When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate committee . Here ’s how it work .
For the first clock time ever , scientist have measured the accurate size of the disk of affair swirling around a supermassive black-market hole . The serendipitous finding could help expand our knowledge of how these cosmic juggernauts develop and how the galaxies that surround them develop over time .
Accretion disk are massive swirling gang of superheated flatulence , dust and blood plasma that rotate aroundblack holesor other tremendous cosmic object , such aspulsars . The disks around black holes are made from remnants of shred stars , exoplanets and other matter that was ripped apart as it was extract toward the issue horizon — the point beyond which nothing , not even light , can turn tail the black hole ’s gravitative pull . As accretion disks rotate , they give off a reach ofelectromagnetic radiationincluding 10 - rays , infrared radiation , radio waves and visible light , make them the only part of a black cakehole that astronomers can find .

An artist’s interpretation of a black hole’s accretion disk might look like.
link up : Do black holes really suck in topic ?
accumulation disks are most clearly seeable in theinfraredspectrum . The spinning masses give out what researchers call a threefold - peak , which is a pair of vim stiletto heel from excited atomic number 1 gasoline emitted by both halves of an accretion disc — the one-half that is spin away from the observer and the half that is spinning toward them . These dual - peak start from the edge of an accretion magnetic disc that is close-fitting to the case horizon , which imply they can show where the spinning phonograph recording bug out but not where they finish .
But in a new study publish Aug. 8 inThe Astrophysical Journal Letters , research worker notice a second dual - elevation coming from the out-of-door boundary of an accretion disc beleaguer the supermassive black hole III Zw 002 , which is located more than 22 million scant - years from Earth and is at least 400 million time the pot of oursun . Based on the pair of dual - peaks they spot , researchers look that the radius of the accretion disk around III Zw 002 is around 52.4 light - days , which is more than 9,000 time the space from Earth to the sun .
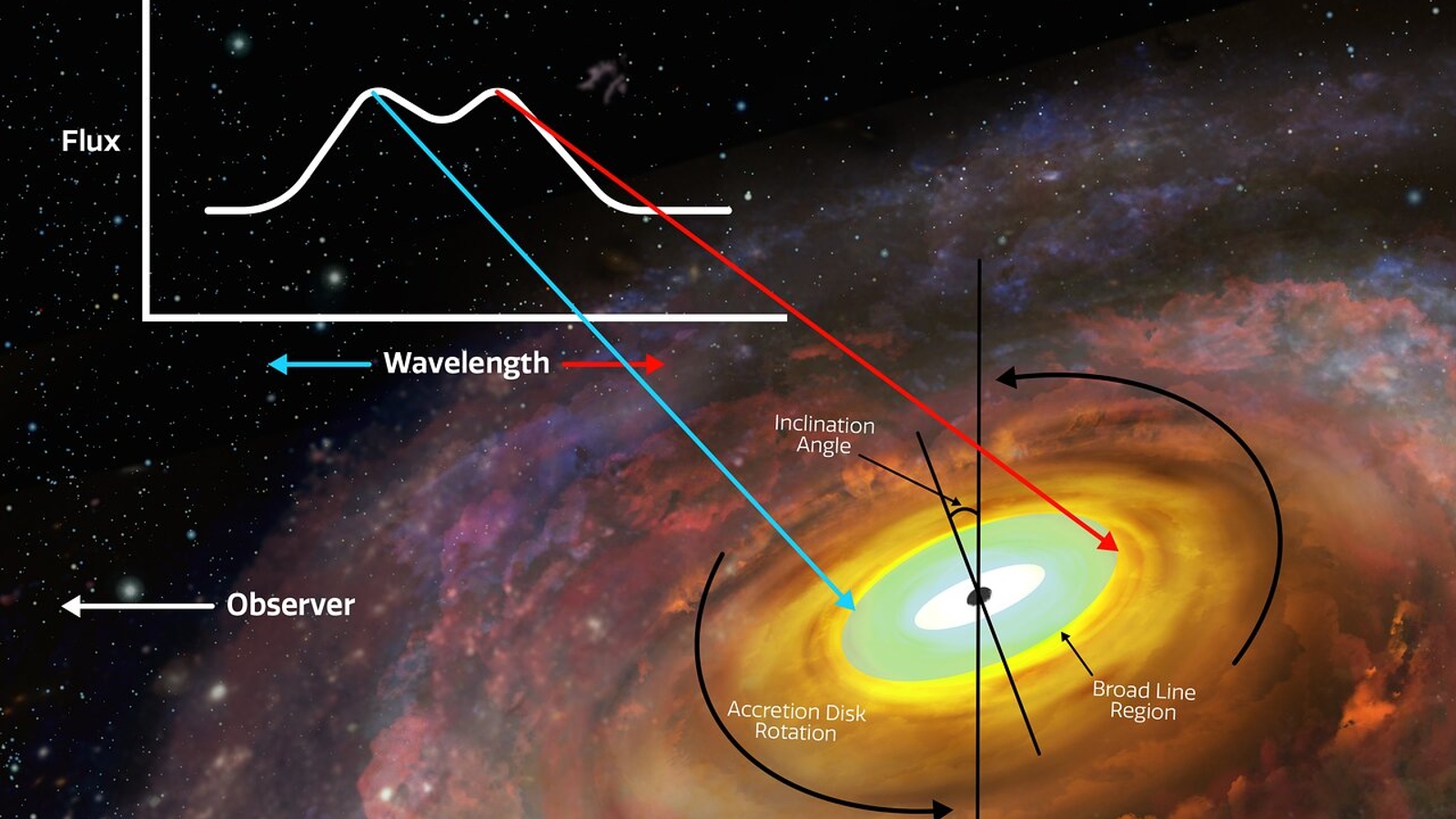
This diagram shows how a standard infrared double-peak is produced by a black hole’s accretion disk.
The researchers had not been searching for the second double band around III Zw 002 when they made the find . Instead , the team was garner datum to confirm the bearing of the accretion disk , which wasfirst detected in 2003 .
Researchers used the Gemini Near - Infrared Spectrograph ( GNIRS ) from theGemini North telescopein Hawaii to becharm the raw data point . GNIRS quantify a slightly wider range of wavelengths than regular infrared light usually appear in and can find emission in unlike wavelength at the same time , which is what enabled the squad to spot the second double - tiptop .
Related : First - ever finale - up of a supermassive black hole focalise to ' full resolving power ' by AI

At first , the researchers did n’t trust what they ' get hold , but it soon became apparent to them . " We trim back the information many times thinking it could be a misunderstanding , but every time we see the same exciting final result , " study Centennial State - authorAlberto Rodríguez - Ardila , an uranologist at the Canary Islands Astrophysics Institute , say in astatement .
The researchers conceive the discovery could play an important role in help to uncover the mystery of supermassive black kettle of fish .
" The detection of such double - peaked profiles put firm restraint on the geometry of a region that is otherwise not possible to dissolve , " Rodríguez - Ardila say . This will enable researchers to observe the " feeding process and the inner structure of an active galax " for the first time , he added .

— James Webb scope bring out the universe of discourse may have far fewer active calamitous hole than we remember
— Could a black maw devour the universe ?
— ' Twisty ' novel theory of gravity says information can turn tail black hollow after all

The squad will continue to monitor the accretion disc around III Zw 002 to see how it grow over time .
This is not the only major find scientist have made in understand accumulation disc this yr . In May , researcher revealed that they hadcreated artificial accretion record out of plasm in the labfor the first time ever . The fake ring only last for a fraction of a 2nd but confidential information at how accumulation disks are formed .











