When you purchase through link on our land site , we may realize an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
old ancestor of all living : Approximately4.2 billion old age
First human coinage : Homo habilis , whichlived from about 2.0 to 1.6 million days ago
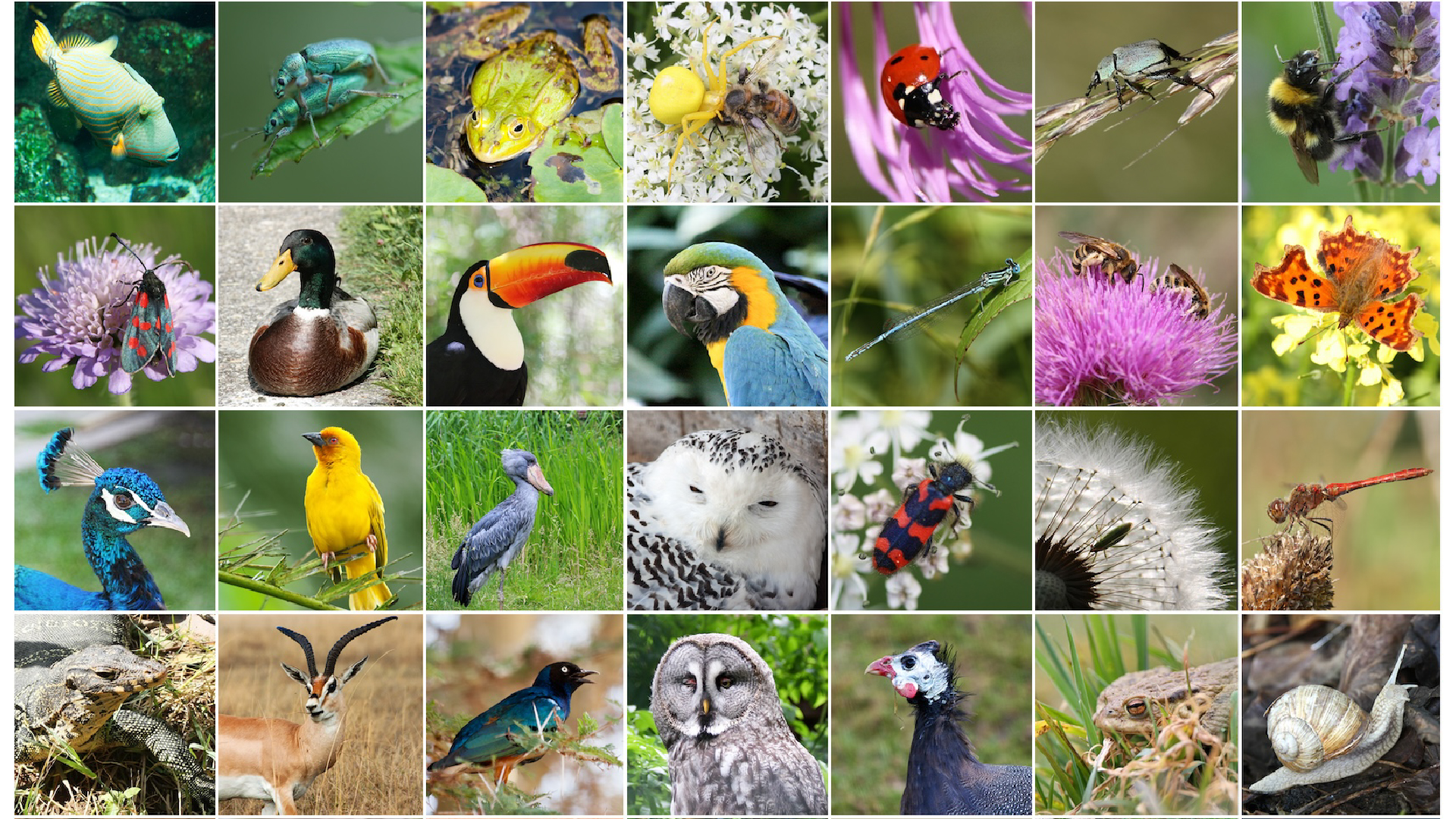

There is vast diversity of life on our planet. Evolution explains where this diversity comes from.
issue of species on Earth : Around9 million
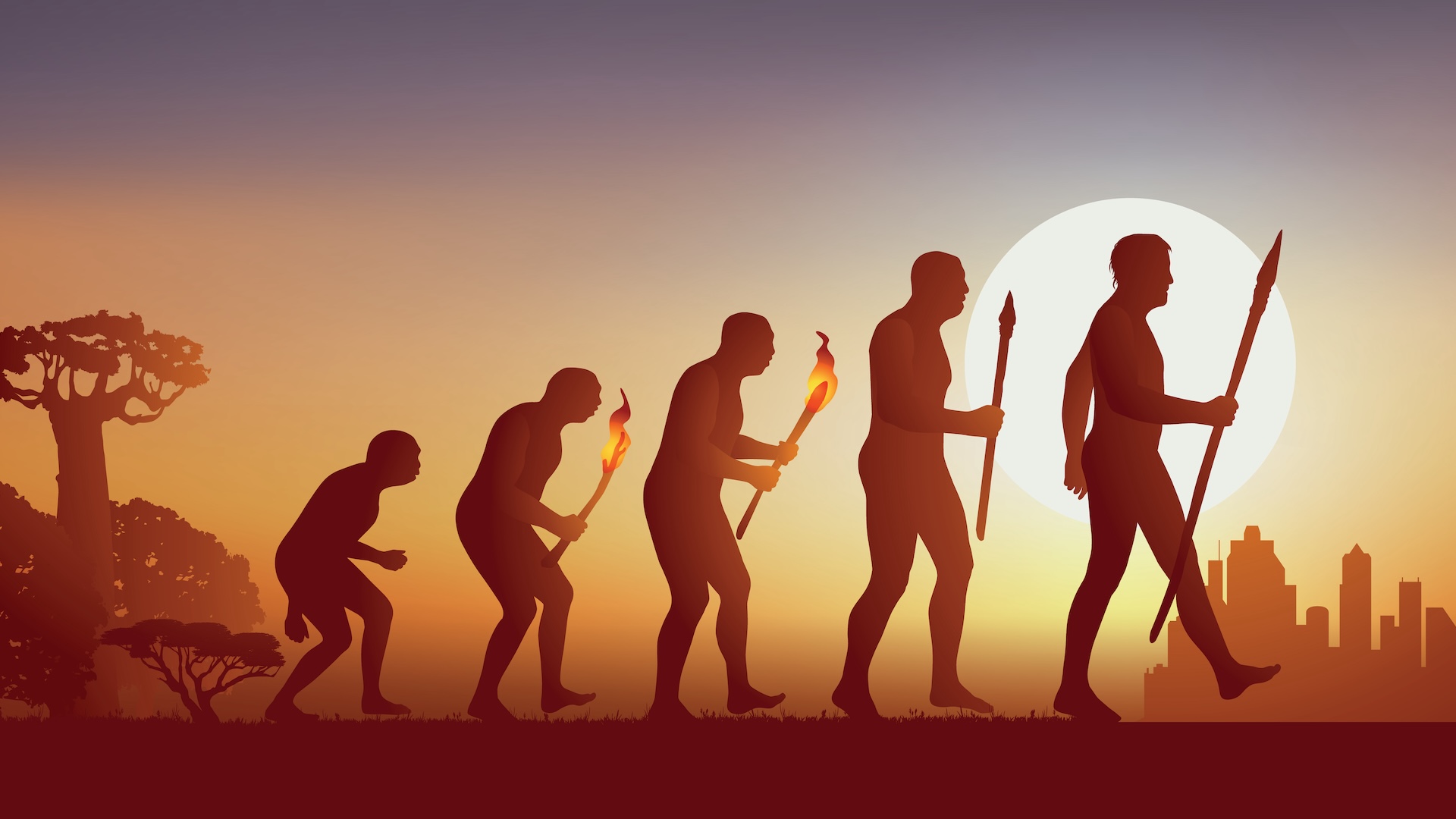
Evolution is the way groups of life - forms change over time to considerably fit the places they hold out .
It is why life require " such endless figure most beautiful and terrific , " as British life scientist Charles Darwin wrote in his famous 1859 Scripture " On the Origin of Species . "

