When you purchase through links on our site , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
astronomer have blot the light and calorie-free satellite galaxy ever incur : a minuscule , tight - knit grouping of stars get behind theMilky Way . The funny uncovering could represent a new socio-economic class of impossibly faint , drab - matter - prevail star systems that had fudge detection until now .
Tentatively named Ursa Major III / Unions 1 ( UMa3 / U1 ) , the newfound lead system domiciliate in the configuration Ursa Major , about 30,000 promiscuous - years from the sunlight . It is the newest accession to our beetleweed ’s assortment of at least 50 satellite galaxies . Even the smallest of these galaxies host thou to jillion of stars .

A group of bright stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. A newly discovered satellite galaxy named Ursa Major III/Unions 1 may be the smallest ever, with just 60 stars.
The newfound organisation , by contrast , has just a sprinkling of 60 stars . As such , its mass is just 16 times the multitude of the sun , scientist report in a fresh field of study . For comparison , theMilky Way ’s mass is about 1.5 trillion time that of our whiz , according toNASA .
UMa3 / U1 also defies the conventional image of a distinctively shape galaxy .
" This discovery may challenge our understanding of wandflower formation and perhaps even the definition of a ' galaxy,'“Simon Smith , a alum student at the University of Victoria in Canada and the lead author of the subject area , say in astatement . " UMa3 / U1 had scat detection until now due to its extremely low luminosity . "
