When you buy through links on our site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
The ever - honest Curiosity roamer is about to begin a newfangled quest to study giant " spiderwebs " on Mars ' surface , after successfully concluding its old mission , NASAhas announced . The web - comparable rocks span for miles and may hold secrets about the Red Planet ’s washy past .
Over the last yr , Curiosity has been exploring Gediz Vallis — a channel carve into the steep slopes of Mount Sharp at the warmheartedness of Gale Crater . During this phase of its 12 - year charge on Mars , the rover made some significant breakthrough , includingaccidentally unveiling crystallization of pure sulfurandfinding " wavey " rocks leave behind by an ancient lake . delegation scientists also first noticed alarge hole in one of the rover ’s wheelsas the wandering robottraversed this region ’s steep slopes .
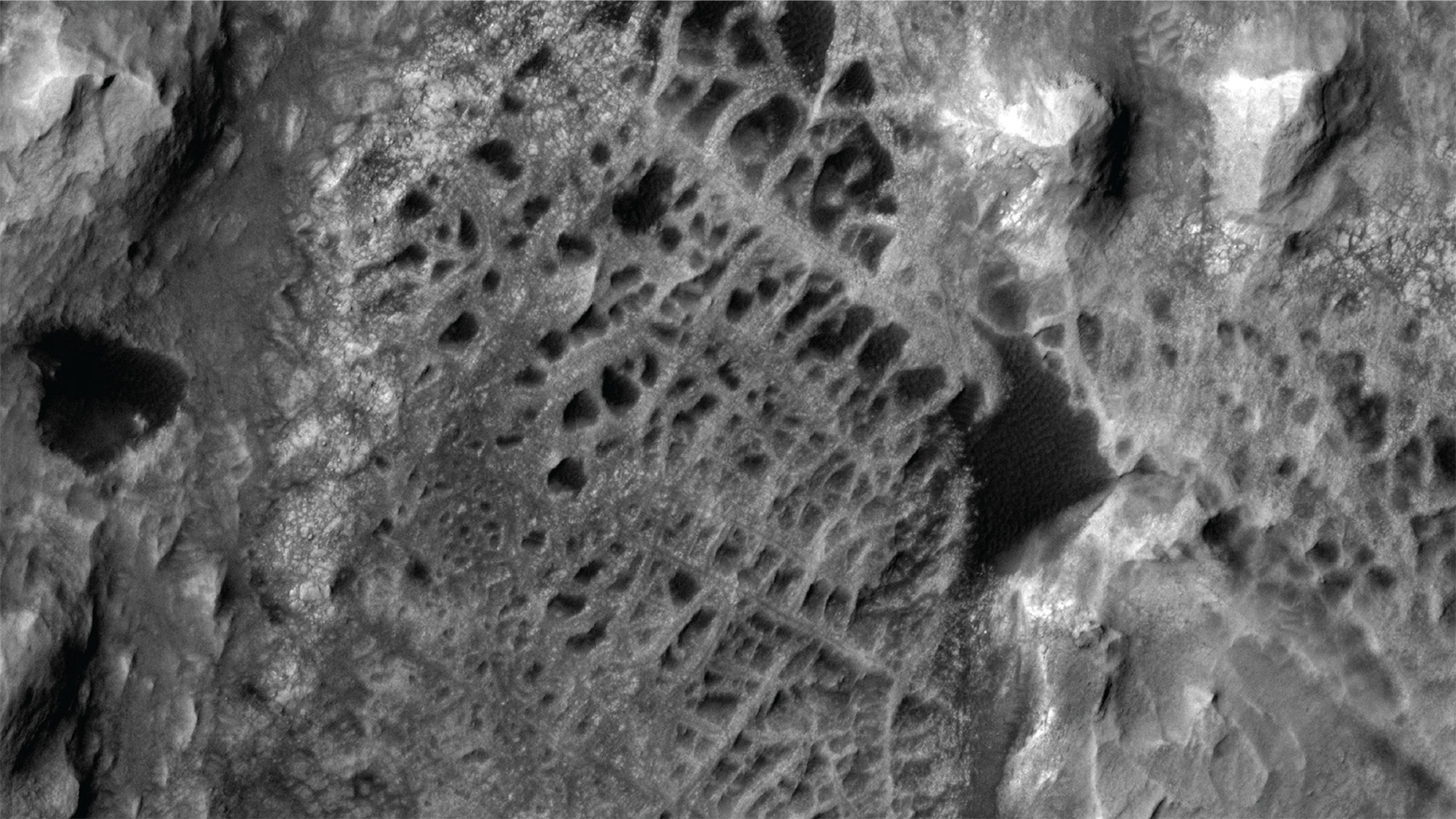

NASA’s Curiosity rover will soon explore a patch of spiderweb-like “boxwork” features on Mars. This photo, taken in 2006, shows a similar area to the one that the rover will explore.
