When you buy through connexion on our site , we may realise an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it lick .
A new character of flat , razor - fragile telescope lens could transform deep - space stargazing by making it possible to climb lightweight but powerful telescopes onto aircraft and satellites , scientists say .
Refractor telescopesnormally apply curve lens to blow up removed object through a cognitive operation calledrefraction . Similar to a magnifying looking glass , the curving lens of a telescope bend light and organise it to a focal point , making object appear larger .
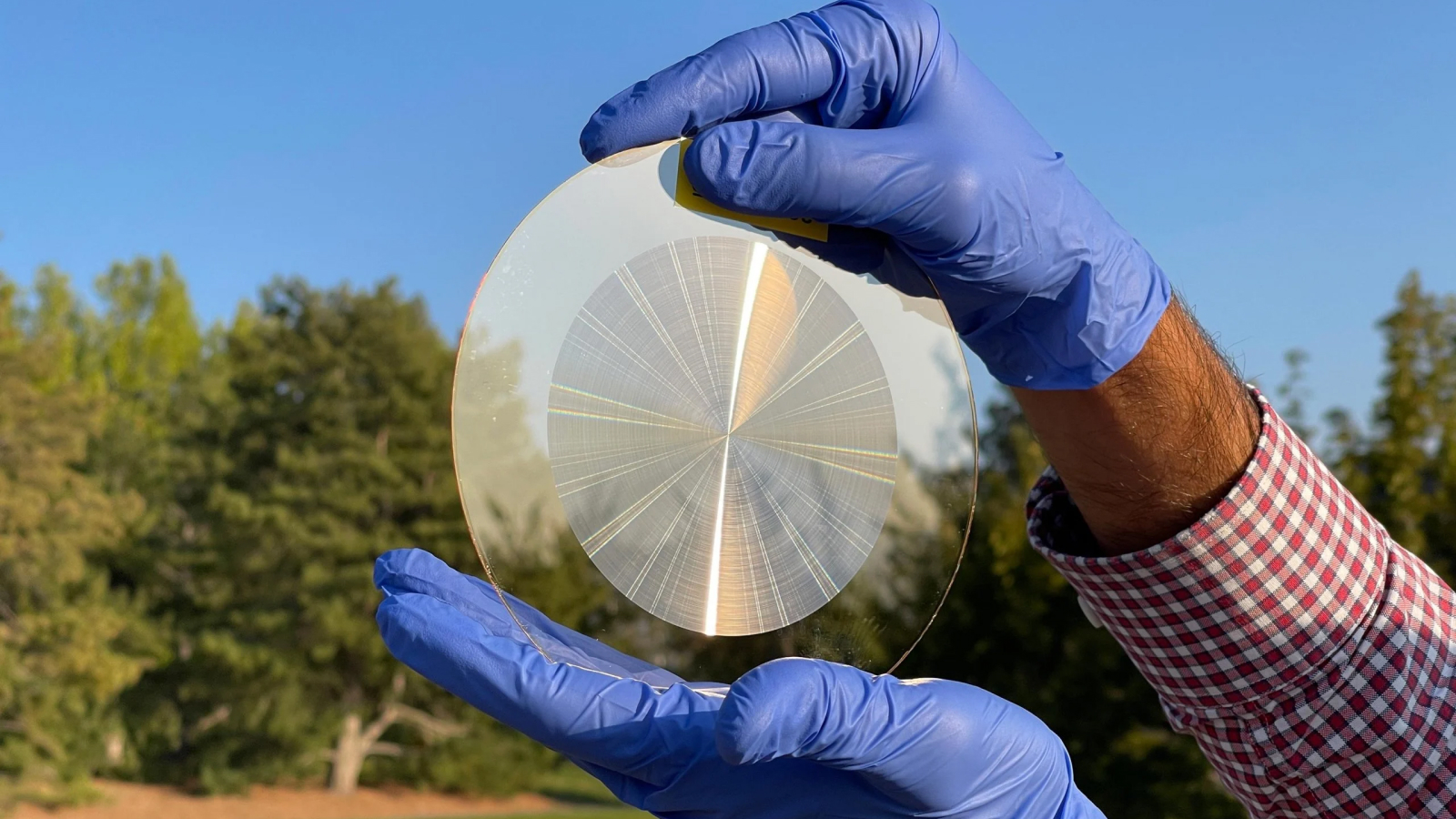
However , traditional lenses quickly become impractical for space telescopes studying star orgalaxiesmillions of easy years away . This is because the further out an objective is , the more blowup is require to bring it into focal point , and therefore the dense and heavier the electron lens require to be .
That ’s why scientist have explored flat lenses , which should in theory be lighter and less bulky . The challenge with them , however , is that light interacts with them differently than with kink lenses .