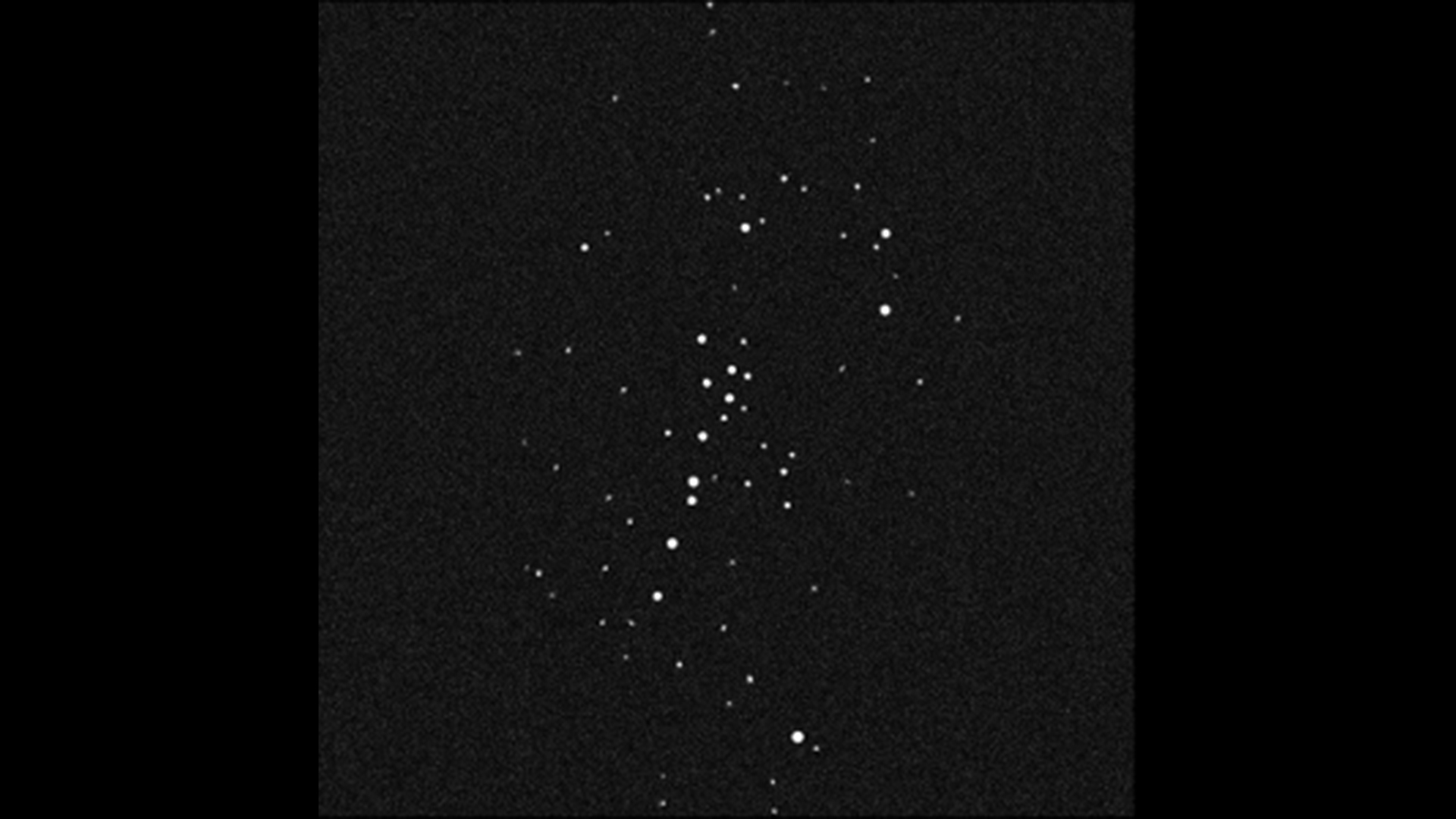

UMa3/U1 was found hidden in this deep-sky image captured by the Canada France Hawaii Telescope.
Related:13 billion - year - old ' streams of stars ' discovered near Milky Way ’s center may be early edifice blocks of our galaxy
Astronomers are baffled by how the petite UMa3 / U1 has remained entire for at least 10 billion years , which is the estimated years of its stellar residents and more than twice the old age of our own 4.6 billion - year - old sun . From observations of other gonzo stars in the Milky Way , astronomers bang that our galaxy ’s gravitational pull , also called the tidal strength , has previously wrenched aside nanus galaxies that adventure too secretive . For instance , a well - have sex cannibalized galaxy isGaia - Enceladus , which our home galaxy ripped aside about 8 billion to 10 billion age ago .
Yet , although UMa3 / U1 ’s domain takes it through inner regions of the Milky Way , where our galaxy ’s tidal forces are the impregnable , the dwarf Galax urceolata appears to have escaped destruction for eons .
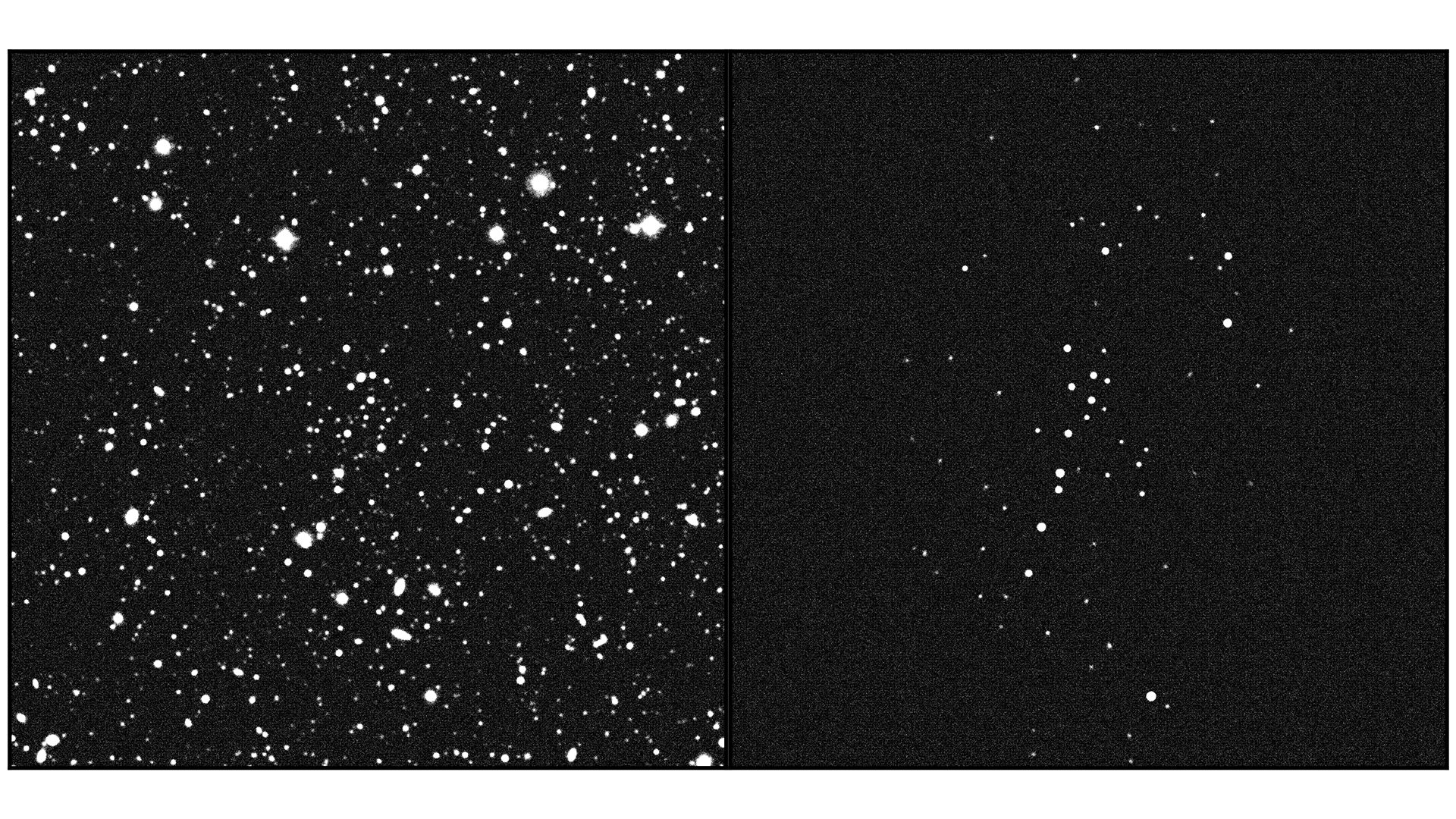
Side-by-side images of the span of sky where UMa3/U1 was found (left) along with the 60-or-so stars that make up the newly discovered star system (right).
" The object is so runty that its long - term survival is very surprising,“Will Cerny , a graduate student in the Yale University Department of Astronomy and a atomic number 27 - writer of the study , say in the instruction . " Either UMa3 / U1 is a midget galaxy stabilized by large amounts of sorry matter , or it ’s a star cluster we ’ve observed at a very especial sentence before its close at hand demise . "
— 13 billion - yr - old ' streams of stars ' discovered near Milky Way ’s shopping center may be early building blocks of our extragalactic nebula
— Study of ' twinned ' stars encounter 1 in 12 have pour down and eaten a planet

— freshly discovered ' spring of youth ' phenomenon may help stars delay death by billions of years
The former possible action is particularly exciting because in galaxies elsewhere in the universe , astronomers have so far been abortive in detectingdark matter , the invisible kernel opine to make up the majority of the matter in our cosmos . If dark matter is indeed responsible for holding the newfound headliner scheme together , succeeding observations could offer valuable clues about obscure matter ’s composition and behavior , the study authors said .
" Whether future watching confirm or reject that this system contains a large amount of morose affair , we ’re very mad by the opening that this object could be the bakshis of the iceberg lettuce — that it could be the first example of a new class of exceedingly faint stellar systems that have eluded espial until now , " Cerny concluded .

Gamma - ray burst reveal with child social structure in the universe is big and closer to Earth than we knew : ' The jury is still out on what it all mean . '
Universe may revolve once every 500 billion years — and that could solve a trouble that threaten to break away cosmogony
The incessant surveillance of modern spirit could worsen our brainiac procedure in ways we do n’t amply empathize , touch study intimate







