When you buy through link on our website , we may earn an affiliate deputation . Here ’s how it crop .
Fifty million years ago , lush rainforests blanketed modern - day Antarctica , Australia , New Zealand and the bakshis of South America . Now , researchers have discovered new fossils that reveal which flora coinage populated these forests and how they adjust to life near the South Pole .
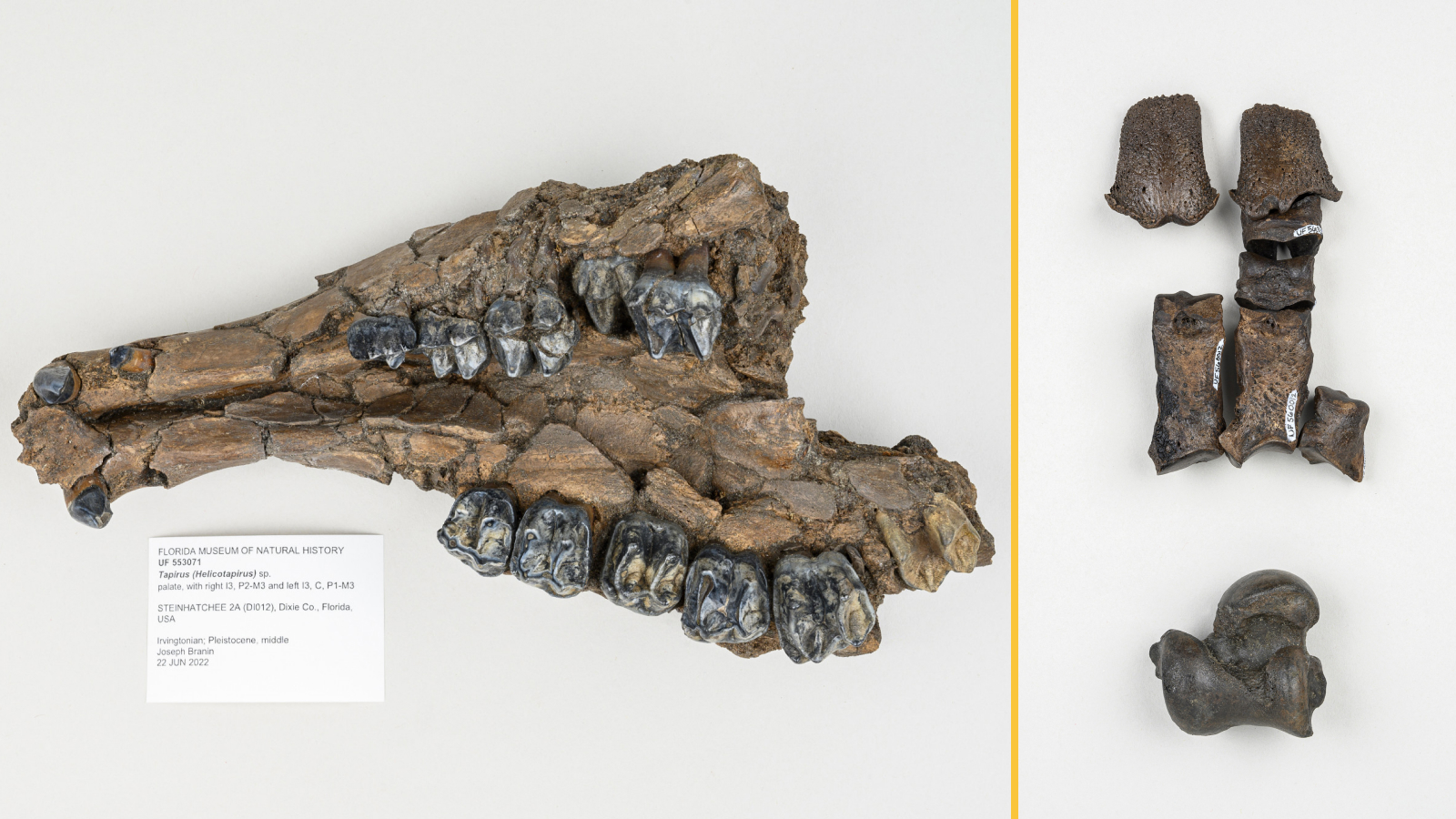
late excavations in westerly Tasmania uncovered a number of flora fossil , including the clay of two coinage of conifer antecedently unknown to science that were part of a 53 million - twelvemonth - old " polar forest . "
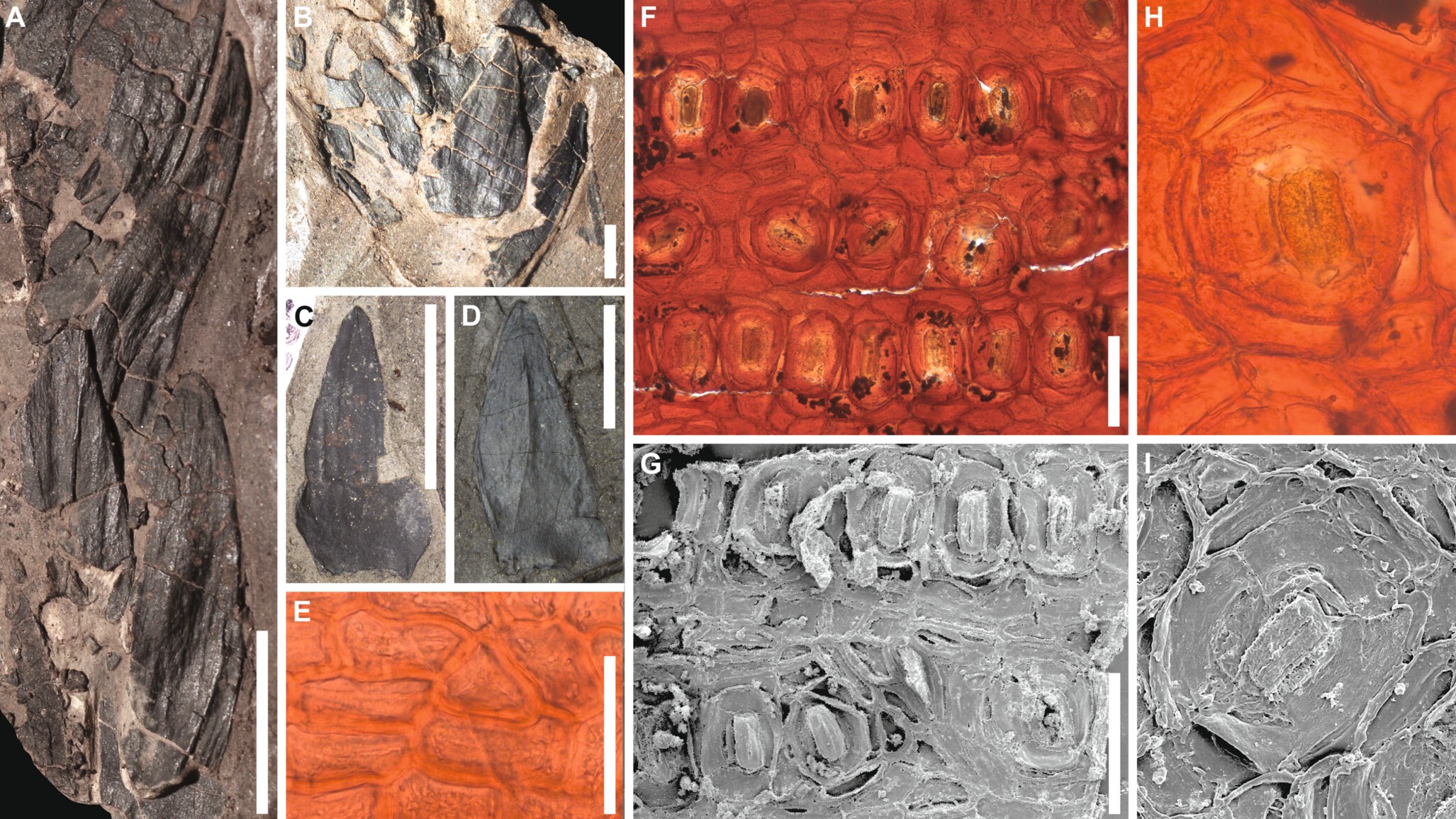
Plant fossils discovered near Macquarie Harbor in western Tasmania.
