When you purchase through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Parasitic horsehair wrestle that dwell in the guts of implore mantises obligate their emcee to walk to urine and overwhelm themselves .
Now , scientist have discover the secret to these worm ' horrifying mind control : They slip their innkeeper ' genetic codification .
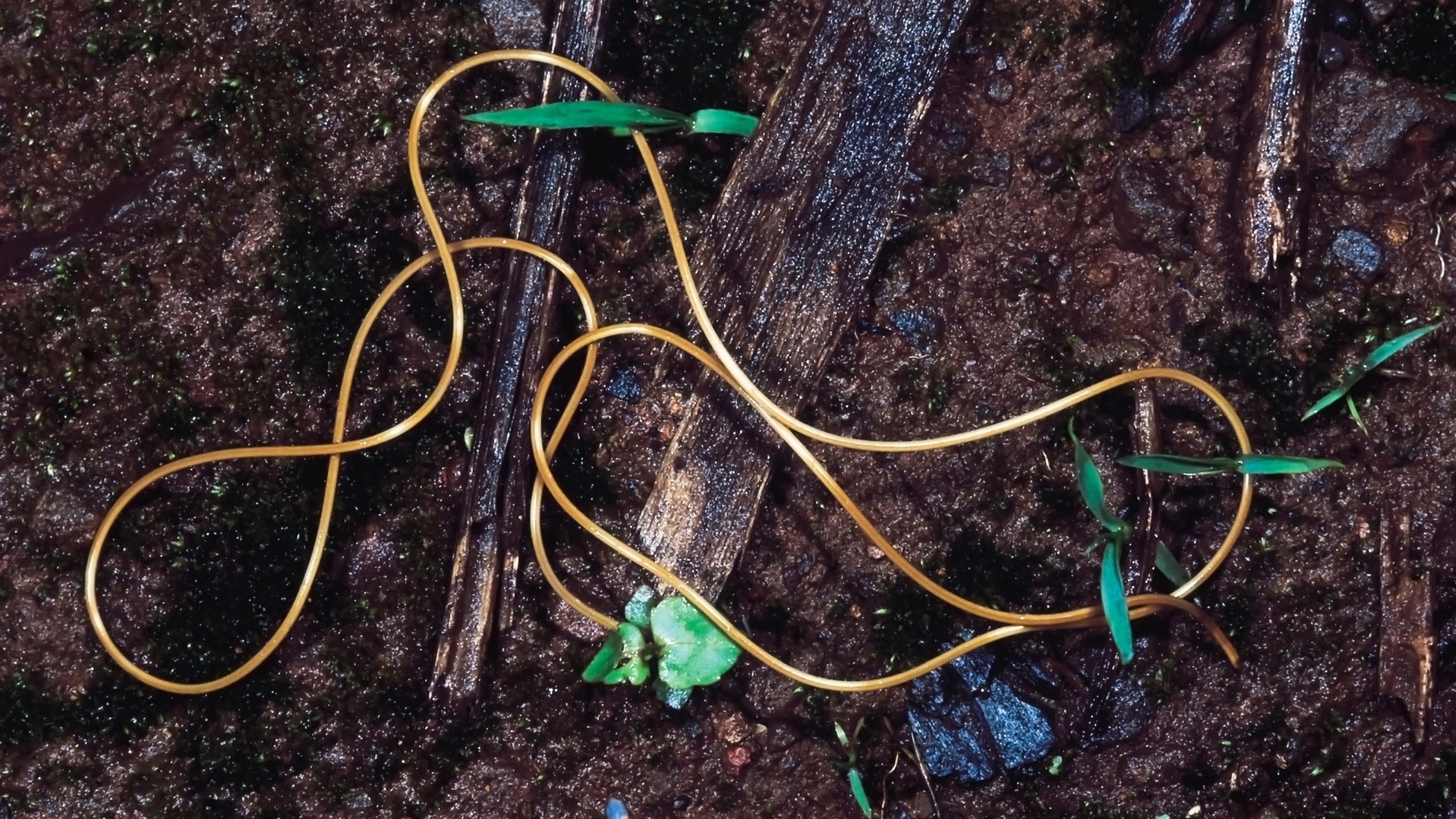