Visible lightis a character ofelectromagnetic radiation , which is transmitted in wave or particles at different wavelengths and frequencies . When light pass by through a flat lens , it diffract , dust wavelength in multiple direction and resulting in a blurry , unfocused image .
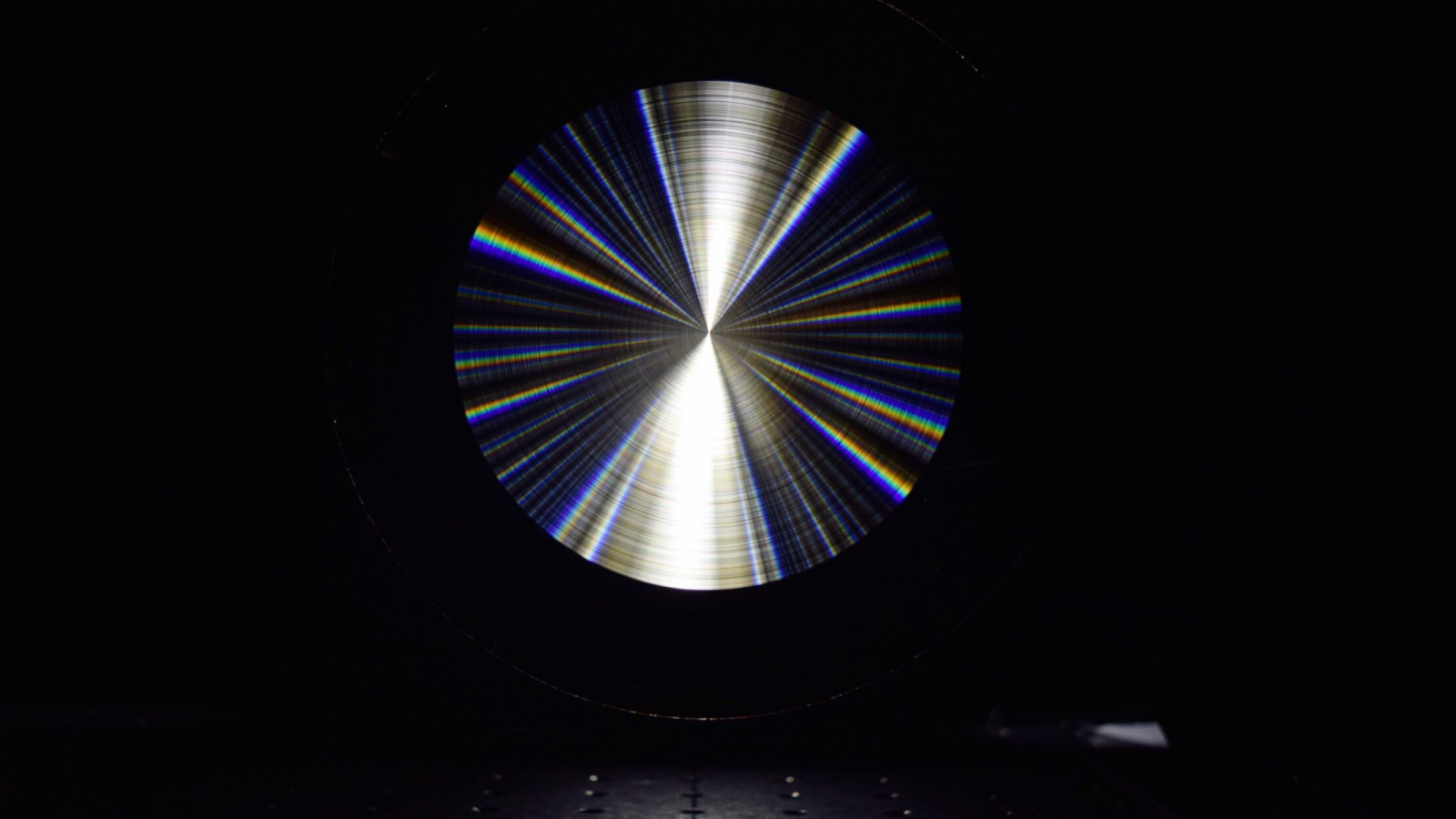
But a new " multilevel diffractive lens system " ( MDL ) make grow by scientists features a multi - flat structure lie of " microscopically small concentric rings . " These effectively canalize different wavelength of light towards the same focal spot to create a incisive , color - precise image .
Related : Could we turn the sun into a mammoth telescope ?
The new 100 - millimeter ( 3.9 - inch ) diam lens , which has a 200 mm ( 7.8 in ) focal duration , is just 2.4 micrometer thick . Optimized for the 400 to 800 nm wavelength range for visible light , this lens is much lighter than a conventional curved genus Lens and eliminates color straining .

