When you buy through links on our site , we may gain an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
NASAsatellite images show the lurid speed at which theland is drop down beneath major U.S. cities , including Baltimore , New York and Charleston .
The images , revealed by NASA Earth Observatory on Feb. 20 , show demesne movement across the East Coast , with areas in dark blue sinking at the truehearted rate . The subsidence threatens infrastructure , tilled land and wetlands — peculiarly assea stratum rise .
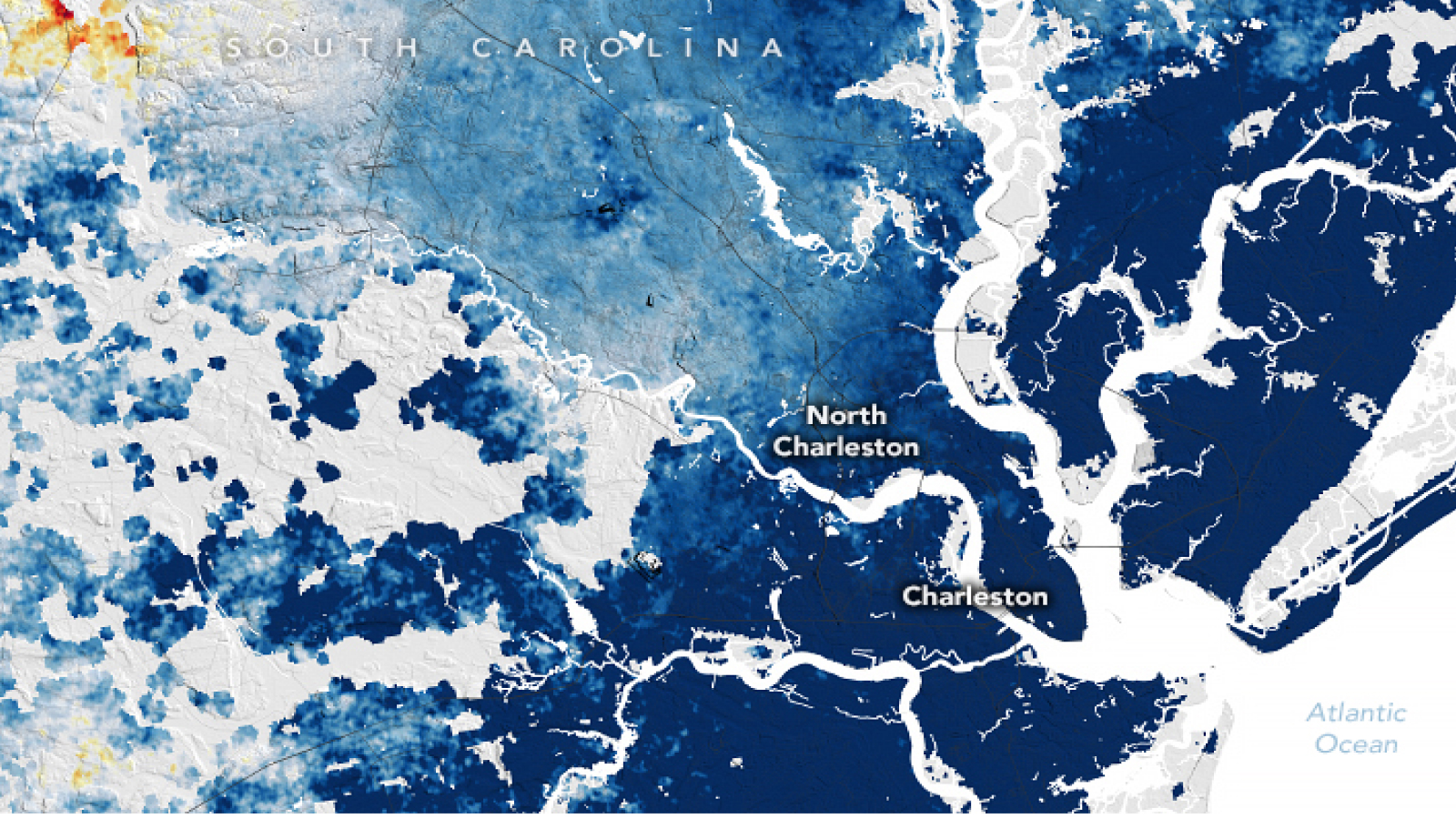
Charleston in South Carolina is one of the cities sinking at the fastest rate, with the ground subsiding by 0.16 inches every year.
Between 2007 and 2020 , the soil underneath New York , Baltimore and Norfolk , Virginia , sank by an norm of 0.04 and 0.08 in ( 1 to 2 millimetre ) a class , the satellite data show . In several counties in Delaware , Maryland , South Carolina and Georgia slide down at forked or threefold that rate , according to a study published Jan. 2 in the journalPNAS Nexus .
" remittal is a pernicious , highly localized , and often overlooked problem in comparing to global sea level ascent , but it ’s a major factor that excuse why water levels are rising in many parts of the eastern U.S.,“Leonard Ohenhen , a geophysicist at Virginia Tech and one of the authors of the study , tell NASA Earth Observatory .
relate : New York City may be pass under its own exercising weight because the building are too lowering , scientists warn
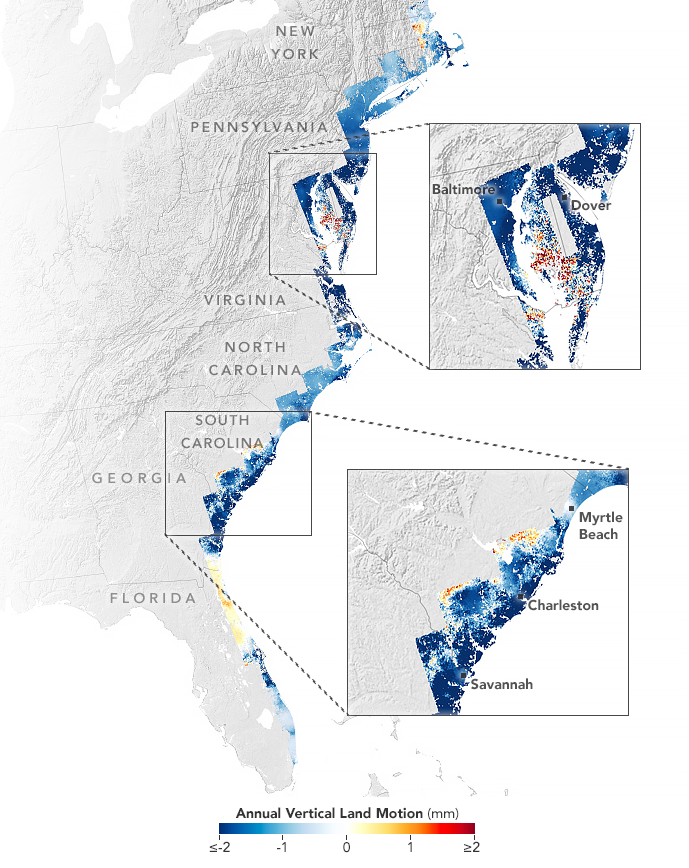
Researchers analyzed satellite and GPS data to establish the movement of coastal land from New England down to Florida.
Subsidence has many consequences for people living along the coast , include a great jeopardy of flooding and harm to homes and infrastructure because of mentally ill ground . At least 867,000 dimension and critical infrastructure — include highways , railroad track , airports , dam and levees — were all subside , according to the study .
Sinking soil can also head to salt water intruding into farmland , crops and fresh water provision , as well as impact wildlife home ground like marshlands , fit in to NASA Earth Observatory .
One of the quickest - sinking urban center is Charleston , South Carolina , where the business district expanse is just 10 feet ( 3 meter ) above ocean grade . The city is sink by around 0.16 inch ( 4 mm ) per year .

