When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
researcher have discovered vast landforms deep beneath the North Sea that suggest the area was swallowed by a giant water ice sheet toward the centre of thelast chicken feed historic period .
The scientists fascinate these landforms in " clear and amazing " item bury under 0.6 miles ( 1 km ) of clay , Christine Batchelor , a senior reader in strong-arm geography at Newcastle University in the U.K. and Centennial State - writer of a new study describing the landforms , told Live Science .
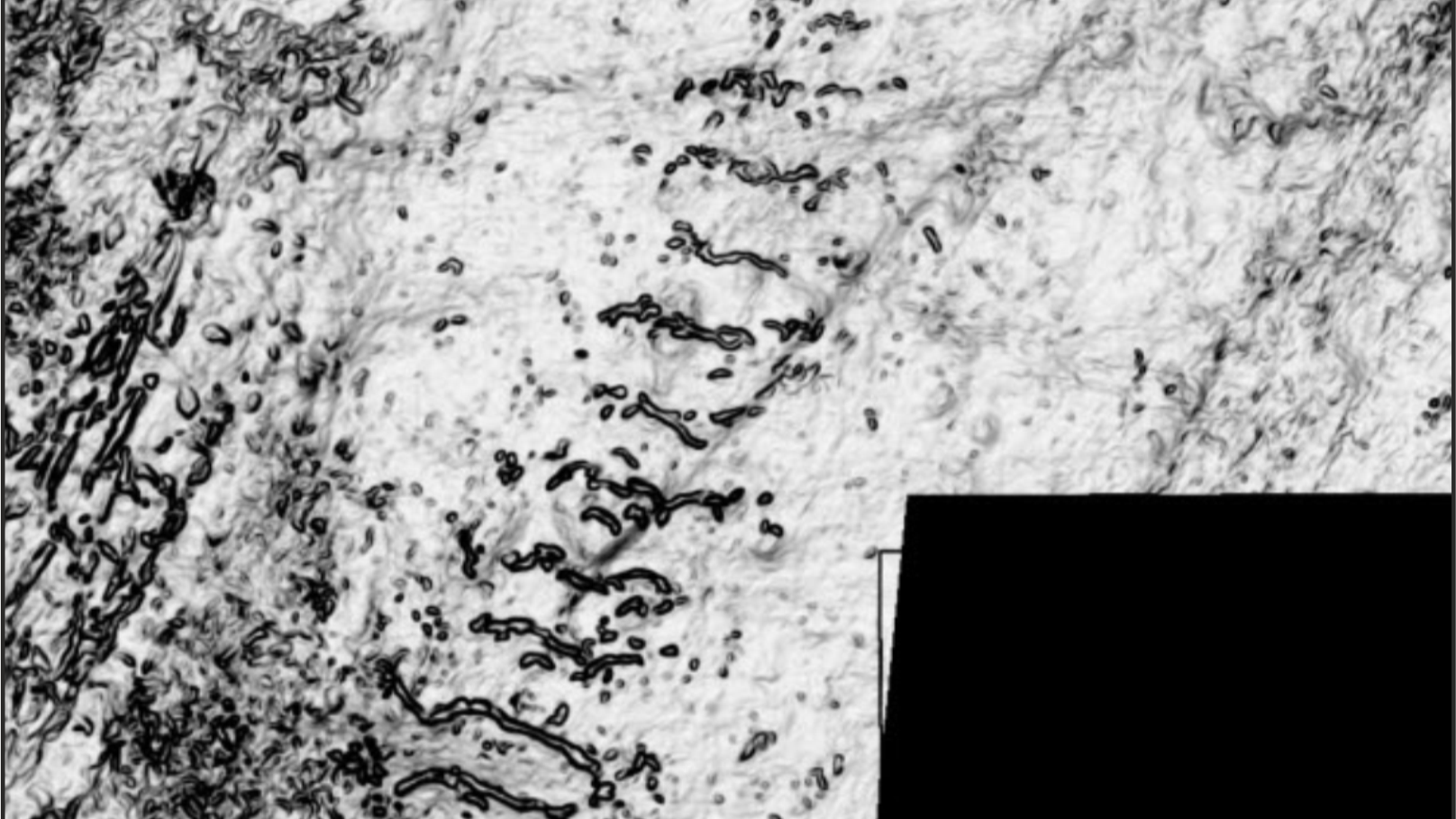
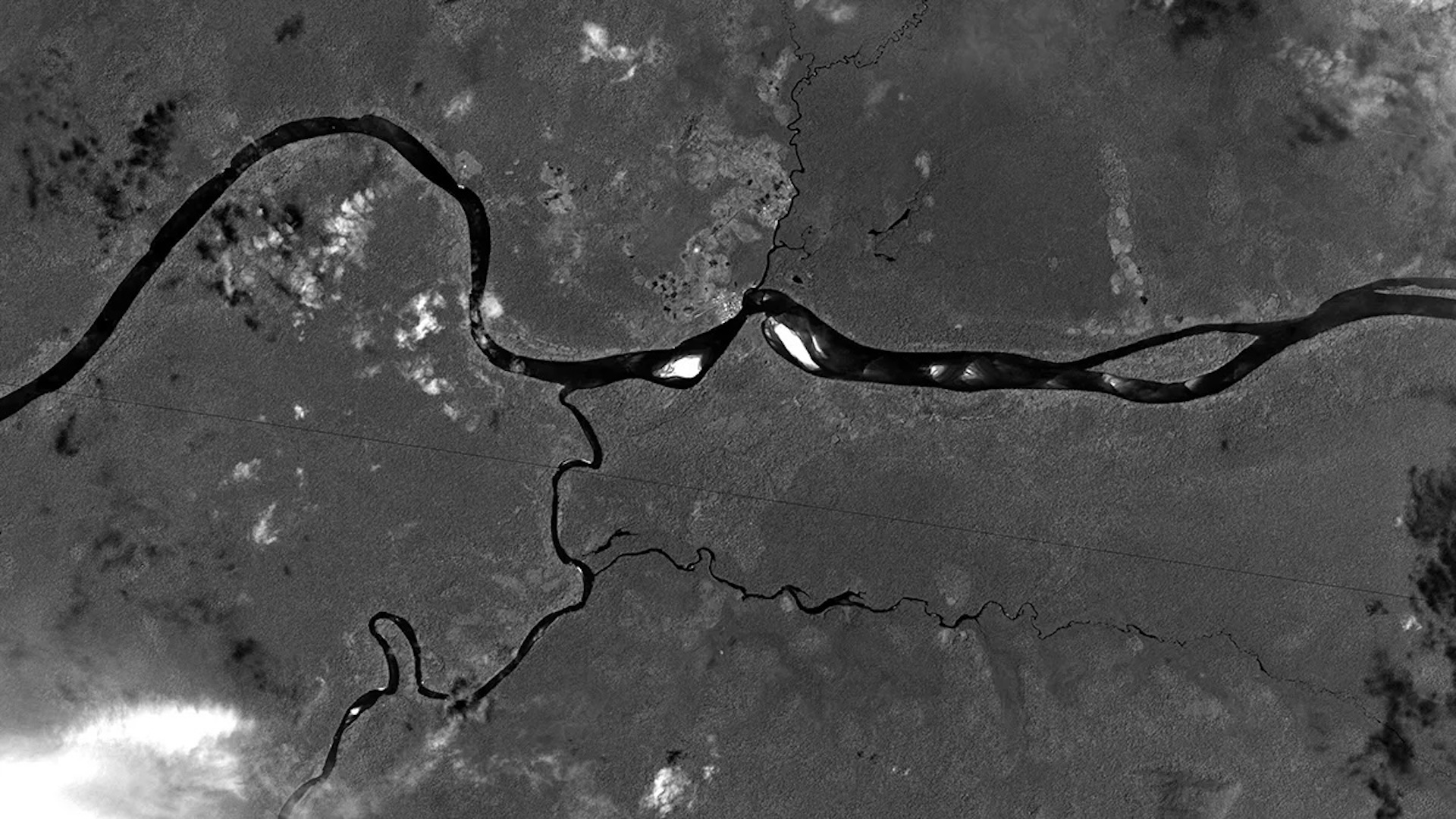
New data from the North Sea have revealed landforms dating to the last ice age.