(Image credit: Bettmann Getty Images)
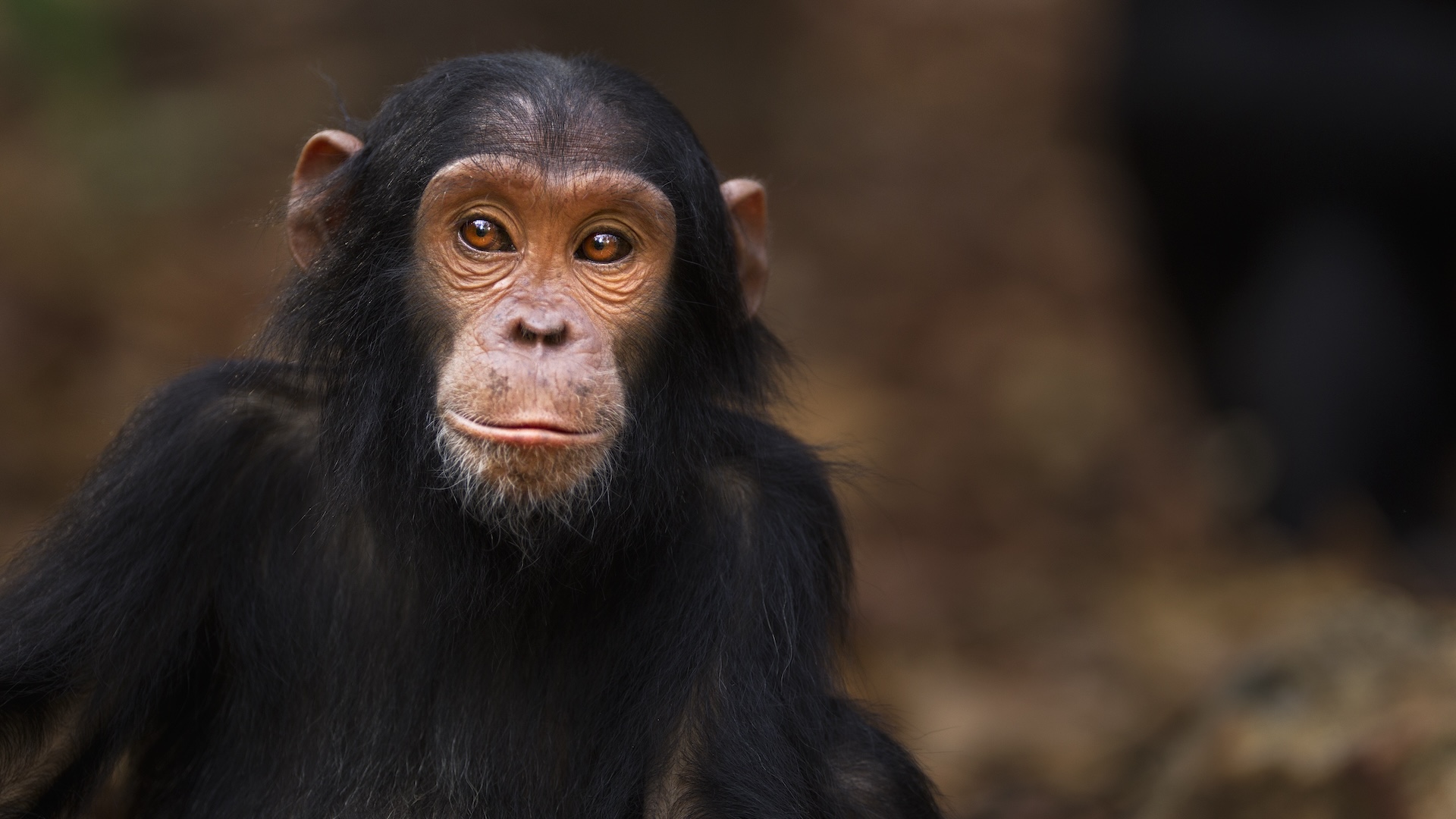
you may give thanks phylogenesis for the diversity of lifespan , from microscopical bacteria to the blue whale , the biggest brute to ever live .
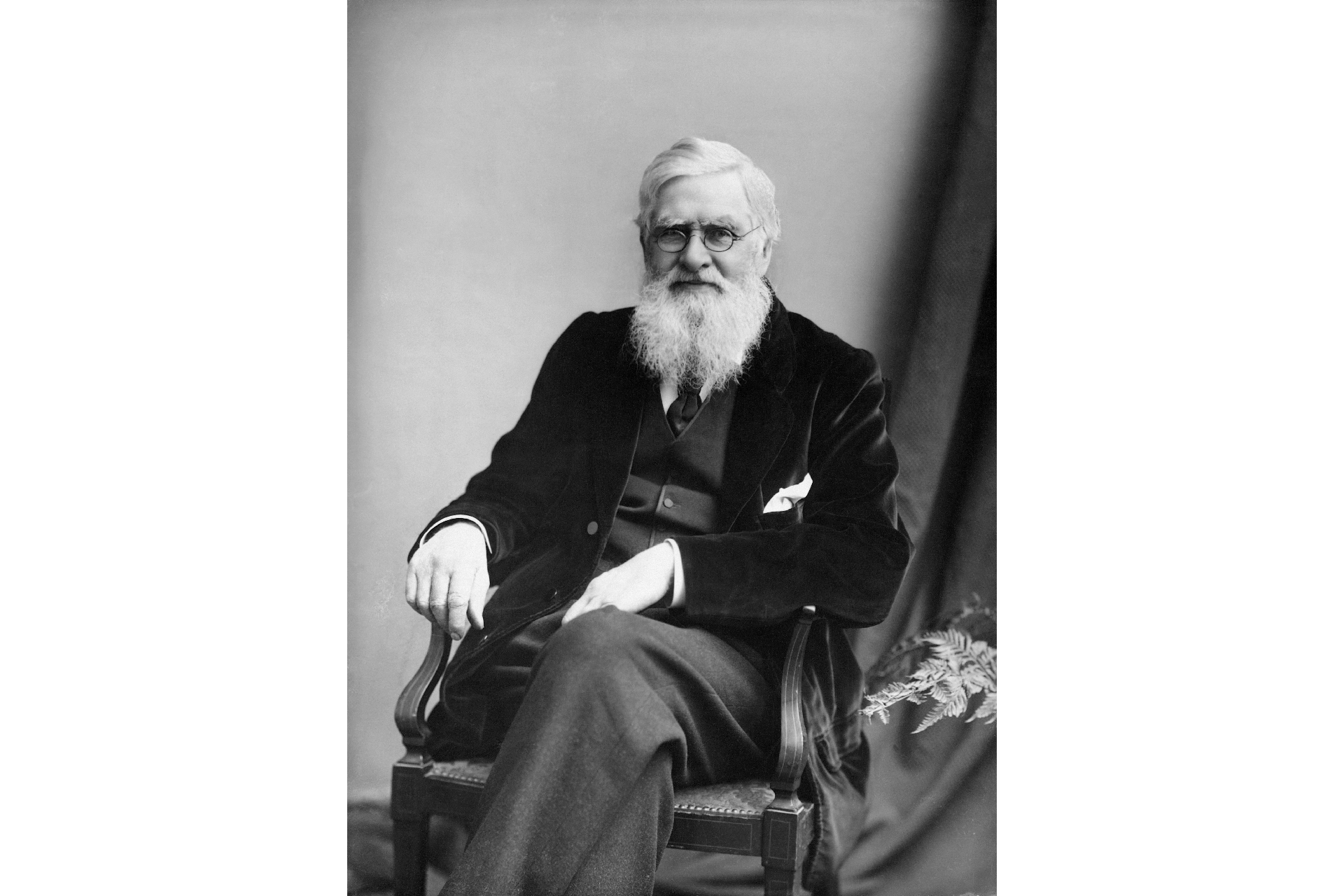
Darwin and fellow naturalistAlfred Russel Wallacedeveloped the theory of evolution in the mid-1800s .
phylogeny solve thanks to a operation shout natural selection . Life - forms that have traits that make them well suited to a certain environment — whether polar tundra or deep - sea volcano — have a good fortune of surviving and passing that trait to their progeny .

