When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it works .
Geologists digging into the monumental methamphetamine sheet of West Antarctica have attain the remains of an ancient river system that once flowed for well-nigh a thousand mil .
The find offers a glance into the Earth ’s history and hints at how extremeclimate changecould falsify the planet , according to their finding , published June 5 in the journalScience Advances .
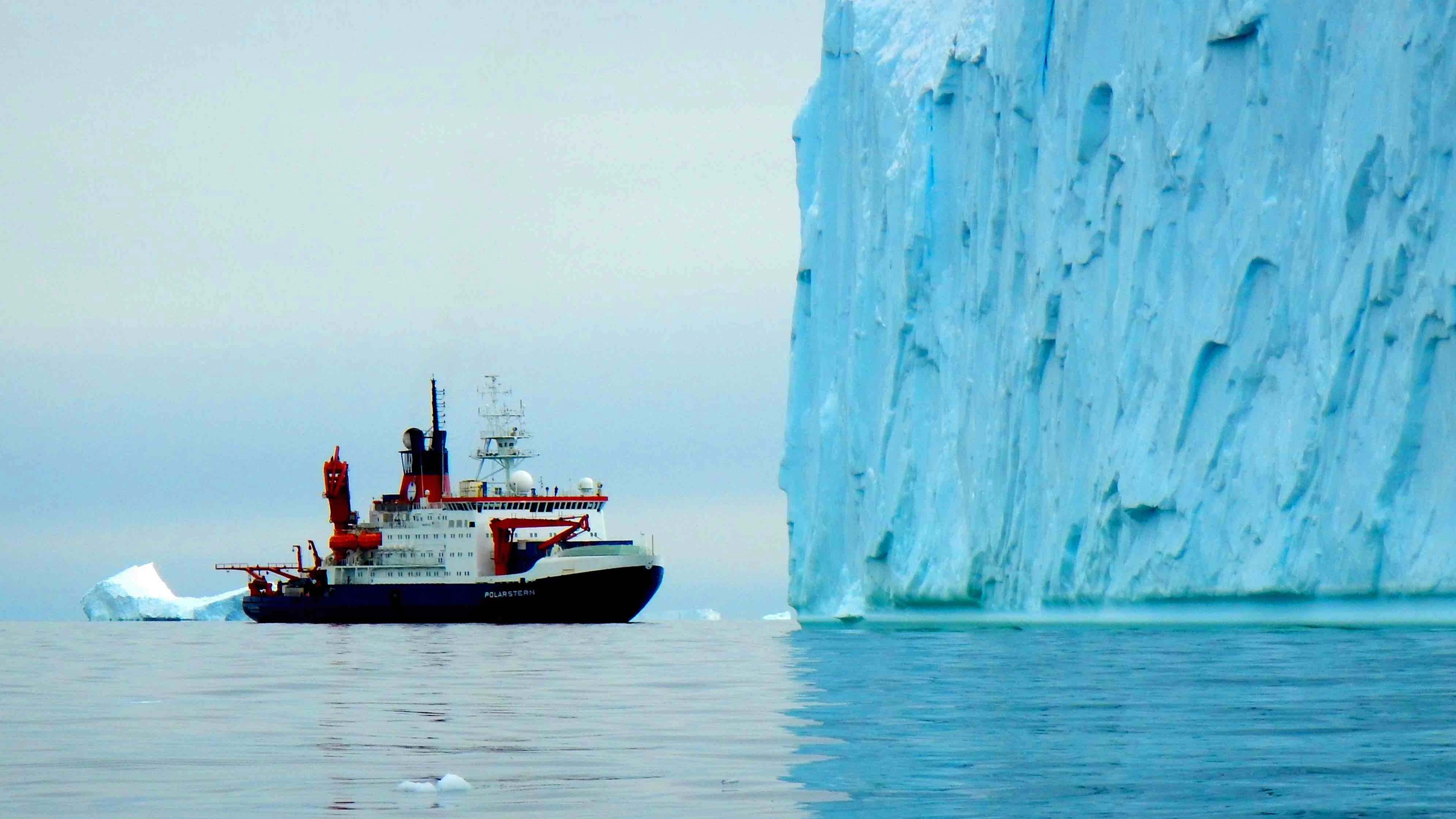

A research icebreaker Polarstern in front of a giant iceberg in the Amundsen Sea. Researchers on this vessel have discovered evidence of a giant river that once ran across West Antarctica.
