When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it act .
The Gulf Stream is almost certainly weakening , a new study has confirmed .
The flow of warm water through the Florida Straits has slowed by 4 % over the past four decennium , with grave entailment for the world ’s mood .
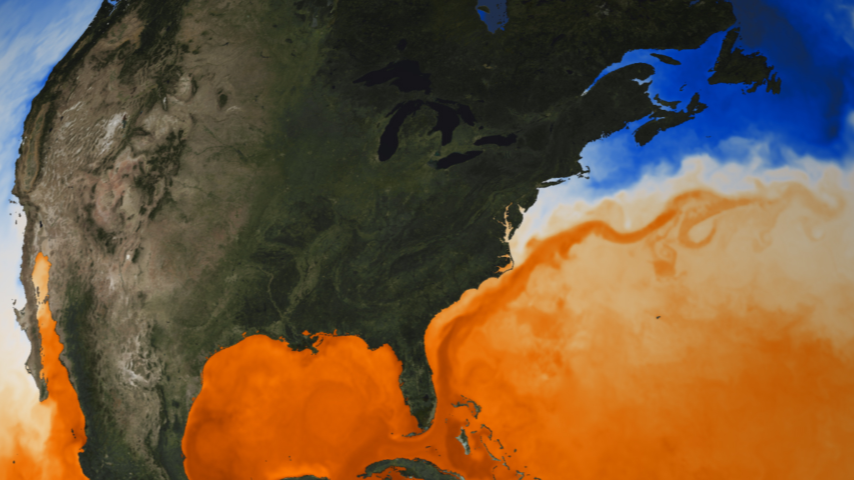
A color-enhanced image of surface water temperatures shows the Gulf Stream crossing the Atlantic Ocean from the Florida Straits.
The ocean flow starts near Florida and thread a belt of warm body of water along the U.S. East Coast and Canada before crossing the Atlantic to Europe . The high temperature it transport is essential for maintain temperate conditions and regulating sea levels .
But this flow is slowing down , investigator wrote in a field put out Sept. 25 in the journalGeophysical Research Letters .
relate : Gulf Stream electric current could collapse in 2025 , plunging Earth into clime pandemonium : ' We were actually bewildered '

" This is the strongest , most definitive evidence we have of the weakening of this climatically - relevant ocean current , " lead - authorChristopher Piecuch , a forcible oceanographer at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in Massachusetts , said in a statement .
The Gulf Stream is just a modest portion of the thermohaline circulation — a global conveyor belt of sea current that moves oxygen , nutrient , carbon and heat around the planet , while also helping to master ocean levels and hurricane action .
Beginning in Caribbean before flowing out into the Atlantic through the Florida Straits , the Gulf Stream bring in warmer southerly water ( which are saltier and denser ) northward to cool and drop in the North Atlantic . After dropping deeply beneath the sea and expel its heat into the atmosphere , the urine slowly drift southward , where it heat up again and the oscillation repeats .

This mental process is lively for assert temperature and sea levels across the U.S. East Coast — whose waters are keptup to 5 human foot ( 1.5 metre ) lowerthan piddle further offshore by the sweeping motion of the stream .
As Earth ’s climate warms , anenormous influxof cold , overbold piddle from melting ice sheet is spilling into ocean , peradventure causing the Gulf Stream to slack or even veer towardoutright flop , harmonise to scientists . But due to the scale and complexity of the arrangement , this is tough to raise .
To rule definitive evidence that the stream is slow , scientist analyzed data spanning 40 years from three disjoined seed — undersea cable , satellite altimetry and observation made on internet site — to observe the motions of the current around the Florida Straits .

— Catastrophic climate ' doom loops ' could start in just 15 years , new field warns
— Climate change induce a mint peak frozen for thousand of years to burst
— Global heating will in all likelihood cross serious 1.5 cytosine threshold within 5 years , UN report admonish

Their statistical psychoanalysis revealed that the current had slow by 4 % , with just a 1 % chance of their measurement being a fluke due to random fluctuations .
At first coup d’oeil , a 4 % geological fault may seem like a minuscule modification , but " the worry is that ’s just the dull start,“Helen Czerski , an oceanographer at University College London ( UCL ) who was not involved in the work , told Live Science .
Related : learn about the satellite ’s engine in an audience with Helen Czerski

" It ’s like those former days of COVID . People were like : ' Oh , there ’s only 60 cases . We do n’t care about this , ' " she added . " There ’s only 60 cases , yeah , but yesterday there were 30 and the solar day before that there were 15 . If you just think a week in front , we ’ve have a job . "
To notice classic test copy thatclimate changeis the culprit , scientists will need to tease apart the differences between the rude variability of the ocean system and the impact made by spherical warming — a crafty task given the comparatively short time that humans have been straightaway measure the sea flows in detail .










