When you buy through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
trillion of tiny quad rock fragments may be on a collision path with Earth and Mars afterNASAdeliberately crashed a probe into a far - away asteroid two years ago , a unexampled study reveals . The celestial shrapnel , which could commence collide with our planet within a decade , poses no risk to aliveness on Earth — but it could activate the first ever human being - caused meteor shower .
On Sept. 26 , 2022 , NASA ’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test ( DART ) spacecraft purposefully collided with the asteroid Dimorphos , smash right into the middle of the infinite rockat around 15,000 miles per hour ( 24,000 km / h ) . The larger-than-life encroachment , which come about more than 7 million miles ( 11 million kilometre ) from Earth , was the first mental test of humanity ’s capability to airt potentially wild asteroid that pose a threat to our planet .
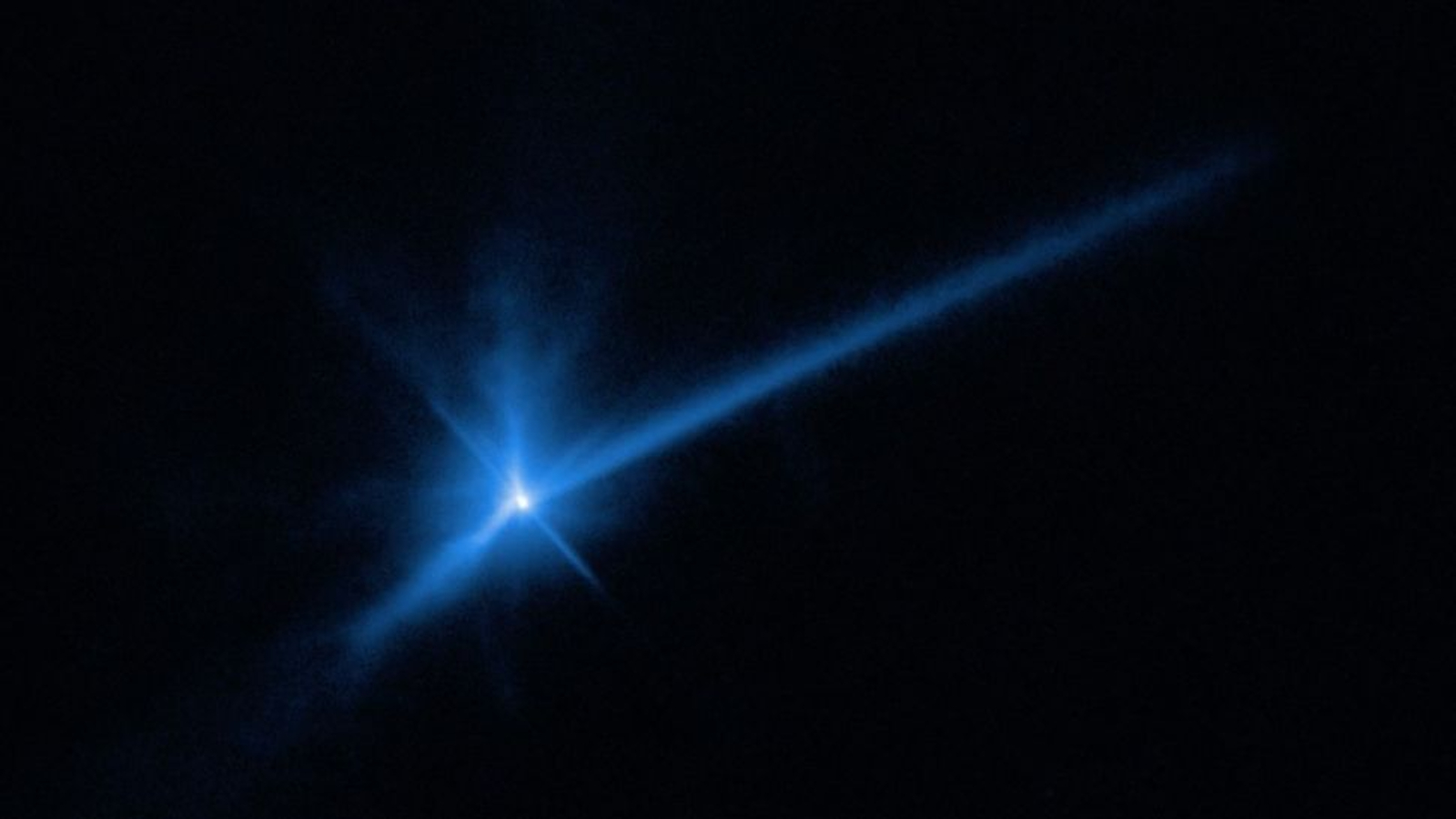

The Hubble Space Telescope photographed the dust plume and extended tail of asteroid Dimorphos after NASA’s 2022 DART collision.