The scientist published their findings Feb. 3 in the journalApplied Physics Letters . The study was fund by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency ( DARPA),NASAand the Office of Naval Research .
" Our demonstration is a step stone towards make very large aperture lightweight flat lenses with the capableness of capturing full - color images for use in air- and space - base telescope , " lead study authorApratim Majumder , assistant prof in electrical and reckoner engineering at the University of Utah , say in astatement .
Ahead of the curve
Scientists have designed matte electron lens in the past tense , most notably thefresnel zone plate ( FZP ) , which features concentric rooftree etched across the open . However , the ridges of FZPs break light into separate wavelength and diffract them at different angles , resulting in color twisting .
The MDL is singular in that its concentric doughnut live at varying depths within the lense itself . As light passes through , the microscopic indenture adjust how different wavelengths diffract , forestall them from spreading asunder as they commonly would . This controlled diffraction brings all wavelengths of visible radiation into direction at the same time , resulting in a sharp , color - accurate figure of speech .
As well as avoiding the color distortions of FZPs , the researcher said the young flavourless lens offer the same Light Within - bending power as traditional curved lens system . In the study , they used the MDL to capture images of the sun and moonlight . Lunar images they take divulge key geological feature , while they also used it in solar imaging to capture visible macula .

— holographical - inspired lens could unlock ' 3rd dimension of imagery ' in future VR headset and impudent specs
— NASA captures stunning new prototype of shock waves from next - gen ultrasonic planer as it fly across the sun
— X - ray vision chip gives phones ' Superman ' power to view objective through bulwark

" Simulating the performance of these lenses over a very large bandwidth , from visible to most - infrared , involved work complex computational problem involving very large datasets , " Majumder said in the statement . " Once we optimise the design of the lens system ’ microstructures , the manufacturing outgrowth required very tight physical process restraint and environmental stability . "
The researchers said the applied science had applications in astronomy , astrophotographyand other " long - range imaging project " admit " airborne and blank - establish imagination applications . " What ’s more , yield may not be far off .
" Our computational proficiency suggest we could contrive multi - level diffractive matted lenses with large aperture that could concentrate visible radiation across the visible spectrum and we have the resources in the Utah Nanofab to in reality make them , " discipline co - authorRajesh Menon , professor of electrical and computer engineering at University of Utah , say in the statement .

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be motivate to enrol your display name .
' Rabbits sometimes make mistakes or get lazy . That ’s when the tortoise grab its chance ' : Chinese scientist make atomic power breakthrough using abandoned US research
How will the latest coevals of fighter K suffer out ? The solution lie in stealth technical school .

The constant surveillance of modern life could worsen our brain procedure in ways we do n’t fully understand , disturbing survey indicate