" If we think about a potentially severe climate change in the future , we call for to pick up from periods in Earth ’s chronicle where this already happened,“Johann Klages , study co - author and a sedimentologist at the Alfred Wegener Institute Helmholtz Center for Polar and Marine Research in Germany , told Live Science .
Between 34 million to 44 million years ago , an epoch known as the middle - to - late Eocene , Earth ’s atmospheric state transformed drastically . As C dioxide level plummet , spherical cooling system triggered the formation of glaciers on an deoxyephedrine - loose Earth .
Scientists are interested in investigate how this major climate event blossom forth in Antarctica , especially as carbon dioxide levels on Earth persist in to rise due to human being - caused climate change . The amount of carbon paper dioxide during the late Eocene flow was almost double the amount we have today . However , it may be similar to levels predicted in about 150 to 200 years if levels ofgreenhouse gasescontinue to rise , Klages said .
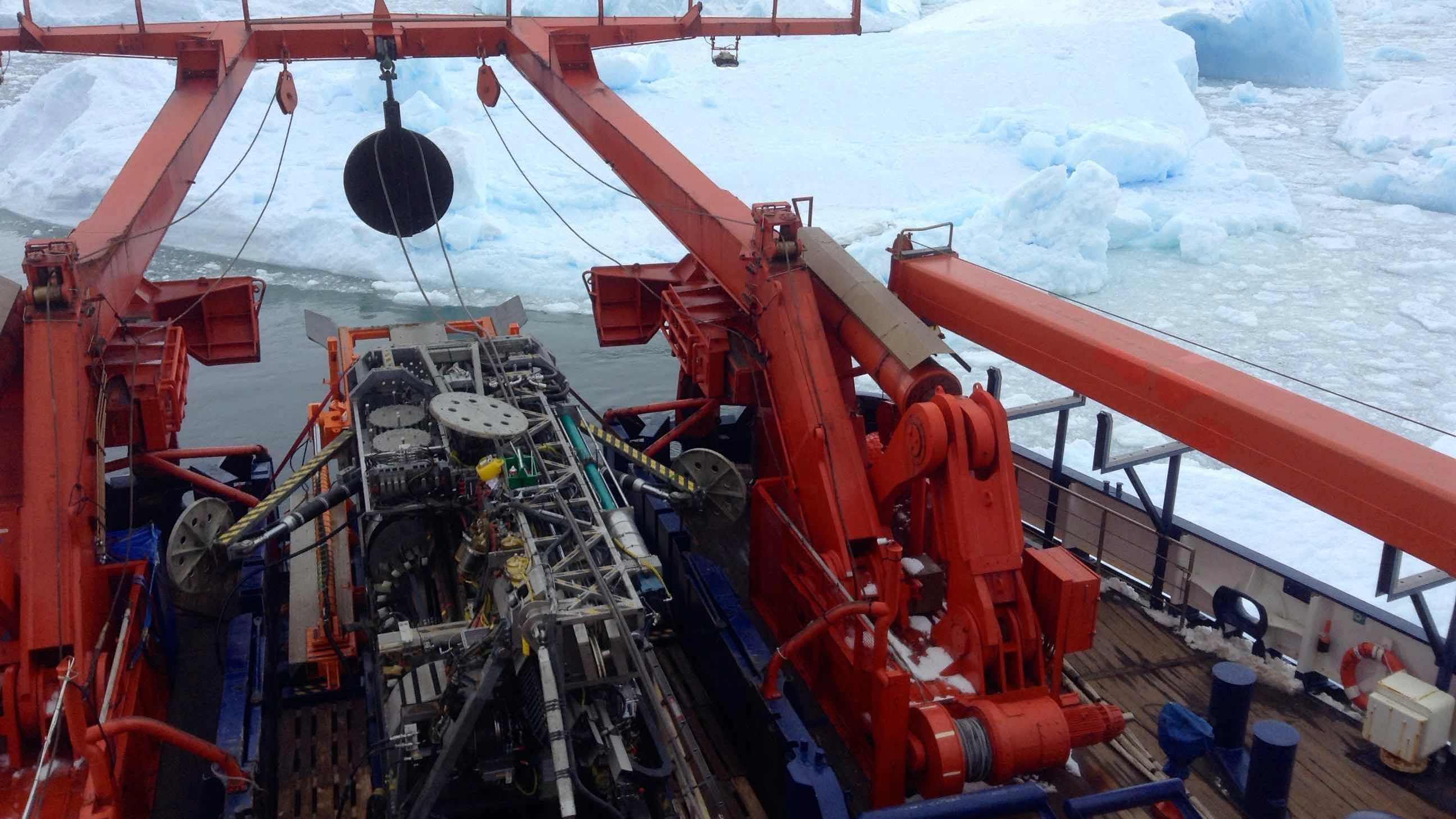

Researchers aboard the research vessel “Polarstern” found an ancient river in West Antarctica that existed 40 million years ago using advanced drilling equipment.
