When you buy through inter-group communication on our land site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
mammoth clumps of invisibledark matterthat roam the universe may be wreaking havoc on binary stars , slow tearing them asunder , a young field suggest . Those violent effect could help reveal the true nature of the universe ’s most elusive entity .
Over the decades , astronomers have amass an enormous amount of grounds point to the existence of dark topic , an invisible shape of matter that report foraround 85 % of the massin almost every galaxy . Initially , stargazer think dark matter might be a newfangled kind of particle have it away as feeble interact massive particles ( WIMPs ) , which would interact only with each other throughgravityand the faint nuclear force .
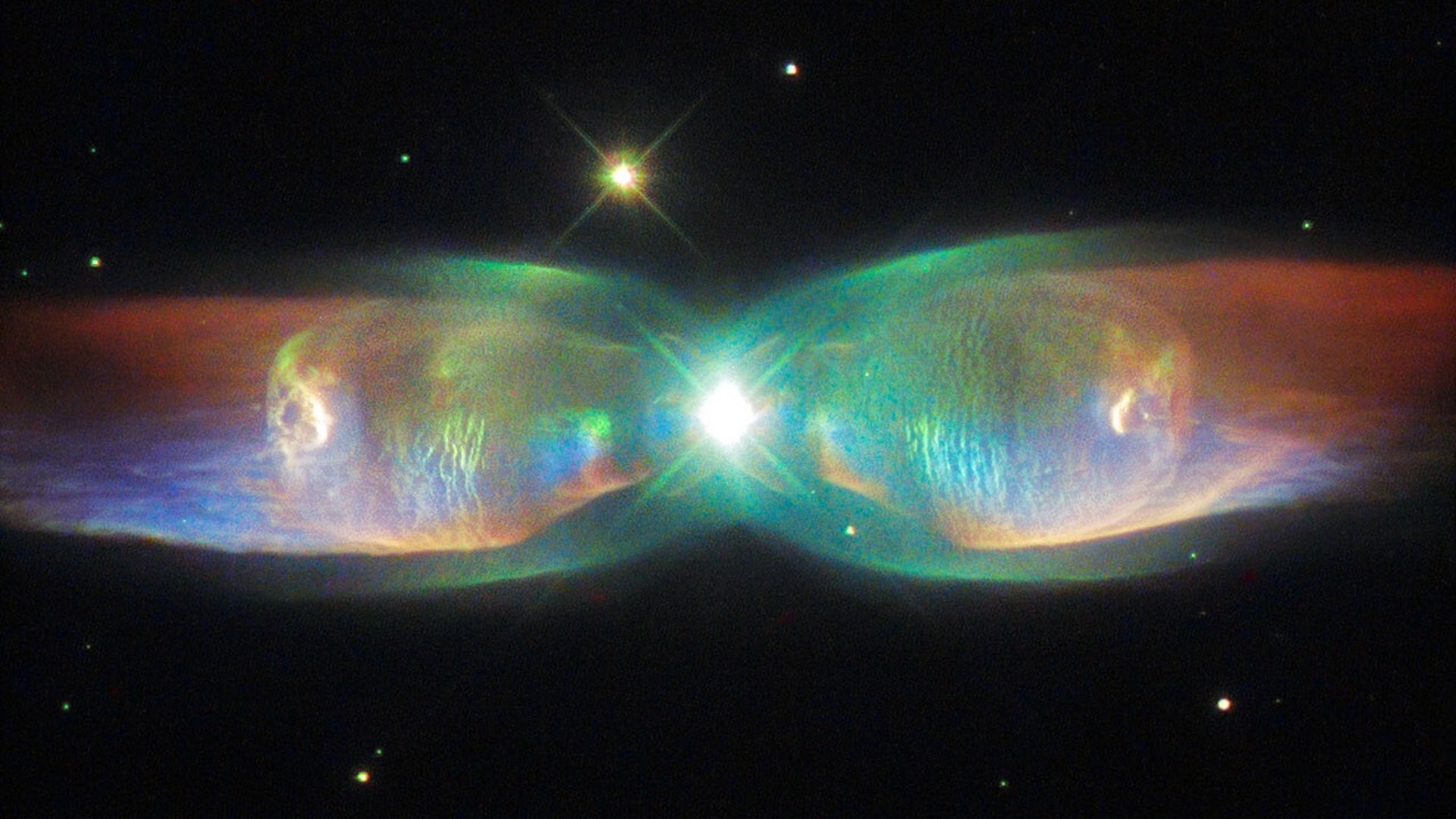
A Hubble Space Telescope image of the Twin Jet Nebula, a planetary nebula created by a pair of binary stars. The influence of dark matter may alter the behavior of stars like these in detectable ways, new research suggests.
But experiment design to find oneself the hint signals of WIMPs as they float through Earth have n’t found anything , and the WIMP theoretical account has some difficulties matching the densities of matter within astronomic cores . Because of this , scientists have been more and more looking toward an substitute model in which the dark topic particle is extremely light — even lighter than the lightest experience atom , theneutrino .
In these model , the dreary matter subatomic particle would be more than a billion billion prison term light than an electron . And we bang fromquantum mechanicsthat all particles have a wave - like nature associated with them , which we can normally detect only in subatomic experiment . But in this scenario , the sullen matter would be so light that it would do more like a undulation at exfoliation the size of it of thesolar systemor gravid .
late , a team of astronomers inChinaexamined this example and looked for ways to observationally notice this kind of dark matter . They reported their workplace inan article publishedto the preprint server arXiv in April . ( The subject has not been peer - reviewed yet . )
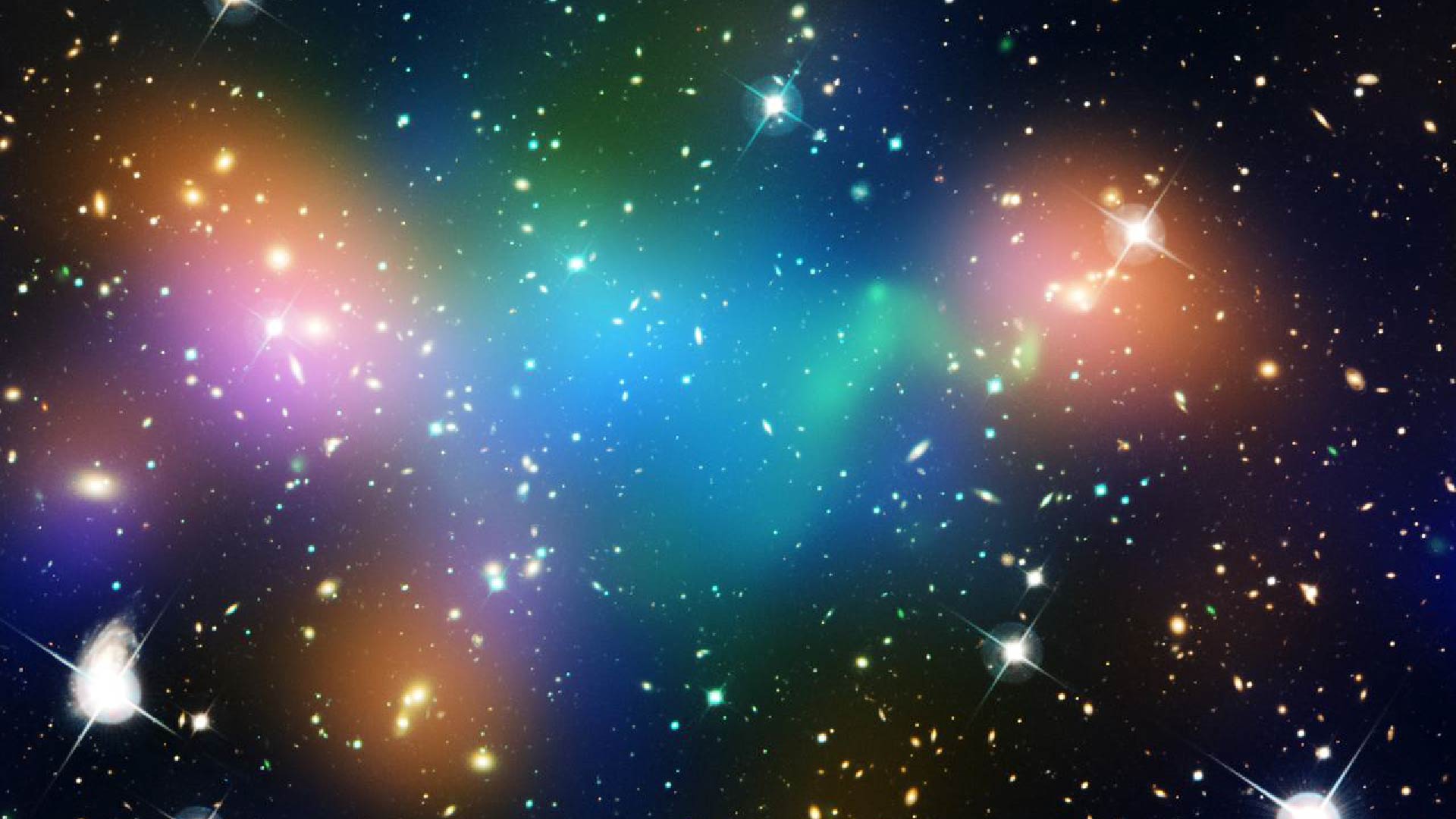