(Image credit: Bettmann Getty Images)
Members of the group that do n’t have that trait , meanwhile , will either buy the farm or make fewer young . Over time , more members of the universe will inherit that beneficial trait .
phylogenesis aid explain how humans came to be , why bacterium can resist antibiotic drug and why unexampled disease , like COVID-19 , are always emerging .
Tiffany Taylor is a professor of Microbial Ecology and Evolution at the University of Bath in the U.K. , where her research radical studies evolution in real - time in the lab , using bacteria . She has also author three children ’s rule book on evolution and genetics .
(Image credit: Print Collector via Getty Images)
5 fun facts about evolution
Everything you need to know about evolution
How does evolution work?
Evolution by instinctive selection is where a trait is weeded out or becomes more vulgar in a population depend on how well the trait helps organism ( populate things ) survive and reproduce . Three key ingredient in lifelike pick are magnetic variation , inheritance and competition .
First , there isvariation . For example , some social lion are bigger or smaller , have longer mane or shorter 1 , are more aggressive or cautious , and so on . Every population of organisms has variation in almost any trait you may imagine . trait are encoded through cistron inDNA , a molecule establish in every living cell that gives instruction on how to develop , populate and reproduce . Traits vary within a universe partially because when DNA gets replicate , sometimes some of the letters in the code get changed — a process called sport .
Next there isinheritance . Many of these variabletraits are inherit . cistron are passed on from one coevals to the next through breeding .

(Image credit: Jack Taylor / Stringer via Getty Images)
at last , there iscompetition . Every creature in a population is competing with others in their grouping for intellectual nourishment , shelter , resources and mate .
Here ’s how all those factor wreak together .
To survive , an organism must be well suited to its environment . For model , a plant in the Mojave Desert needs to make do with very little water , while a tree diagram in the Amazon rainforest needs to keep its leaves from getting waterlogged .
(Image credit: WHPics, Paul Campbell, and Attie Gerber via Getty Images; collage by Marilyn Perkins)
Those with a trait that is a good fit for their environs — say , a cactus that needs less water in the desert — are more successful in the contest for resource , shelter , intellectual nourishment and better half .
They ’re likelier to survive and multiply than their counterparts without the trait . Their progeny inherit these trait that give them an reward over their challenger , continuing the cycle of evolution .
Eventually , more of the member of the population carry the trait that establish them an edge in selection and replication . That ’s organic evolution in a nutshell .

(Image credit: Helen Reid via Shutterstock)
Evolution explain how species emerge and commute over prison term . While scientist have describedbetween 1 million and 2 million species , they know they ’re missing a passel . There could be 9 million — or even up toa trillion — species on Earth .
Is evolution completely random?
lifelike selection postulate magnetic declination , and variation within a population for the most part comes from DNA mutations .
Most mutation are random , but some areas of DNA mightmutate more well than others .
In human , children are unremarkably put up withabout 60 raw mutant , or DNA modification that their parent did n’t have .

(Image credit: Paul Kay via Getty Images)
Different living - forms have different rates of variation , and there are always some mistakes . Most of these mutations do n’t affect the organism in any detectable way . ( These are called indifferent genetic mutation . ) But sometimes , mutations can make it easier or grueling for an organism to exist or reproduce . This is where natural selection come in .
If a mutation helps an organism compete easily , it is more likely to survive and make pass on the beneficial mutation to its progeny . On the other hand , if a mutation makes survival or reproduction harder , the genetic mutation is less probable to be passed down .
So , while genetic mutation mostly go on randomly , phylogeny is not random .

(Image credit: Hulton Deutsch / Contributor via Getty Images)
However , natural selection is not perfect , and mutations that have no or very small negative effects can perplex around in a population .
For representative , a lot ofpeople have wisdom teeththat once helped us craunch up plants in our dieting , but now in the main herd other teeth and ordinarily have to be pull out . But because receive wisdom dentition does n’t make it heavy to survive or reproduce , it has n’t been weeded out yet .
How long does evolution take?
normally , organic evolution is thought of as a process that occurs over thousands or million of years , but some being can evolvewithin day . The rate of evolutiondepends on several cistron .
First , organism that reproduce apace germinate quicker because evolution occur through inherited changes , with each generation dissent slightly from the last . Over time , these small modification add up to big differences .
Second , population size matter . tumid population are likelier to have at least one individual with mutations that affect survival or reproduction . innate selection then either weed these out or makes the genes more common depending on whether they ’re dependable or bad for a species .
(Image credit: Saiful52 via Shutterstock)
The mutation pace also influences the speed of evolution . More mutations have in mind more chances to evolve , but becausemost mutations are neutral or harmful , organism often evolve protein to fix deoxyribonucleic acid copying mistake , which keeps the mutation rate humiliated . Sunlight , chemical and factors tied to different mintage ' error - correction put-on can all affect how cursorily genes mutate .
Lastly , the surround take on a vital role in the rate of organic evolution . In harsh consideration , natural excerpt cursorily remove individuals that are not a good fit for their surround , leading to more rapid evolutionary change .
These factors mean minor organism that make copies of themselves quickly — like bacteria — evolve much more quickly than big ace that take a long time to reproduce , like elephant . This speedy organic evolution in microscopical organisms can aid scientist study adaptation through laboratory experiment .