But the rover ’s fourth dimension in Gediz Vallis is about to come up to a close . On Nov. 18 , NASA ’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory ( JPL ) released afinal 360 - degree " selfie " of the areataken by Curiosity as it prepared to steer off on the next leg of its epical journey , which has already survive a decade longer than initially anticipate .
Curiosity ’s next target is a turgid compendium of spiderweb - same Earth’s surface characteristic , known as " the boxwork , " spanning between 6 and 12 stat mi ( 10 and 20 kilometers ) across . This unusual patchwork quilt of zag - zagging rocks , or boxwork deposit , was first make out X ago but has never been studied up closely , according to aJPL statement .
The entanglement - like features should not beconfused with the infamous " spider on Mars " — a geological feature created whencarbon dioxide internal-combustion engine on the major planet ’s airfoil sublimates , or call on into gas from a upstanding . Scientists recentlyrecreated these strange feature on Earthfor the first time .
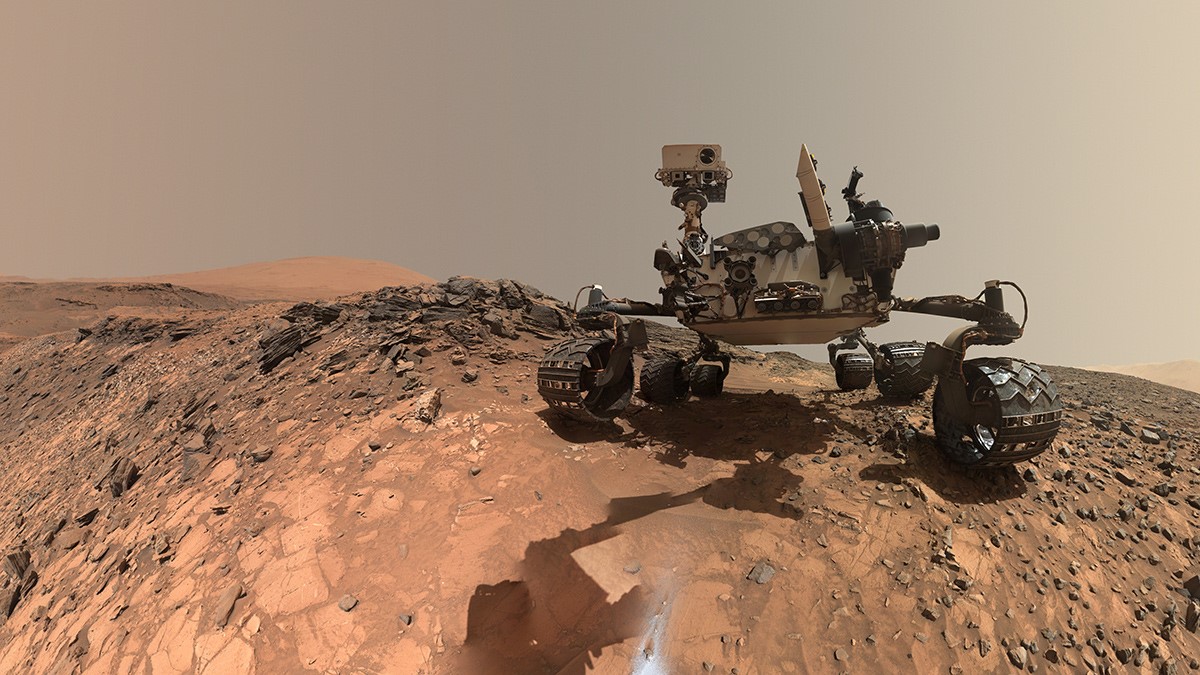

Curiosity has traveled more than 20 miles (33 km) on Mars since first landing in Gale Crater on Aug. 6, 2012.
Related:32 thing on Mars that look like they should n’t be there
Boxwork deposits are also found in caves on Earth . They form when calcite - rich water fills break between rock and hardens before eventually gnaw at away , creating " thin blades of crystalline cloth jut out from rocky rampart " similar tostalactites and stalagmites , according to theNational Speleological Society . The best deterrent example of this on our major planet are found in Wind Cave National Park in South Dakota , according to theU.S. Geological Service . However , terrestrial boxwork features are never more than a few feet across-the-board .
Martian boxwork , which has been identify at several fix across the Red Planet , is believed to take form via a similar process as sublunar boxwork . However , instead of H2O dripping through caves , the sprawling mineral veins were left behind by the last remnants of ancient , mineral - rich lake and oceans .