The missionwas a major success . Not only did DART alter Dimorphos ' trajectory — abridge its trip around its partner asteroid Didymosby around 30 minutes — it alsocompletely changed the soma of the asteroid . It demonstrate that this case of action , known as the kinetic impactor method , was a potentially viable option for protect our planet from grievous distance rock .
Photos of Dimorphoscaptured in the aftermath of the impactshowed that the collision also ejected a large plume of debris into blank , including dozens of big bouldersthat investigator believecould dash into Mars in the next few decade . None of these great fragments are expected to tally Earth .
But in the new study , which was upload Aug. 7 to the preprint serverarXivand has been accepted for publication in The Planetary Science Journal , researchers call on their tending to Dimorphos ' small shard .

DART’s final moments before it crashed into Dimorphos’s surface.
The researchers used a NASA supercomputer to analyze data collected by theEuropean Space Agency ’s Light Italian Cubesat for Imaging of Asteroids ( LICIACube ) space vehicle , which wing alongside DART as the spacecraft smashed into Dimorphos . They then simulated the initial flight and velocities of 3 million sherd . This revealed that many of the asteroid pieces will in all probability reach Mars or the Earth - Sun Myung Moon system .
link : Could scientists stop a ' major planet killer ' asteroid from hitting Earth ?
The ejected fragments are harmless because of their diminutive sizing — between 0.001 inch ( 30 micrometer ) and 4 inches ( 10 centimeters ) across . But their arrival in Earth ’s atmosphere could trigger a young light show in the dark sky .