The wood thrived during the Eocene date of reference ( 56 million to 33.9 million years ago ) , when orbicular surface temperatures averaged80 degrees Fahrenheit ( 27 degree Celsius)and the southern continents formed one giant landmass around the South Pole , according to a study publish Aug. 27 in theAmerican Journal of Botany .
" This discovery offers rare brainstorm into a time when world-wide temperature were much higher than today , " study authorMiriam Slodownik , a paleobotanist and late doctorial alumna from the University of Adelaide in Australia , read in astatement . " Tasmania was much closer to the South Pole , but the affectionate global mood allowed lush forest to boom in these regions . "
worldwide temperatures spiked during the Early Eocene Climatic Optimum ( 53 million to 49 million years ago ) , a period raven the separation of Australia from Antarctica between 45 million and 35 million year ago . New fossil unearthed near Tasmania ’s Macquarie Harbor suggest tropic plants from the polar forest traveled north as the continent cast apart , seed rainforests that still be today .
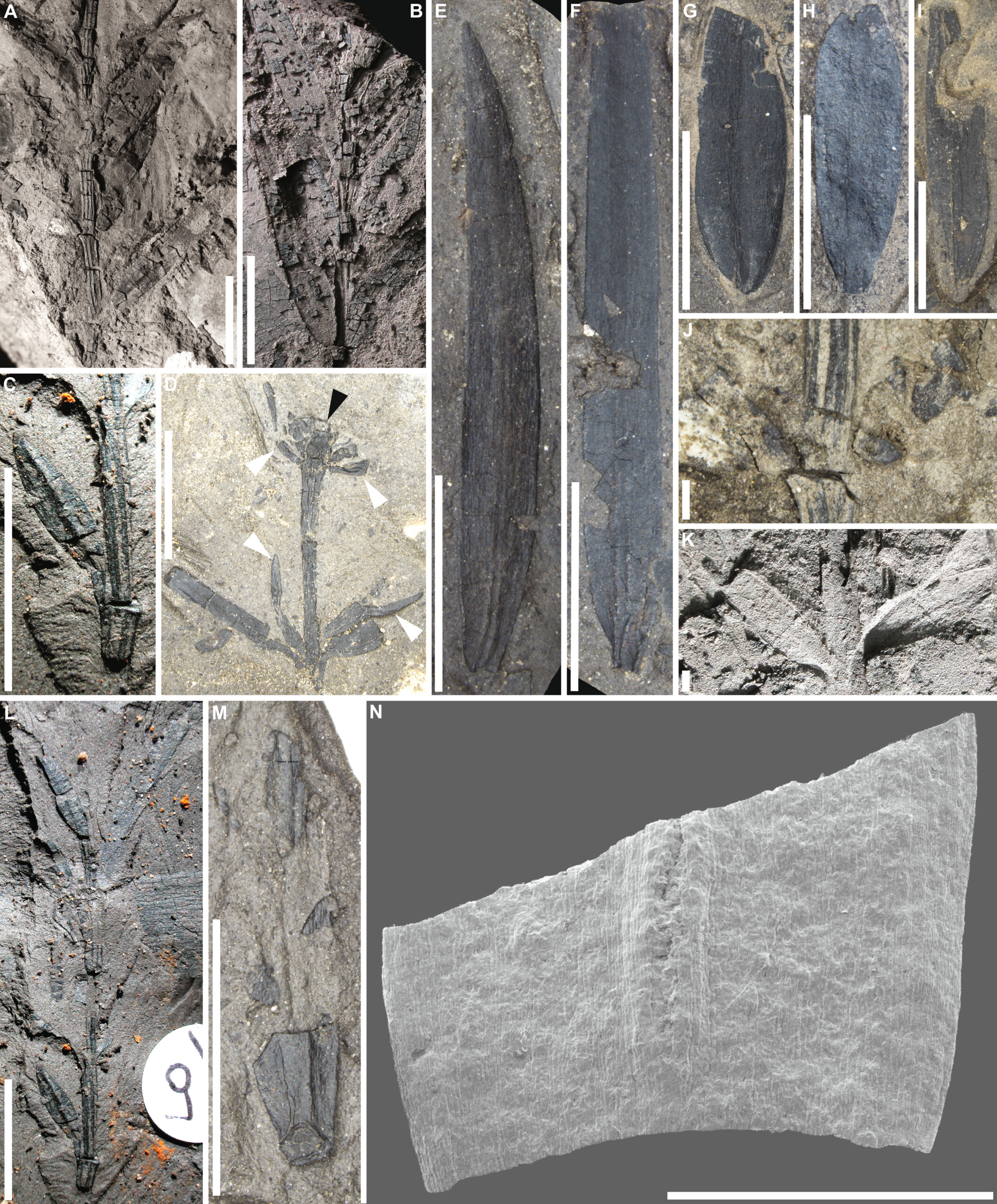

Plant fossils discovered near Macquarie Harbor in western Tasmania.
Related:390 million - year - old fossilized forest is the previous ever discover