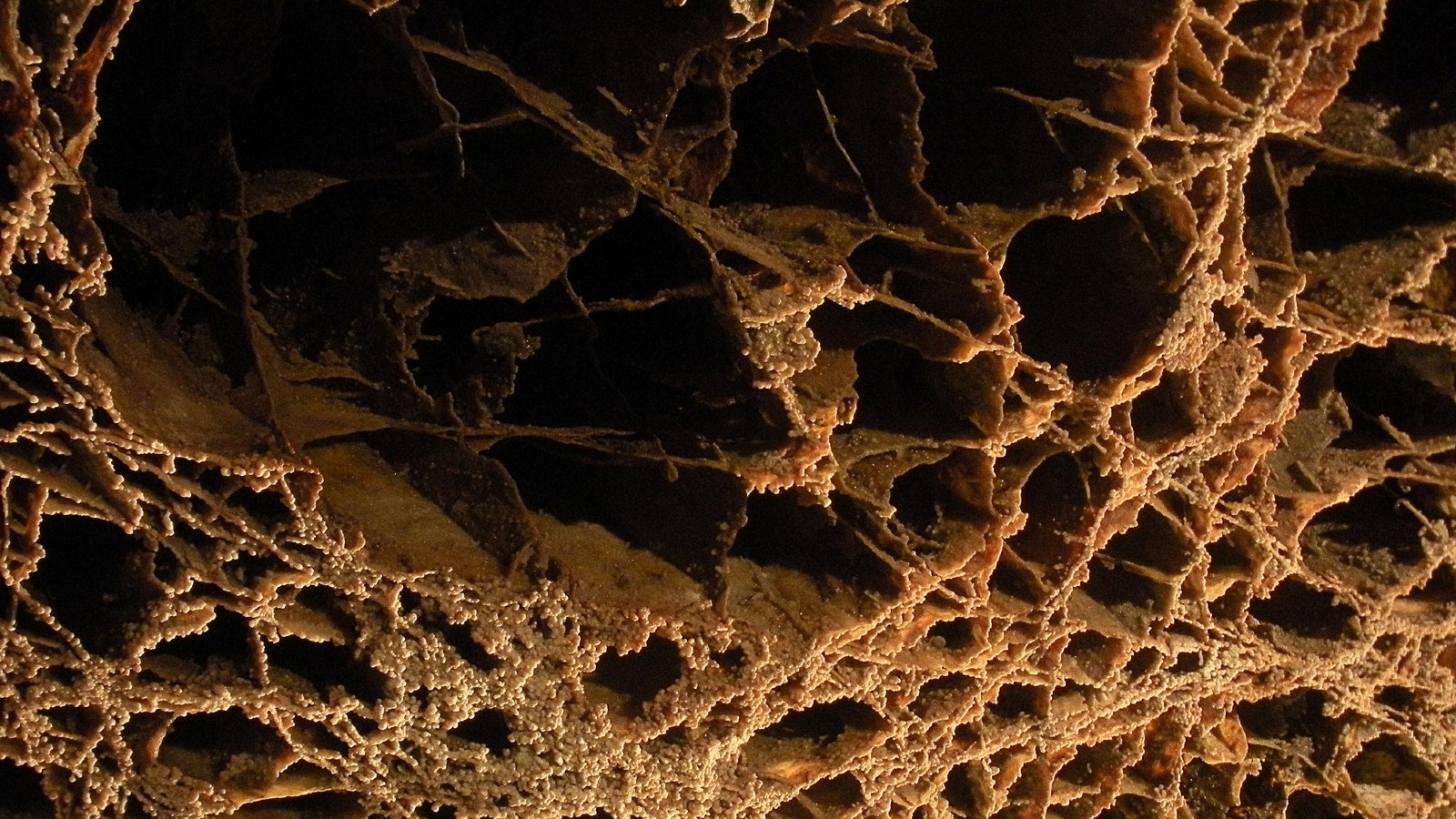
Prominent boxwork deposits can be found in Wind Cave National Park but are significantly smaller than their Martian counterparts.
— 13 billion - class - old ' streams of virtuoso ' discovered near Milky Way ’s centre may be earliest construction engine block of our coltsfoot
— Study of ' twin ' stars find 1 in 12 have killed and eaten a satellite
— Newly discover ' spring of youth ' phenomenon may help headliner check expiry by billions of years

Researchers desire that Curiosity will learn more about just how this befall and what it can tell us about Mars ' weak past . delegacy scientist are peculiarly interested in the minerals that make up these entanglement - like anatomical structure because they could shed brightness level on whether extraterrestrial life once existed on the Red Planet .
" These ridgepole will include mineral that crystallized underground , where it would have been warmer , with salty liquid water flow through,“Kirsten Siebach , a Curiosity commission scientist at Rice University in Houston who has been studying the field , said in the statement . " Early Earth microbes could have survive in a similar environment . That make this an exciting place to search . "
oddity will arrive at the boxwork at some stage in other 2025 .

NASA Mars satellite uncovers markings ' wish key dripping down a rampart ' on Martian surface
NASA roamer discovers out - of - place ' Skull ' on Mars , and scientists are baffled
The constant surveillance of modern life could worsen our mastermind subroutine in way we do n’t fully empathise , disturbing studies propose