But uncovering the yesteryear has proven challenging . Most of West Antarctica today is covered in ice , making it difficult to get at sedimentary rock-and-roll , which are decisive to studying early environments . Geologists often rely on the case of caryopsis , mineral and fogey ensnare within these sediments to go out the kind of conditions that characterise an sphere .
In 2017 , Klages and other scientist onboard the enquiry vessel Polarstern despatch traversed from the southernmost part of Chile , across the rough Drake Passage and into the western part of the icy continent . Equipped with sophisticated seafloor drilling equipment , Klages and his squad plant out to accumulate cores from soft sediments and severe rocks within the frozen Davy Jones’s locker .
After drilling nearly 100 foundation ( 30 cadence ) into the seafloor , the researchers retrieved sediment with layers from two distinct periods .

By compute the half - life of radioactive elements , such as the ratio of atomic number 92 and guide in the sediment , they come up that the lowly part of the deposit was formed during the mid - Cretaceous flow , about 85 million years ago . This deposit contained fogy , spore and pollen characteristic of atemperate rain forest , which be at that time . The upper part of the deposit contain mostly sand from the mid - to - later Eocene epoch , about 30 million to 40 million years ago .
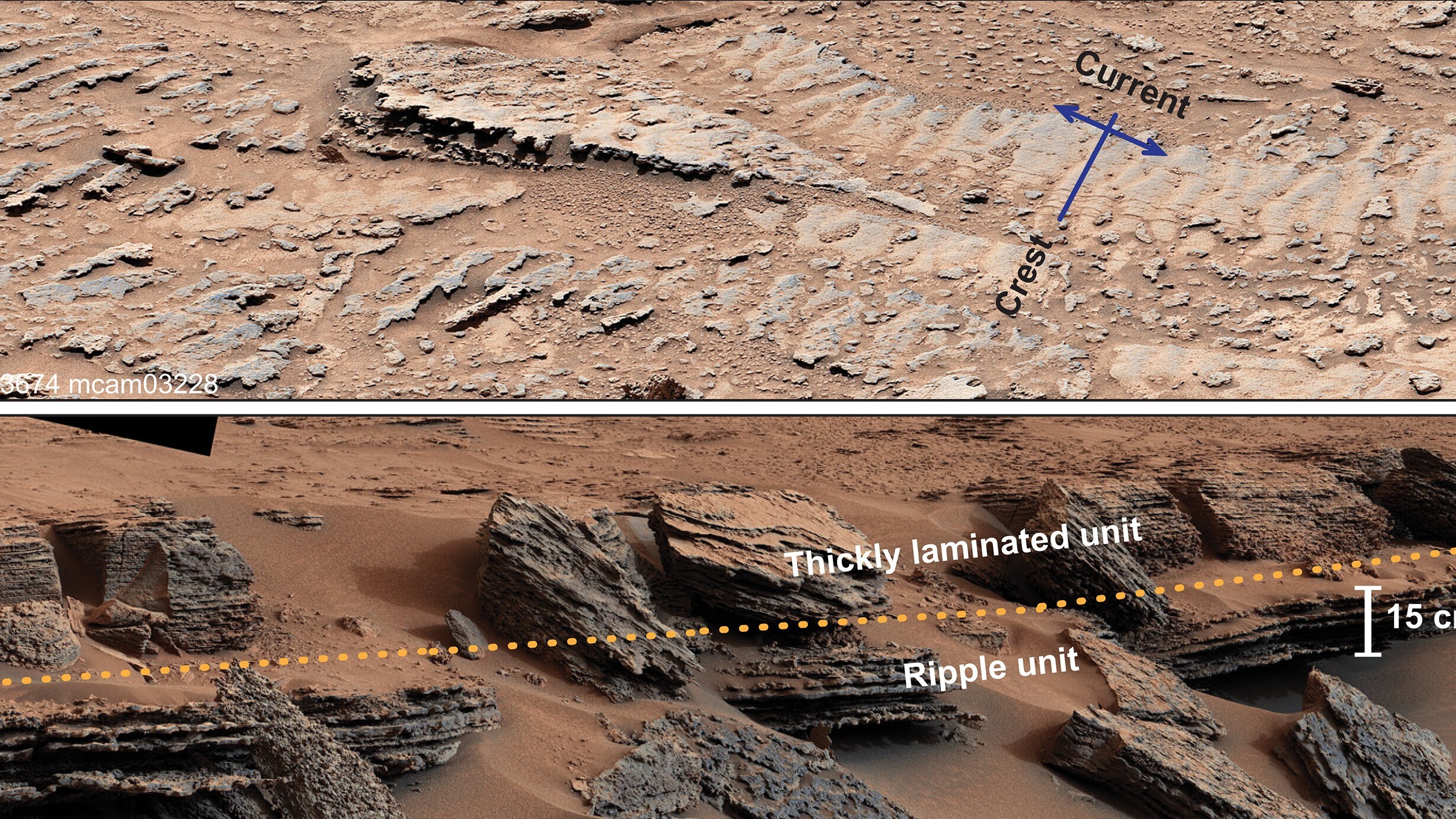
Upon closer inspection , they recognized a strongly stratified pattern in the Eocene sand layer that resemble those coming from a river delta , very similar to something one would meet in the Mississippi River or Rio Grande , Klages say .
The scientist performed a lipid biomarker depth psychology , in which they quantified the amount of lipid and sugar in the sediment , and found a unique molecule normally found in cyanobacteria that last in freshwater . The determination corroborate their suspicions that an ancient river once snaked across the continent .

— rip Falls : Antarctica ’s cherry falls formulate from an ancient hidden inwardness
— quick ocean water is rush along beneath Antarctica ’s ' Doomsday Glacier , ' making its collapse more likely
— Antarctica is covered in volcanoes , could they erupt ?

The researcher traced the Eocene texture to a distinct salt region in the Transantarctic Mountains , traversing an country that spanned about 930 miles ( 1,500 kilometers ) before draining into the Amundsen Sea .
" This is exciting — just having this exciting image in your mastermind that there was this gigantic river system flowing through Antarctica that is now plow by kilometers of water ice , " Klages said .
Klages and his squad are now analyzing parts of the core group sediments that belong to to a more recent Oligocene - Miocene period , about 23 million years ago . That will help refine models to well omen future climate .