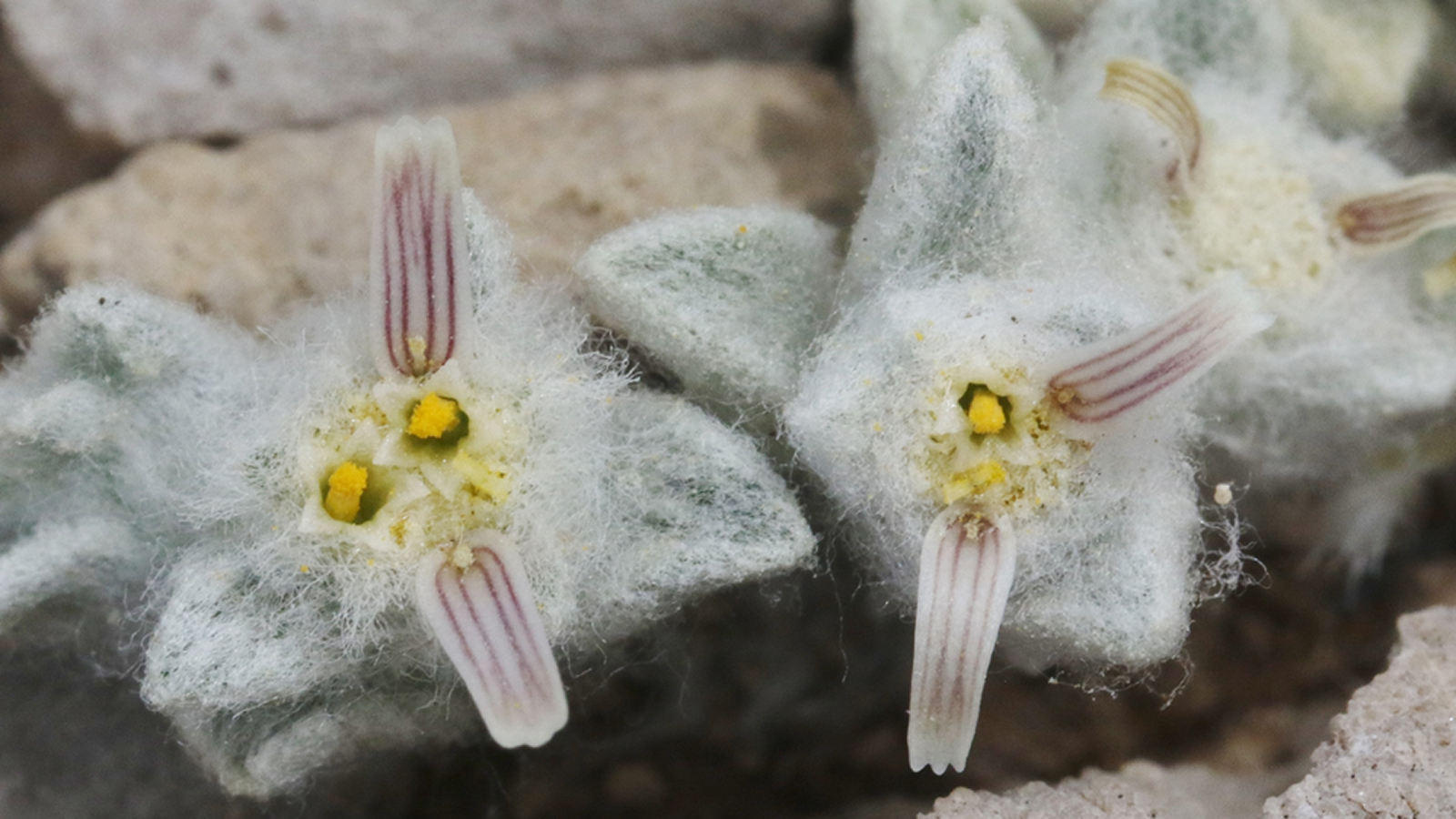
Researchers excavate more than 400 plant fogy and analyzed them in the science lab using advanced microscopes and ultraviolet photography . These techniques reveal well - preserved leaves and cellular social structure that helped the squad identify 12 unlike plant metal money . Most of these were ancestors of flora still found today in Australia , New Zealand and South America , allot to the statement . These three landmasses stayed joined together after the dissolution of the ancient supercontinent Gondwana and remained sountil at least 49 million years ago .
Of the 12 species , at least nine were conifers , accord to the study . " The most spectacular fossils are relatives of the Kauri [ Agathis ] , Bunja [ Araucaria bidwillii ] and Wollemi [ Wollemia nobilis ] pine that give clues about the development of these iconic Australian trees , " Slodownik pronounce .

The researchers , in quislingism with the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre , also identified fern , a cycad and two newfound , extinct Sir Herbert Beerbohm Tree coinage , which they namedPodocarpus paralungatikensisandAraucaria timkarikensis . " Paralungatik " is the original name of Macquarie Harbor and " Timkarik " that of the beleaguer domain in the Aboriginal words of Tasmania , accord to the program line .
— ' We were gobsmacked ' : 350 million - year - old tree diagram fossils are unlike any scientists have ever seen
— 23 million - twelvemonth - sure-enough petrified mangrove forest discovered concealing in plain sight in Panama

— ' aliveness fogy ' tree freeze in time for 66 million years being planted in secret locations
The analysis revealed that the fossilized plants adapted to the diametrical environment , which would have experienced the same extreme seasonal light authorities 53 million years ago as it does today . The plants evolved expectant leaves to maximize light preoccupancy in the summer and deciduousness to uphold resources in low - calorie-free shape during the winter , according to the study .
" The analyses showed how these plants accommodate and flourish across the Southern Hemisphere in warm , ice - free condition , even with the extreme seasonal changes near the polar rope , " Slodownik tell .

But the new fossils disclose details of even wider changes . " These plants tell the story of big changes in climate and the shifting tectonic plates over millions of year , " Soldownik read .