(Image credit:Brian Baer and Neerja Hajela,CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons)
What is Lamarck’s theory of evolution?
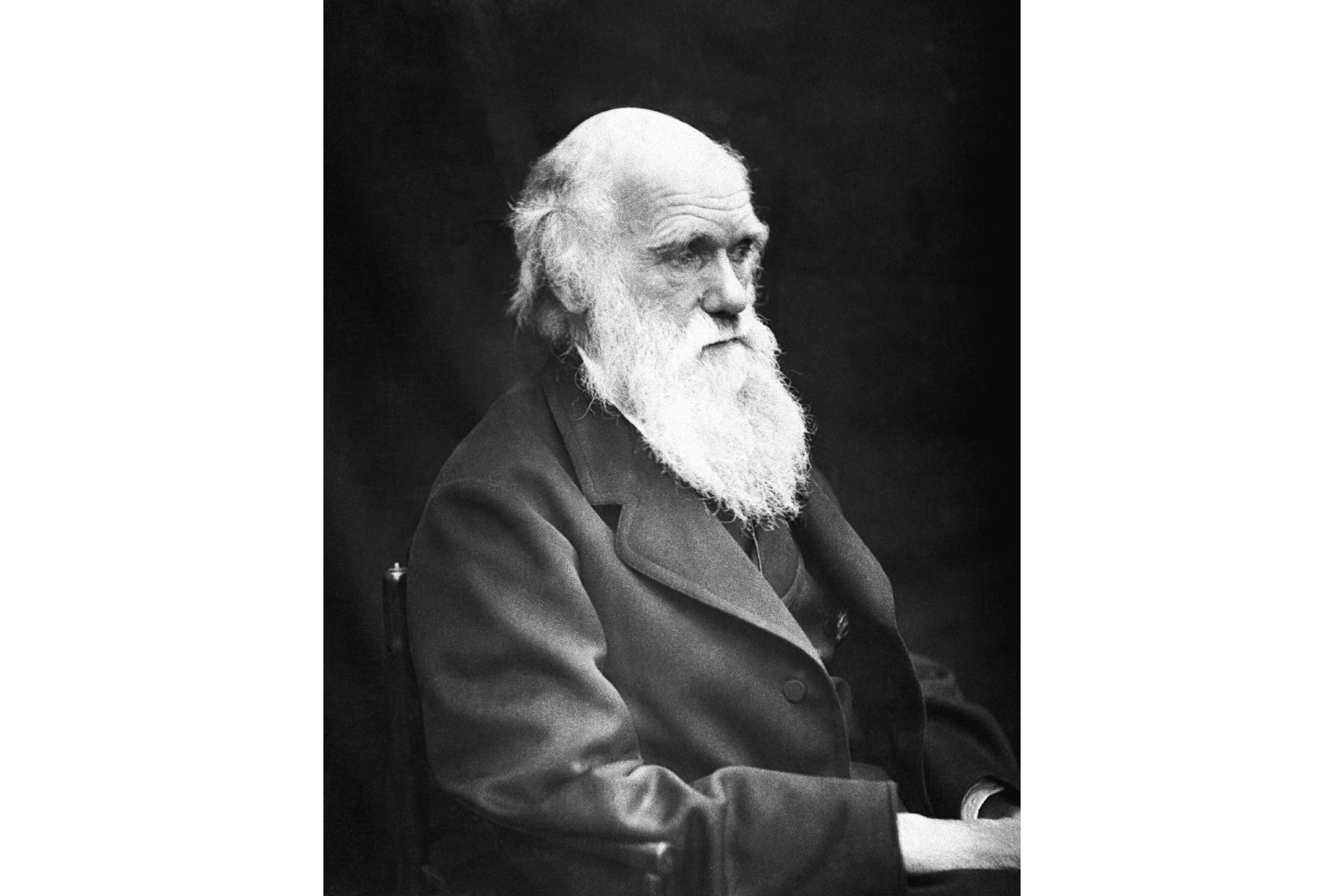
Charles Darwin get along to mind when we think of thetheory of phylogeny .
But before Darwin release his groundbreaking work in 1859 , other scientist were already try out to explain the diversity of life on Earth . One such scientist wasJean - Baptiste Lamarck , a French research worker who purpose a different possibility of evolution 50 years before Darwin published his work .
Lamarck believed that traits or characteristics that were used more often would grow stiff and expectant , while those that were n’t used would step by step go away . He also thought that any traits that were better through use could be passed down to issue .

A ordinarily used example is the Giraffa camelopardalis . According to Lamarck ’s possibility of evolution , giraffes have foresighted necks because their ancestors constantly unfold to reach leaves high up in tree diagram , cause their neck opening to get longer . He believed that this stretching moderate to retentive neck , which were evanesce on to the next generation .
We now know thatthis is not correct , and it is through genetic mutation that nature selects the most successful neck opening lengths in the population .
But Lamarck ’s idea were still an essential stepping rock that inspired Darwin ’s ideas of lifelike pick .