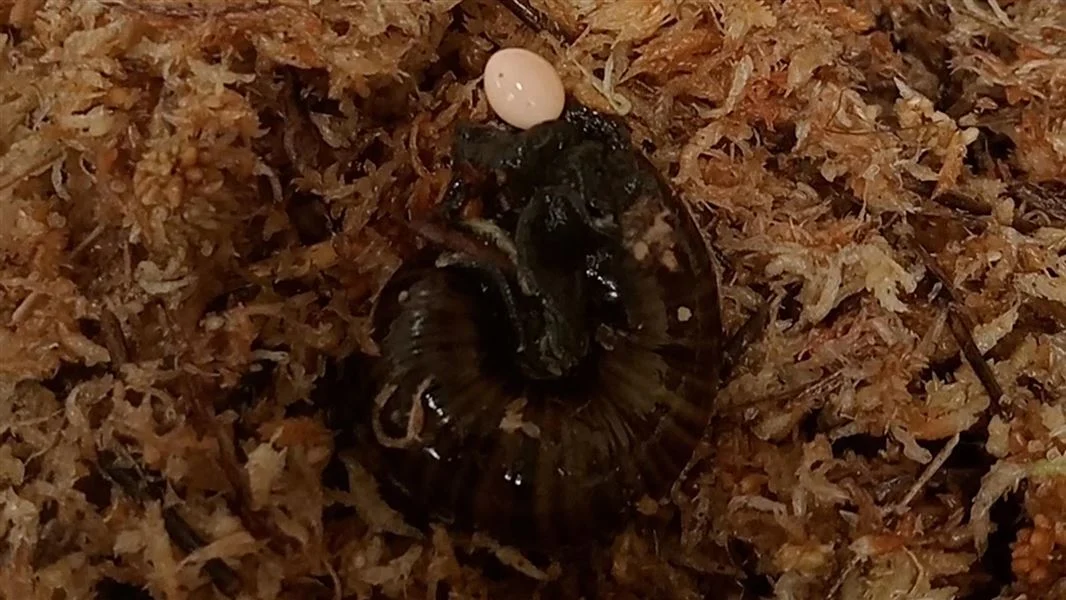
A horsehair worm writhes on the soil near Rajgad fort, India.
By turn the mantid ' own genes against them , horsehair worms ( Chordodes formosanus ) hijack their hosts with a molecule that have them to march toward light shimmer off pee . Once their victims have hurled themselves in , the grownup worms writhe liberal . The researchers published their finding Thursday ( Oct. 19 ) in the journalCurrent Biology .
Related : Green - banded broodsac : The brain - highjacking parasite that create disco zombie snails
Horsehair wriggle ' lifetime cycle typically commence in ponds , puddles , pools and streams , where they think up from egg before hitchhiking to shore by sticking to aquatic insect . After being eaten by pray mantid and cricket , they grow speedily inside their hosts , before unleashing a barrage of biochemical signaling — unco similar to those used in the legion ' body — to transubstantiate their victim into powerless zombies .

