 18.5 % , on medium , under totally stable conditions .
This means that if survival and replication decreased by a third , adaptive evolution would help a population recover in three to seven generations . Bighorn sheep ( Ovis canadensis)evolved hornsthat were 0.7 column inch ( 2 centimetre ) shorter than before over 20 years , or three generations , because Hunter had targeted those with great horns . C. P. Snow voles ( Chionomys nivalis)shrankby up to 0.1 ounces ( 3 grams ) over 10 long time , or eight generations , probably because of changes in snowfall .

But in nature , weather condition are never stable .
" We have populations adapting , but we do n’t know what they are adapting to , " Bonnet said . He explained that environmental change , contention , disease and human race can all instigate rapid phylogenesis . " Evolution is there to stabilize , or at least buffer a bit , the changes that are materialise in the environment , " he added .
mood changeis another major number one wood of adaptative development , Bonnet said , but scientist are n’t quite sure whether population will keep up . As temperatures , weather patterns and sea level rise have changed , some species have responded by moving to cooler billet or adapting to more saline conditions . That say , environments could be deteriorating faster than organic evolution can work , he said .

" Evolution is always occurring,“James Stroud , an evolutionary biologist at Georgia Institute of Technology , told Live Science .
If rude selection is substantial , then " why do n’t thing evolve quickly all the time ? " Stroud wonder , leading him topublish research on the topic . He and colleagues found that natural selection in tropical lizards on short timescales ( generations or years ) was very active but canceled out on prospicient timescales ( million of years ) — leading to near no change .
Rate of change
How do scientists even measure evolutionary rates?Philip Gingerich , a paleontologist at University of Michigan , developed one method , using a unit of measurement appropriately call a darwin . He found that evolution works slowly on long timescales and quickly on shorter unity .
" Rates of evolution can be fantastically fast because of that constant environmental change,“Michael Benton , a vertebrate fossilist at the University of Bristol , told Live Science . But " the short the time weighing machine , the faster the rate , and this is after you have chasten for sentence , " he added .
Stroud and his colleagues at the University of Miami are nowusing foreign-born greenish iguanas as a case studyfor rapid phylogeny . The lovesome - adapted lizard are known to freeze and fall out of trees during Miami ’s infrequent moth-eaten snaps .

" What we see is that some die , but some survive — and the ones that survive can actually stand colder temperature than the ones we measured before , " Stroud sound out . " So it suggests that evolution might be chance . "
— Does phylogenesis ever go backwards ?
— What is the most genetically divers species ?
— How long do most species last before give-up the ghost extinct ?
The fogey book hold some clues , too . In theTriassic period(251.9 million to 201.3 million old age ago ) , after thePermian extinction , large marine reptiles call ichthyosaur evolve to be gigantic inless than 3 million years — more promptly than whales did — because they became the sea ’s top predator .
component such as correct to new term , fill new niches , evading predatory animal and vie with other animals often increase how quickly an animal can germinate , Benton say .

" possibly the solvent is that everything is equal to of hugely crazy fast evolution , if it has to , " Benton said .