What are the different types of evolution?
Evolution can produce different patterns over time . We can label the three primary patterns as divergent , convergent and parallel organic evolution .
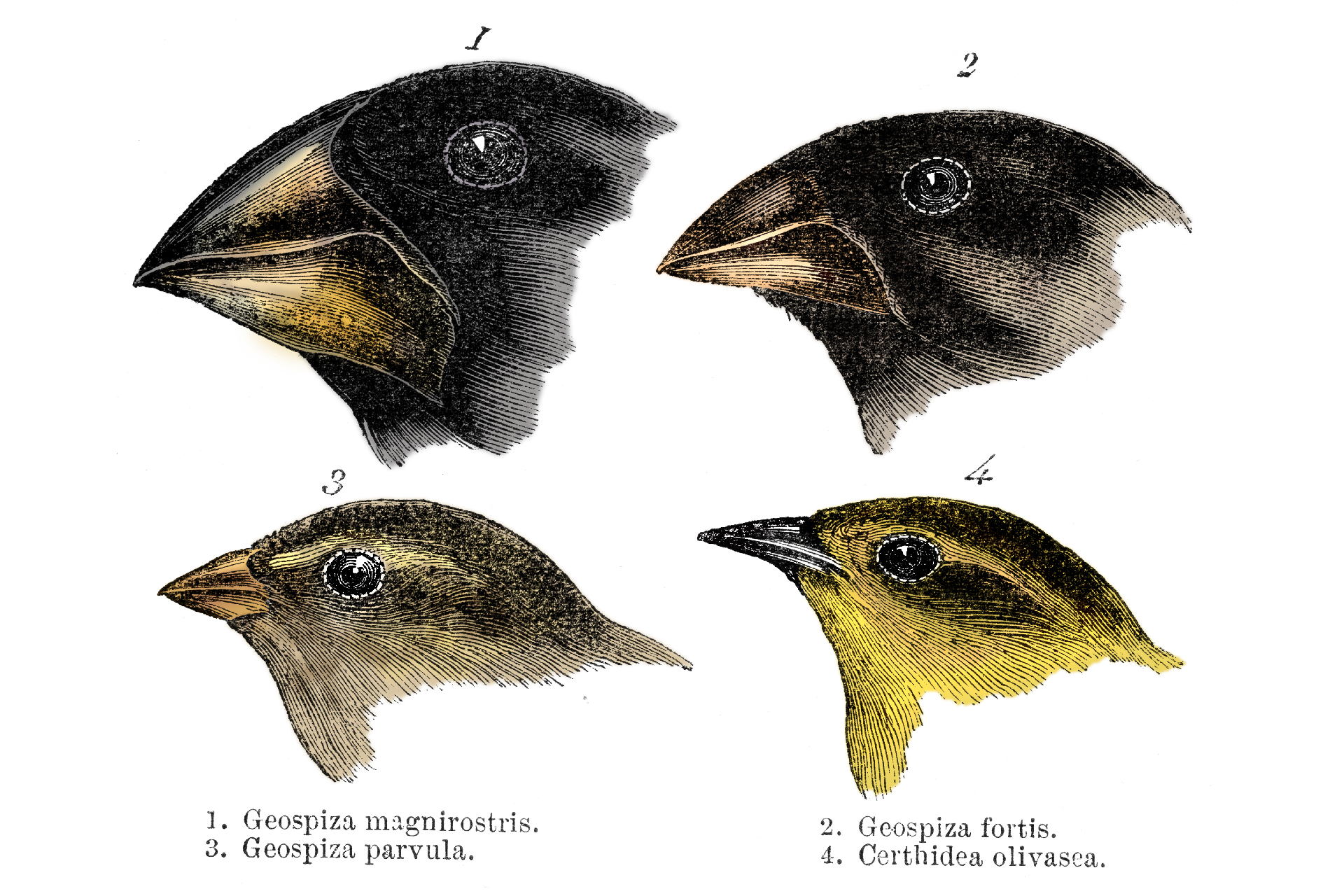
Divergent organic evolution happen when related to populations become more and more dissimilar from each other as they adapt to dissimilar environments . This can sometimes pass to the formation of new coinage . TheGalápagos finchesthat helped Darwin form his theories on phylogeny are a authoritative model : At first , these songbirds were just one species . But over time , birds from different islands evolved unlike beak shapes — from long to short , and slew to straight — to better rust the intellectual nourishment on those islands . life scientist can even see this transmutation happenin real timewhen island rainfall patterns change .
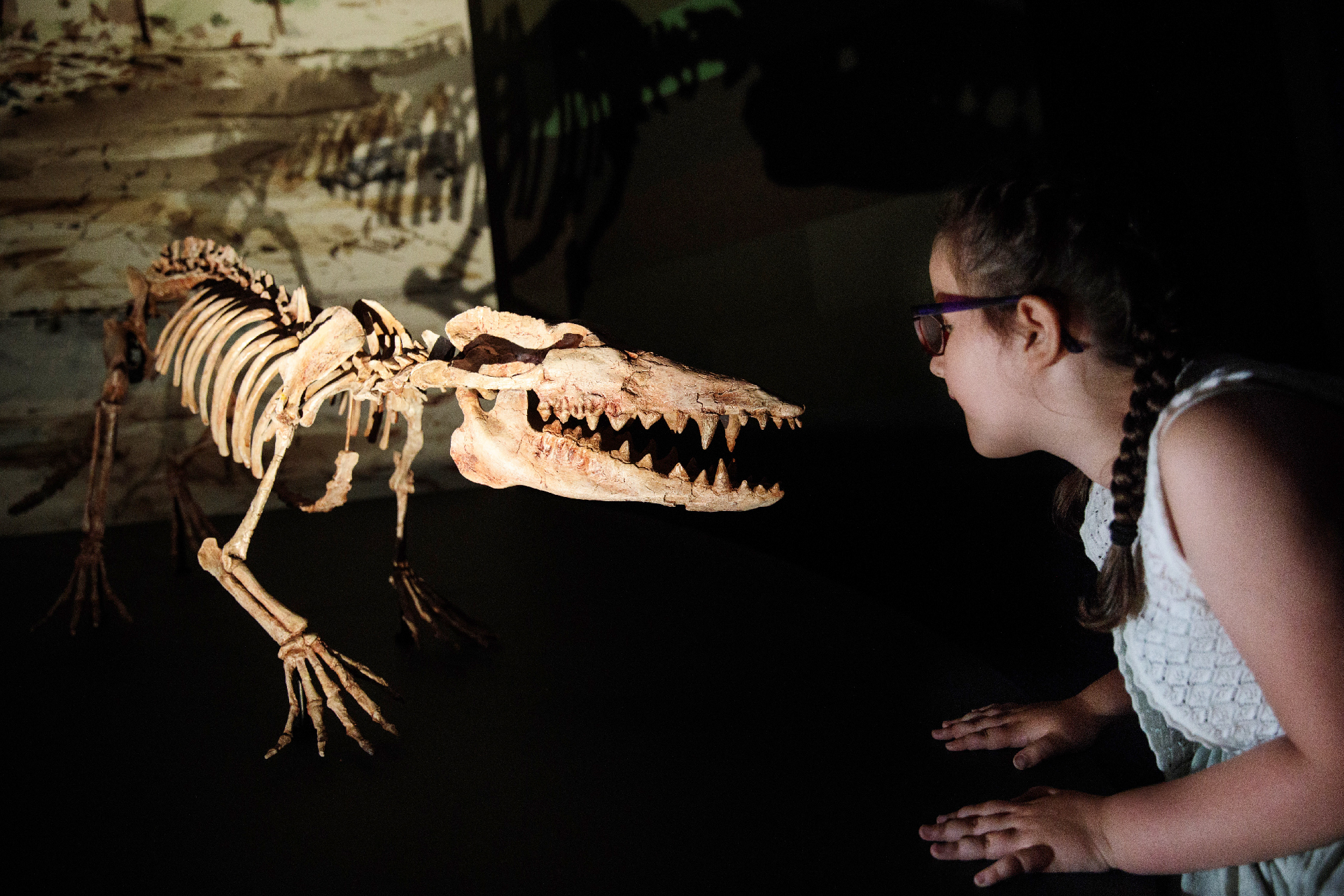
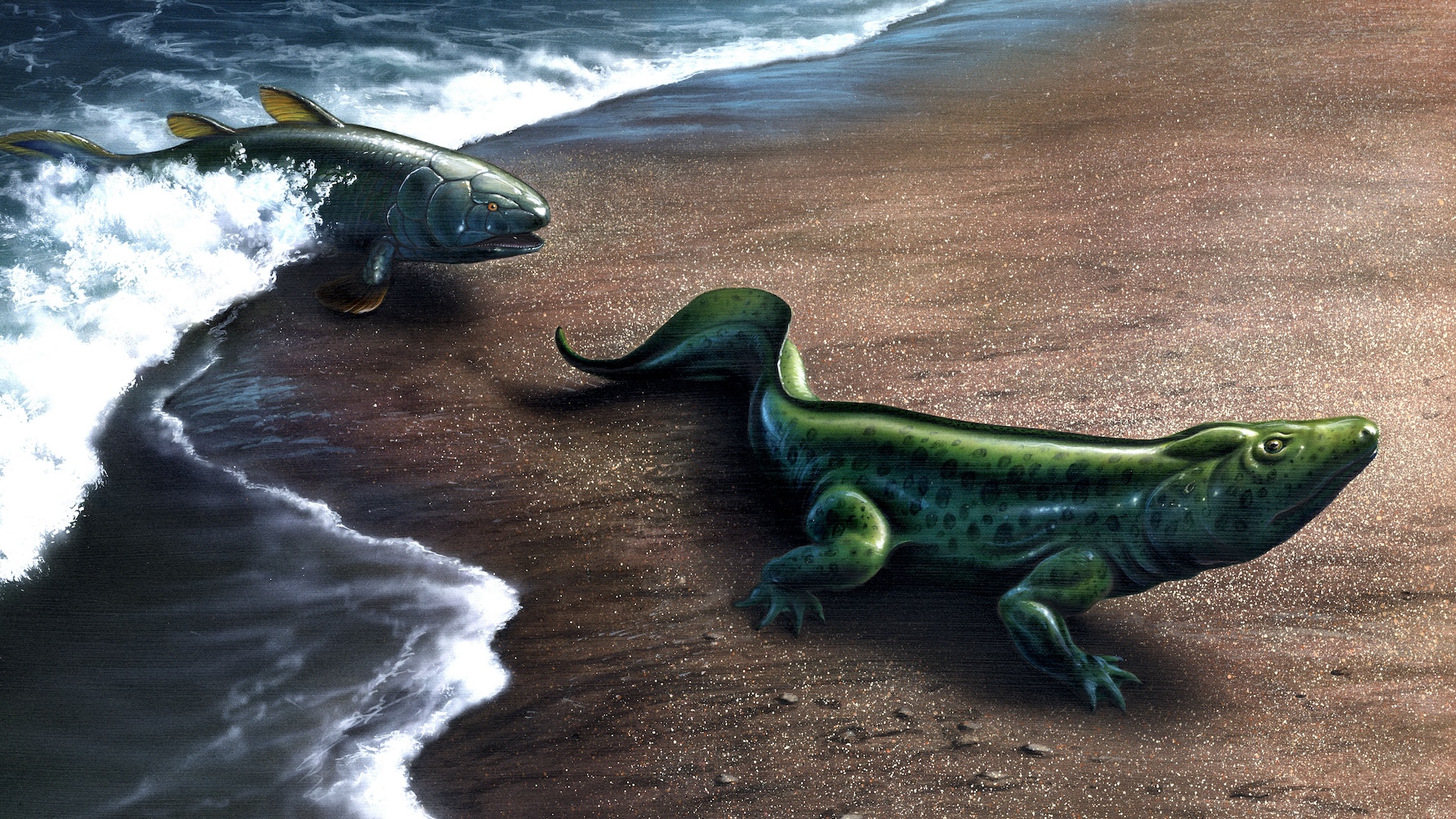
Convergent evolutionoccurs when unrelated organisms start take care or acting more like each other because they live in similar environments or must face the same types of challenges to go and multiply . For instance , dolphinfish and sharks both have streamlined body that serve them swim well in weewee . However , dolphins evolve from a wolf - like mammal calledPakicetusaround 50 million years ago , whereas sharks evolved from their fish ancestors approximately450 million year ago . This pattern can make the delusion that animals share a more late vulgar ancestor than they actually do .