The images divulge radiation diagram in the sea floor ordered with the rise and retreat of a individual , colossal ice sheet that survive roughly 1 million years ago , contradictingtheoriesthat smaller ice bed sheet repeatedly expand and retract around that time . Those possibility were base on abundant scratch marks , which some investigator thought had been because of glacier . But it now turn out they originated from firm ocean stream .
" We only see conclusive grounds for one bragging ice rink advance during that meter catamenia , " Batchelor say , adding that places outside the current sketch region may still hold substantiation of several small ice weather sheet .
Batchelor and her fellow used high - solving levelheaded wafture data point to reveal the landforms . They were n’t research for anything in finical , Batchelor said , and were surprised to feel evidence of a single grounded chalk bed sheet — an chicken feed sheet that sits on country rather than water .

The landforms indicate that a single ice sheet covered Norway and extended towards the British Isles around 1 million years ago.
come to : Never - before - seen shapes up to 1,300 feet long discovered beneath Antarctic trash
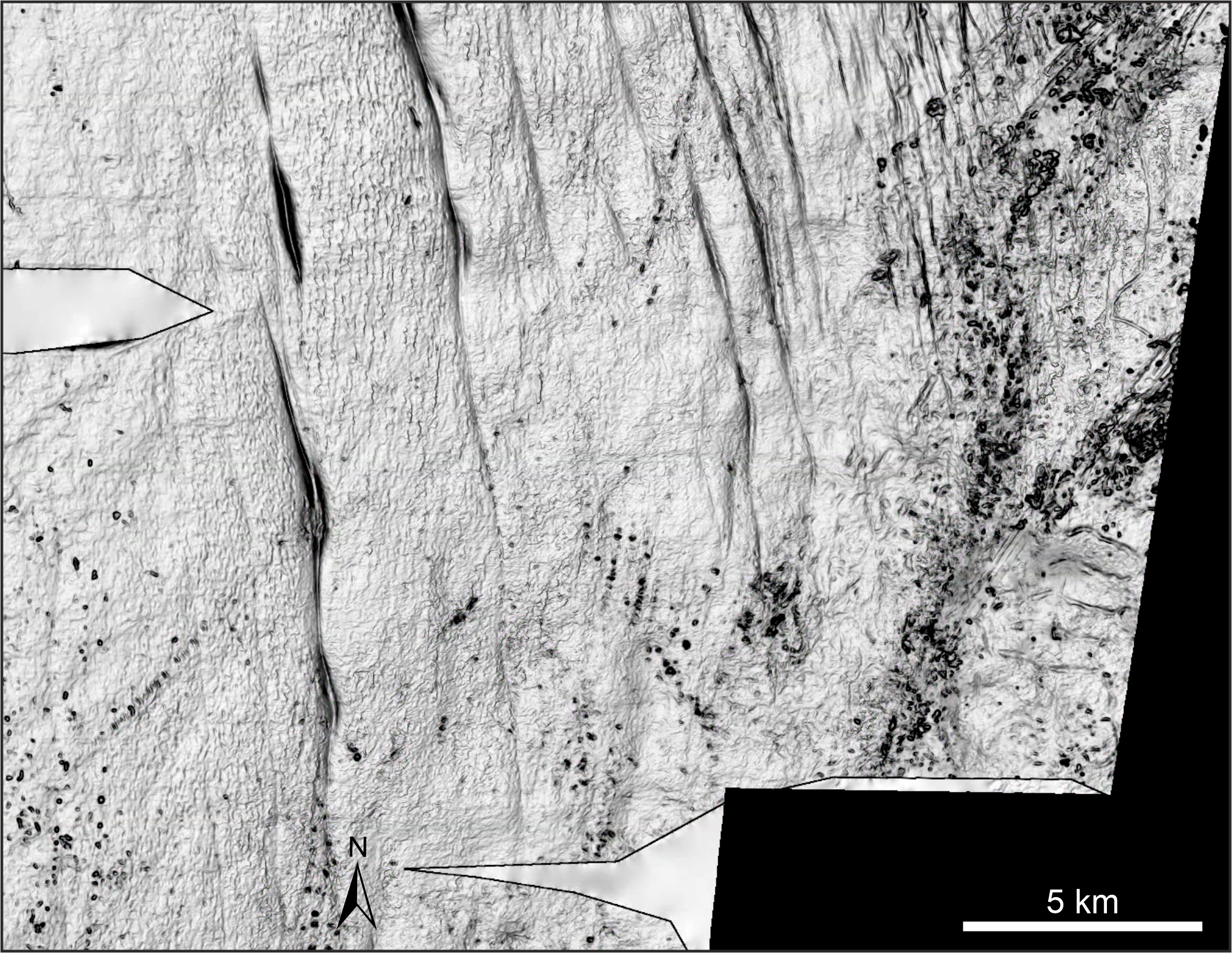
Grounded internal-combustion engine sheets move deposit around as they farm and shrink , create erosional and depositional landforms from which scientists can remodel a region ’s glacial past . " When the ice rink is advancing , it make streamline , elongated feature that are sculpture the sediment in the direction of deoxyephedrine stream , " Batchelor say . " When the ice is back out , you get features that show the imprint of that prime ice gross profit as it steps back , so those incline to be transverse to the frappe current management . "
The giant ice tabloid formed during a period of the last ice old age known as the mid - Pleistocene passage ( MPT ) that lasted between 1.3 million and 700,000 years ago . ( The ice age itself commence approximately 2.6 million age ago andended 11,700 years ago . )