Dark matter (represented in blue in this composite satellite image) dominates up to 85% of the mass of most galaxies.
Ultralight dark matter would n’t buzz around the world like tiny bullets . Instead , it wouldslosh around every galaxylike a huge , invisible ocean . And just like oceans can hold waves , the bath of ultralight dark matter would have oscillation of its own . Some of these Wave could potentially bundle together into a single group that travel interdependently while maintaining their shape — known as a soliton .
These solitons would be completely invisible — like elephantine , rogue waves washing through the coltsfoot but made of matter so light that they would barely affect their environs . But the scientists behind the new study discovered that the solitons ' huge size of it could subtly neuter the gravitational environment around them .
— zillion of invisible ' mirror champion ' could exist in the Milky Way , and astronomers fuck how to get them

— 1st images from the Euclid ' dark population ' telescope are here — and they ’re jaw - dropping
— Large Hadron Collider could be generating dark subject in its speck honey oil
The gravitative influence of the solitons would be so weak that almost everything in the galaxy would be unmoved by them . But binary pair of stars that have wide separation are only weakly hold together by their mutual sombreness , so the solitons would be cock-a-hoop enough to alter their orbits .

The researchers identified all wide binary pairs in theGaia catalogof the billion whiz penny-pinching tothe sunand flagged them for future observations . If the binary star were to commence freewheel away from each other , that might be due to the influence of soliton .
The team find that by watching the binary stars evolve , we could have a very sensitive probe of ultralight drear matter — perhaps even more sensitive than any Earth - based research laboratory designed to detect this kind of dark matter . So , if something unusual seems to be happening to binary stars , we might just have our first clue as to the nature of obscure matter .
Ghostly galaxy without dingy matter baffles astronomers

' operose ' dark matter would rip our understanding of the universe apart , new research suggests
See the reconstructed home of ' opposite dinosaurs ' that thrived in the Antarctic 120 million years ago