Parallel evolution is similar to convergent evolution , but it require related to coinage with recent common stock . In parallel phylogenesis , intimately related species that live apart severally evolve similar trait when confronted with standardised environmental challenges . For example , the ancestors of livingcentipedes did n’t make maliciousness . But many centipede mintage separately develop spitefulness , indicating it was helpful to them .
Evolution pictures
Charles Darwin , aged 60 .
The Galápagos finches were made renowned by Charles Darwin ’s observations of nozzle edition that he collected during his voyage on the HMS Beagle .
Pakicetus , the ancestor of whales and dolphinfish , lived around 50 million years ago .

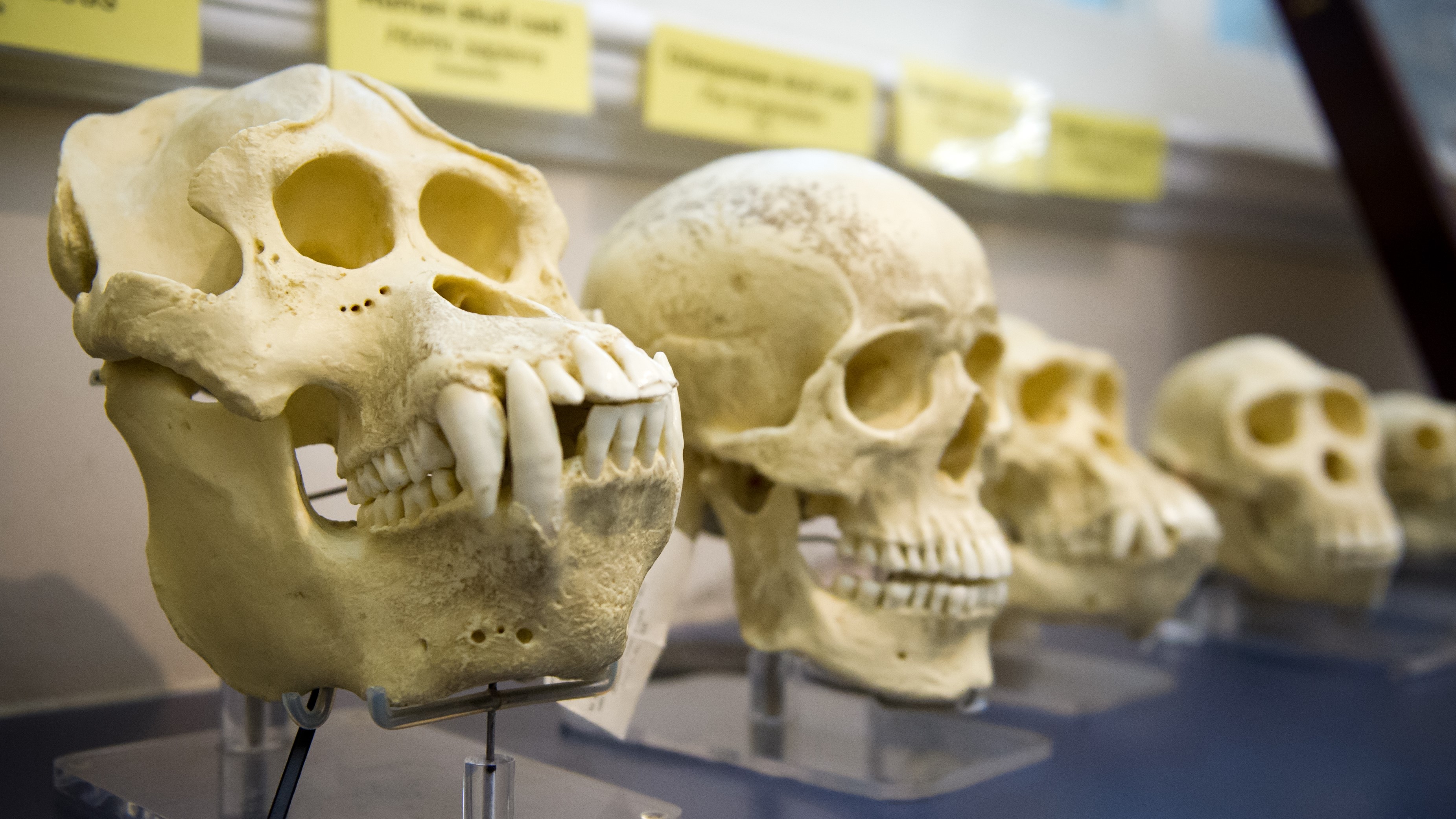
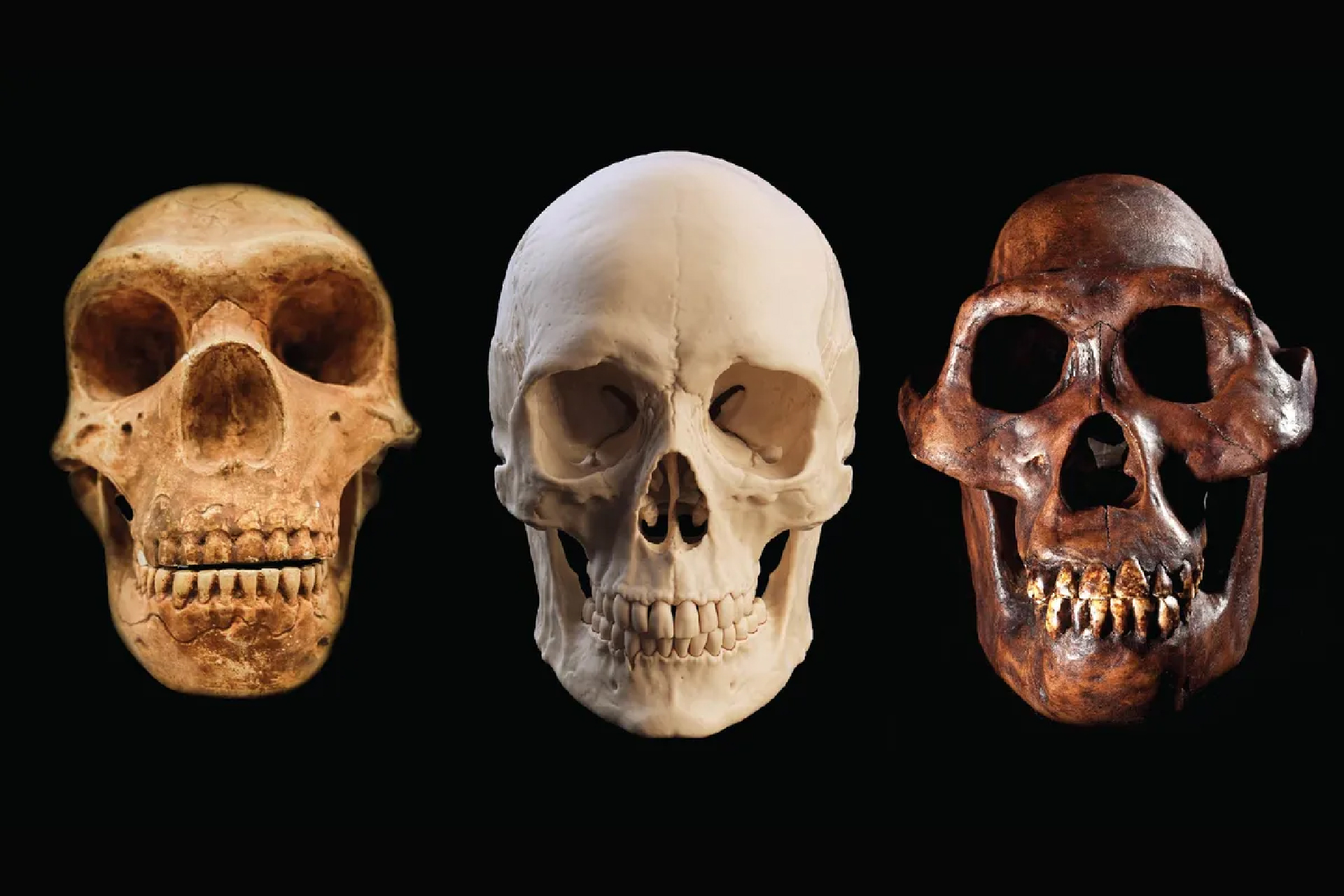
facts of life of skulls from a Neanderthal ( unexpended ) , homophile sapiens ( halfway ) and Australopithecus afarensis ( correct ) .
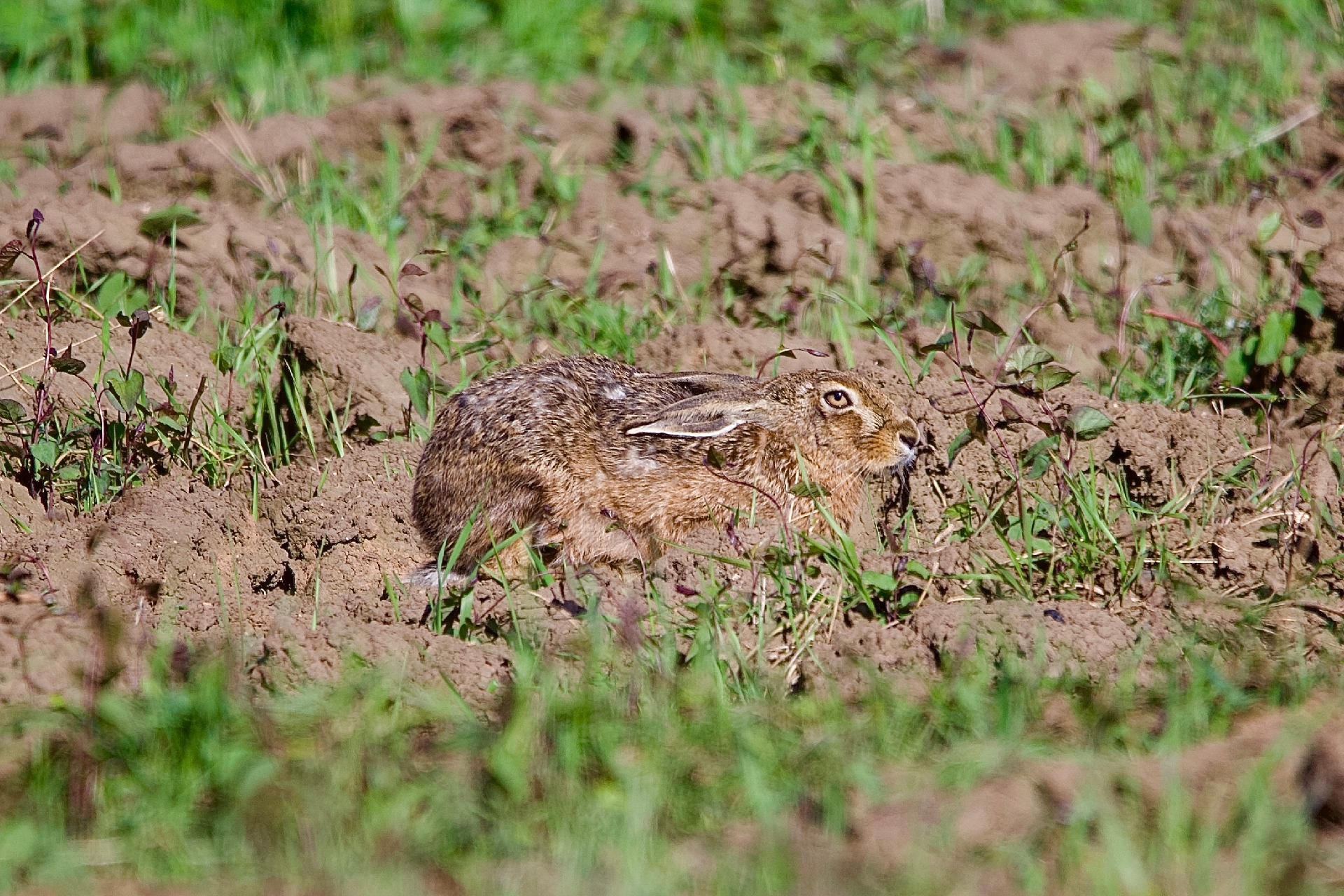
Many fauna have germinate camouflage to protect them from predator .
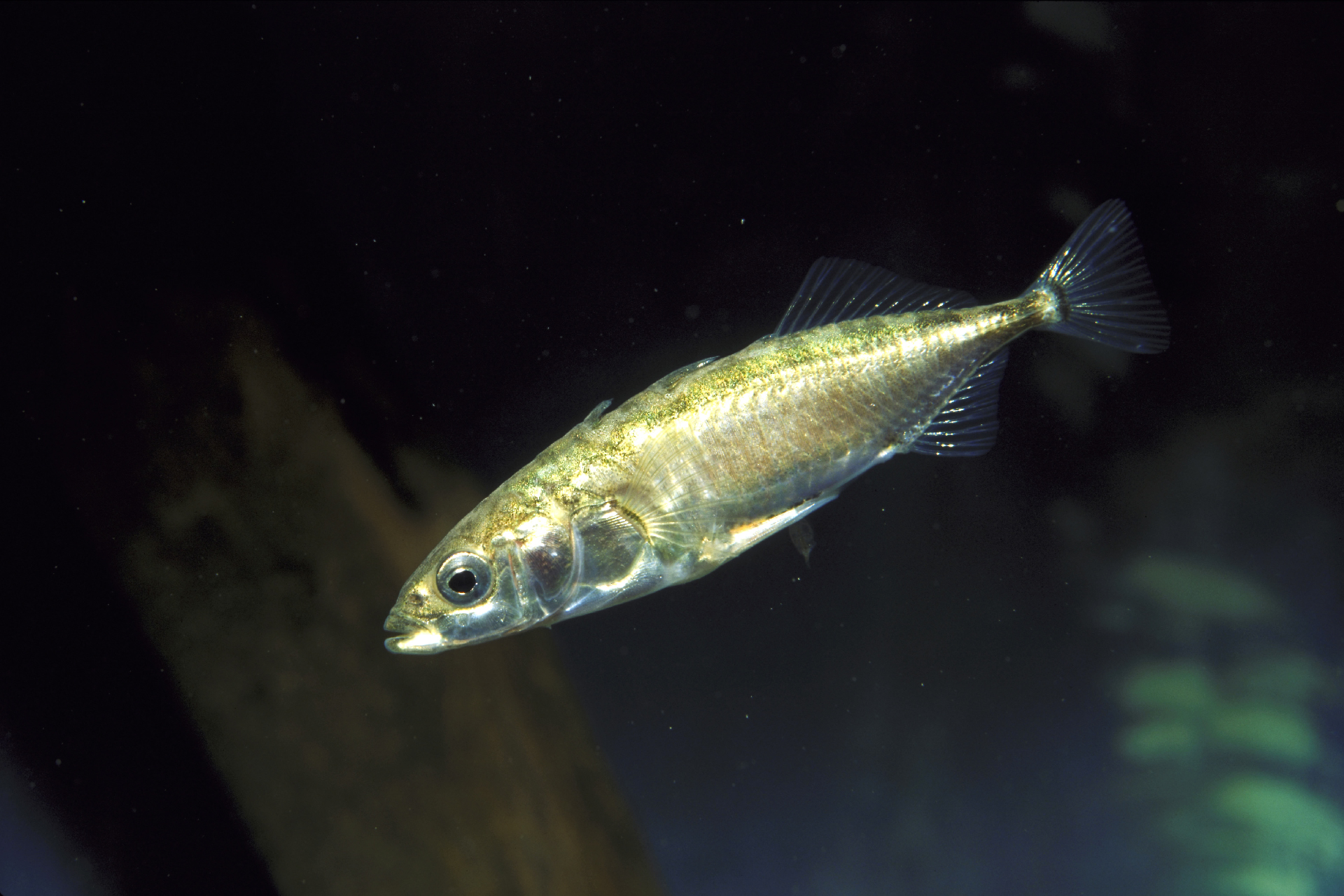
The evolution of stickleback Pisces the Fishes from a shipboard soldier to freshwater habitats gives a gravid instance of parallel phylogenesis .