Research has focused on the MPT because it marks a fourth dimension when glacial period of a sudden became more acute and switched from occurring every 40,000 year to every 100,000 years .
" The independent ground that we ’re interested in this broad time period around 1 million long time ago is because it ’s a time when we have a fault in climate going on , " Batchelor enounce . " The wintry menstruum get longer and they get more acute , so there ’s quite a lot of work that is focused on trying to figure out why that switching happened . "
The new cogitation , publish Dec. 13 , 2024 in the journalScience Advances , does n’t ply an resolution yet , but understanding where the ice extend to during the MPT could aid researchers ramp up a moving picture of the conditions that chair to this global shift in climate .

— dry land is rush toward climate term that fall in key Atlantic currents before the last trash age , survey finds
— scientist peer into a hush-hush Antarctic lake hidden beneath the ice — and uncovered a never - before - seen ecosystem
— ' wraith ' of ancient river - carved landscape discovered beneath Antarctica

The landforms designate that the ice sheet cover present - day Norway and offer toward the British Isles . Some of the imprints left by its retreat resemble crevasse - squeeze ridges — landforms farm when an trash sheet " sits down " into sonant sediment straight off before it pull in one’s horns , pushing the sediment into cracks at the bottom of the ice , Batchelor said . Crevasse - squeeze ridge are save when H2O undercut the ice , cleanly lifting it off the sediment .
Over the millennia observe the hideaway of the ice sheet , the landforms were cover in mud and obliterate away .
The young findings bid clues about how ice sheet grow and decay in reply to climate . " Being able-bodied to infer and to simulate incisively where those ice sheets were facilitate us to empathize those feedback which are still operate on , albeit in a dissimilar shape , today , " Batchelor said .