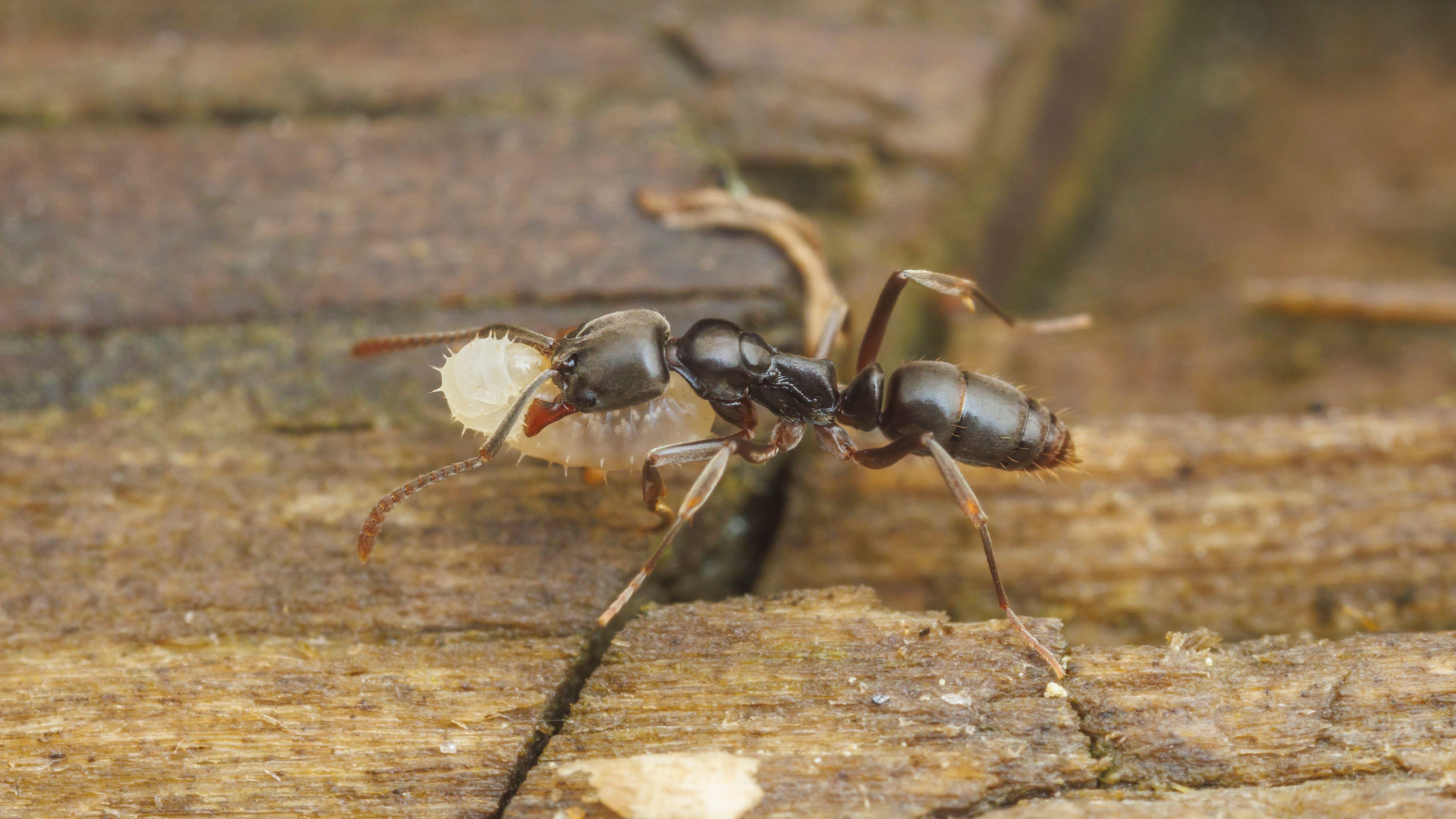
Chordodes formosanusnext to its praying mantis host.
To investigate how the worms achieved this molecular mimicry , the research worker performed a genetic analysis of the louse before , during and after they manipulate their mantis hosts .
The scientists hear that when a host was being manipulated , 4,500 of the worm ’s cistron changed in their expression , while the mantis ’s gene expression remain unchanged — a sign that the worms were using the genes to make their own proteins .
By look up the involved genes in a database , the investigator discovered that 1,400C. formosanusgenes closely equate those belonging to the mantis , whose nerve systems the worm commandeered . These gene were leave out from other horsehair worm species that do n’t practice praying mantis as hosts .

— virile leechlike wasp can sniffle out female mates ready to burst from their hosts
— Cannibal wasp babies eat their siblings , because nature is savage
— 3,000 - year - old mummify bee are so well preserve , scientist can see the bloom the insect consume

" Strikingly , many of the horsehair worm gene that could dally important role in pull strings their host were very similar to mantis genes , suggesting that they were learn through horizontal gene transportation , " first authorTappei Mishina , a biologist at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research , pronounce in a command .
Horizontal cistron transfer , the shuttling of genes between individuals that are not a parent or offspring , was once considered to be a clean rare procedure that materialise only in bacterium . However , scientist lately found that it occurs inwild works , plant parasitesand evenbetween snakes and frogsthrough shared parasites such as leeches .
By kidnap new genes or functions , the process enables organisms to adjust more apace than they could through mutant alone , and it ’s one reason for the uprise antibiotic resistance of many superbugs .

" The many cases of horizontal gene transfer that we have institute in the hairworm can be a good model for study , " Tappei said . " Using this model , we hope to identify the mechanisms underlying horizontal gene transportation and advance our discernment of evolutionary adaption . "