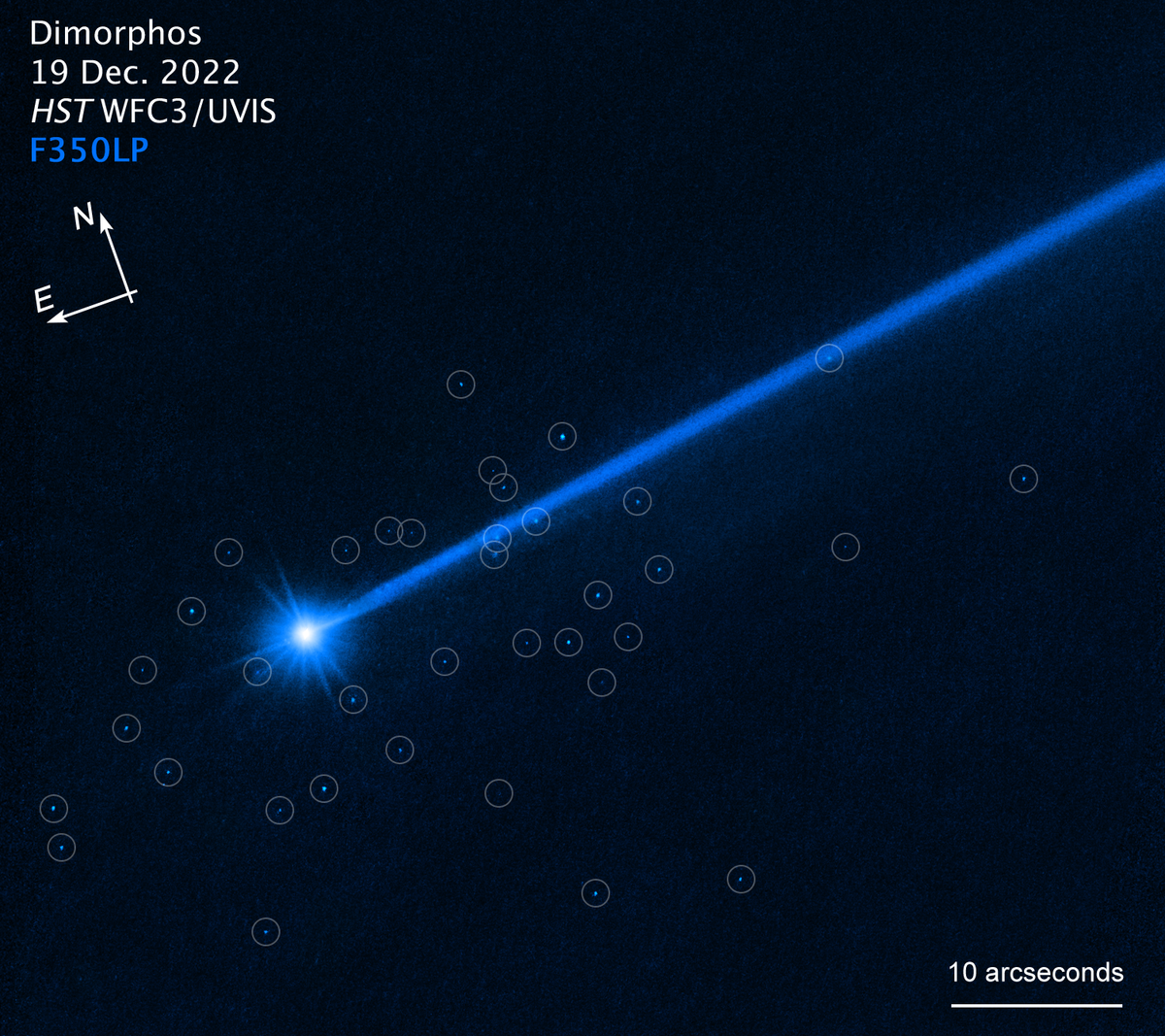
Dozens of larger rock fragments (circled) were spotted in the aftermath of the DART/Dimorphos collision. But none are currently headed for Earth.
" If these squirt Dimorphos fragment reach Earth , they will not pose any risk , " report lead authorEloy Peña - Asensio , an aerospace railroad engineer and astrophysicist at the Polytechnic Institute of Milan in Italy , toldUniverse Today . " Their small size and high speed will stimulate them to disintegrate in the ambience , creating a beautiful lambent streak in the sky . "
However , there is still some uncertainty about when these shard will reach us or when they will be seeable .
— NASA ’s most wanted : The 5 most dangerous asteroids to ground

— ' major planet killer ' asteroid are hide in the sunlight ’s glare . Can we stop them in time ?
— The 8 most solid ground - shatter asteroid discoveries of 2023
The pocket-sized fragments , which are likely travel at upper up to 3,350 mph ( 5,400 km / h ) , could reach us within seven years but will likely be too midget to make any germinate stars in the sky , researchers wrote in the paper . But the declamatory fragments , which could be fleck as they burn up up in the atmospheric state , are move more than four time slower and might not come for more than 30 year .

If and when these enceinte fragments come , they could create a brand new meteor cascade , which the researchers have preemptively nicknamed the " Dimorphids . " However , we wo n’t get laid if this will really happen until these piece initiate getting much closer to our planet .