According to NASA Earth Observatory , the subsidence under Charleston is for the most part make by human activity such as groundwater pumping . When humans drain underground aquifers or extract natural gas from the ground , the empty space left behind can founder , causing the land above to go under . However , in places like New York , a combination of factors are contributing to subsidence , including the mild demesne it is built on and the weight of the buildings .
The investigator used satellite figure of speech and footing - base GPS sensors to study the coast from New England to Florida . They then created a map that let on the variability in the rising and fall of various areas along the coast . That data was measured against information pile up by the ground - base Global Navigation Satellite System to find the charge per unit of sinking .
— A major US urban center is drop , and this time it ’s due to ' underground climate change '

— Climate change causes a lot peak immobilise for yard of years to break up
— Satellite image reveal just how much cities on the US East Coast are sinking
accord to the maps , the mid - Atlantic neighborhood is sinking more than the northeastern U.S. This is for the most part down to a geological process calledglacial isostatic adjustment , which is the ongoing movement of realm once burdened by heavy chicken feed sheet during thelast ice age , which lasted from around 126,000 to 11,700 years ago .

The sharpness of the immense Laurentide glass sheet ran through what are now Pennsylvania and New Jersey , pushing the estate down with the weight of the deoxyephedrine . Meanwhile , the res publica beyond the methamphetamine hydrochloride ’s perimeter was drive upwards . When the chalk began to melt around 12,000 years ago , the land that once come out along the coast began to sink and is proceed to do so .
Study co - authorManoochehr Shirzaei , film director of the Virginia Tech science laboratory , said the researcher trust to map the Gulf Coast next . " Our long - cooking stove finish is to map out all of the world ’s coastlines using this technique , " he pronounce in the press release . " We know that planners in several U.S. cities are already using our datum to make our coastlines more resilient , and we want cities all over the universe to be able to do the same . "