Alfred Russel Wallace ( 1823 - 1913 ) develop a theory of lifelike selection at the same time as Charles Darwin .
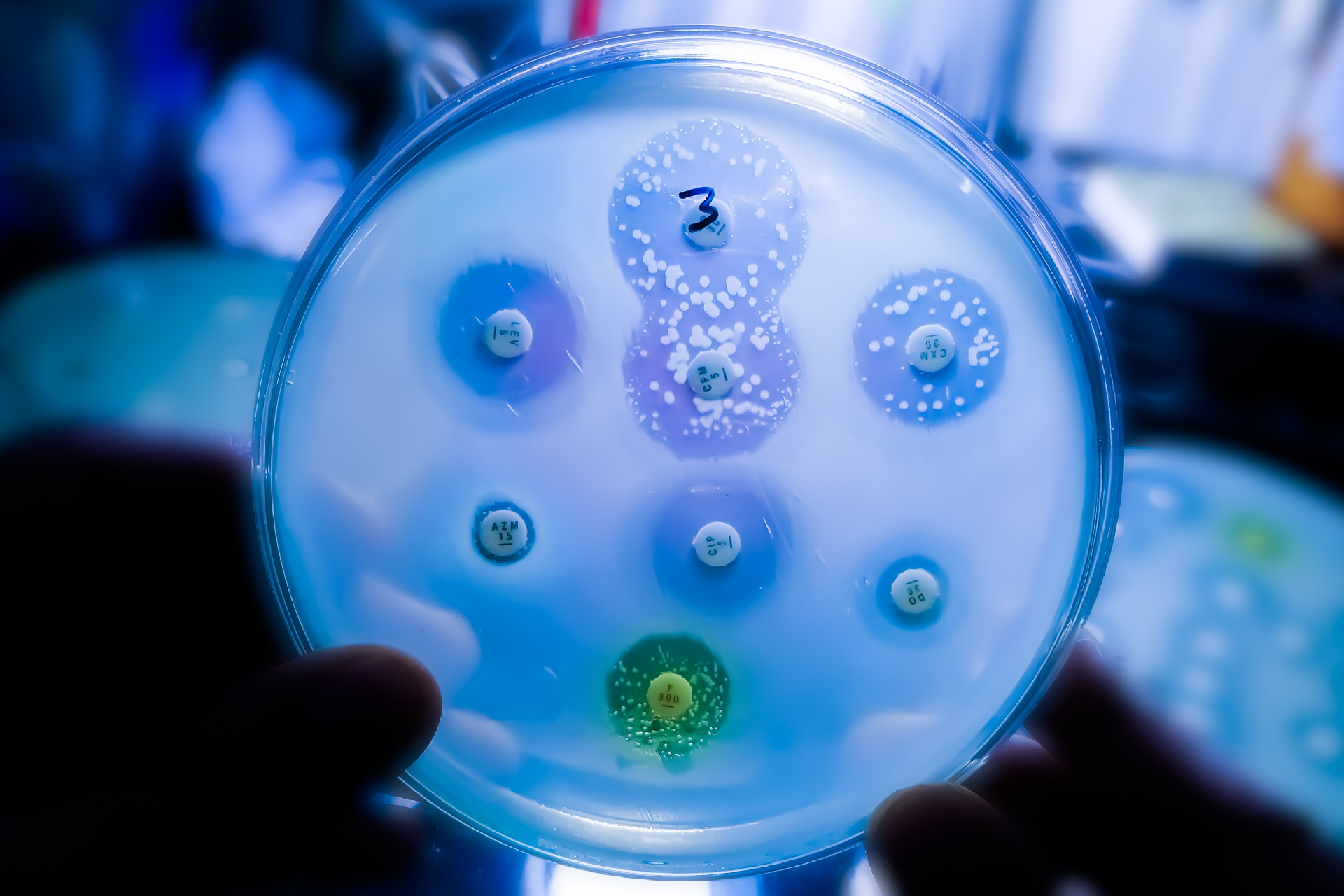
Antibiotic impedance is a global problem that is have by evolutionary processes .
Microbes such as bacterium have been useful to study organic evolution in real time in the lab thanks to how rapidly they develop .

Discover more about evolution
— How long do new species take to develop ?
— How 10 animals evolved their iconic features
— Which animals are evolve fastest ?

Books about evolution
" Amazing development : The Journey of Life,"$13.99 on Amazon
" The Origin of Species : 150th Anniversary Edition,"$6.26 on Amazon
" 30 - moment Evolution : The 50 most significant approximation and case , each explained in half a minute,"$16.36 on Amazon

Evolution quiz












