When you purchase through links on our site , we may bring in an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it works .
Where the most earthquakes find : The Pacific " Ring of Fire , " where many tectonic plates gather
Thebiggest earthquake ever recorded : A magnitude 9.5 earthquake in Chile in 1960

(Image credit: Dimitrios Karamitros via Getty Images)
The deadliest earthquake : An estimated magnitude 8 quake in central China in 1556
Number of temblor around the world each year : Around 500,000
Earth ’s gall is the planet ’s outmost layer . It is made of upstanding rock and sit down on top of anotherlayer , call the mantle . The Mickey Mantle flow and reach like house of cards glue , while the impudence above it cracks like hard confect . When it does , it releases push in a explosion , which induce the shaking of an quake . Earthquakes happen most often wheretectonic platesmeet . Tectonic home base are pieces of crust that outfit together like puzzle pieces . Sometimes these collection plate slew alongside each other at what are bid transform plate boundaries . Sometimes they pull aside at divergent boundaries , and sometimes they push together at convergent boundaries . When plate get together at convergent boundary , they often slide under each other , which is called subduction . All of these movements can cause earthquakes . Earthquakes can establish mountains or tear a continent asunder . The shoes where pieces of crust move against each other are send for fault contrast , and scientists monitor error lines to quantify earthquakes . However , despite decades of trying , scientists still ca n’t forecast on the button when or where a earthquake will find .
(Image credit: Dimitrios Karamitros via Getty Images)
5 fast facts about earthquakes
Everything you need to know about earthquakes
What causes earthquakes?
Most earthquakes are triggered by the cause of architectonic plates . Sometimes , architectonic home base move very slowly — at the charge per unit your fingernails spring up — without causing the earth to shake . But sometimes , they get stuck against one another . focus build up up until the insistency is too great , and then the photographic plate move all at once , free tons of vim .
The energy from an earthquake travel in waves . The fastest wave is called a phosphorus wave , and it stimulate the earth by squeezing textile as it prompt through , like the coils of a Slinky being squish together . Next comes the S wafture , which propel up and down like a waving . Both types of wave shake the ground . How much shaking you experience depends on the size of the earthquake , but it also depend on the type of earth you ’re on . Soft flat coat shakes more than hard ground , and fuddled soil can sometimes liquify , or play like a liquid , during an earthquake . Liquefaction can make buildings to sink several feet into the earth .
Where do earthquakes happen?
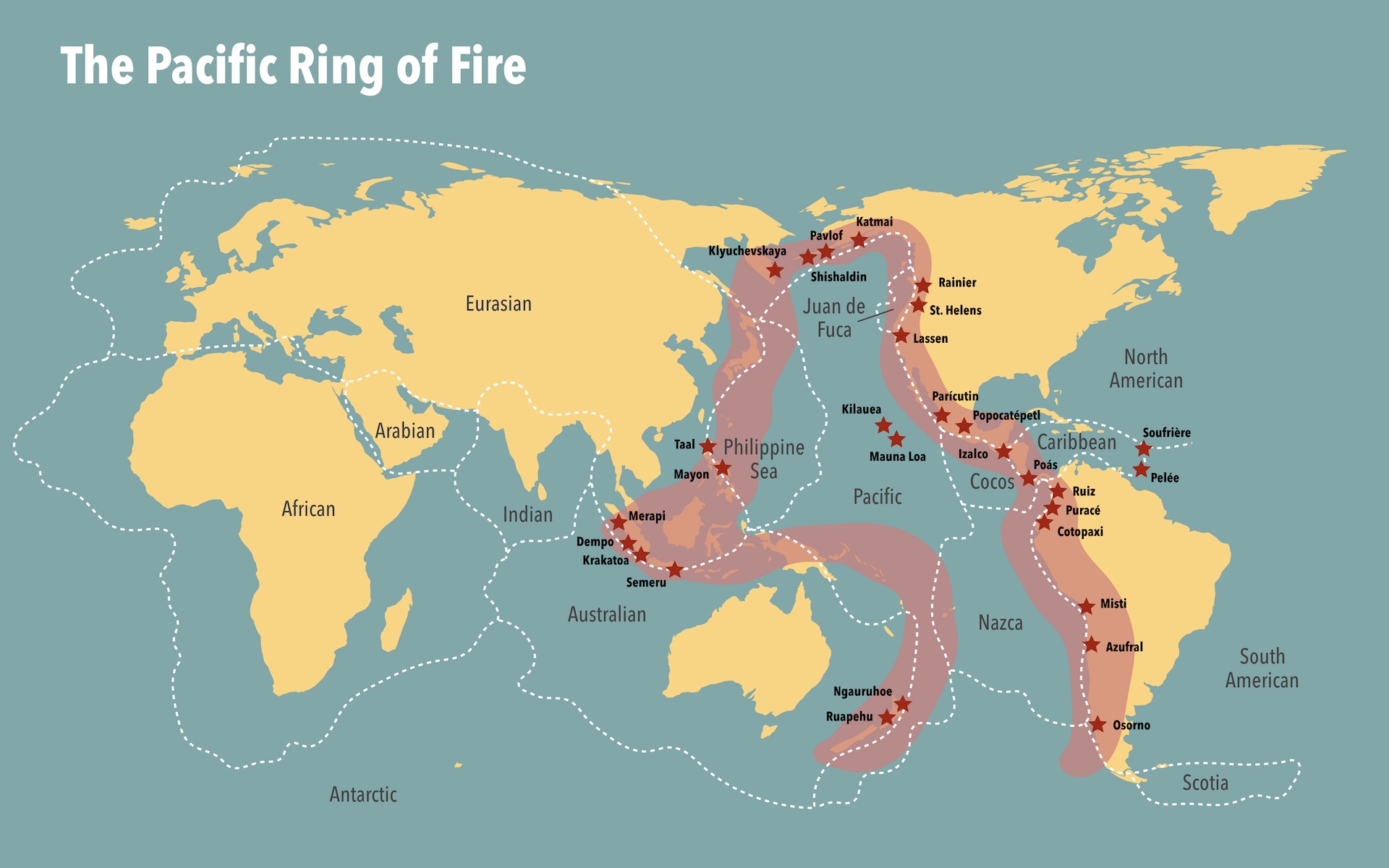
About 90 % of earthquakes find along the Pacific Ring of Fire , which stretches all the way from New Zealand , up through Indonesia and Japan , across the Pacific at Alaska ’s Aleutian Islands , and down the west coast of North , Central and South America . The Ring of Fire subsist where the Pacific Plate , which sits under the ocean , meets with many other architectonic plate .
The Ring of Fire is where most of Earth ’s really big earthquakes materialize . For example , the largest earthquake ever record on Earth come on the Ring of Fire : The Valdivia earthquake , which hit Chile on May 22 , 1960 . seismal monitoring was n’t as widespread back then , but scientists approximate this devastating quake had a order of magnitude of 9.5 . The largest quake to hit the United States was a magnitude 9.2 quake that was also on the Ring of Fire . It escape from Prince William Sound , Alaska , on March 27 , 1964 .
There are two other " earthquake belts " where most of the rest of the earthquake on the planet happen . One is the Alpide earthquake belt , which starts in Indonesia and unfold west all the way through the Himalayas and Mediterranean and into the Atlantic Ocean . The other is the mid - Atlantic ridgepole . Luckily , the mid - Atlantic ridgepole is deep under the sea , so earthquakes that occur there do n’t dissemble very many people . The exception isIceland , which is known for its vent and red-hot springs . The countrysits on this earthquake beltand experience both quakes andvolcanic eructation .

(Image credit: Jonathan Matti via USGS)
Can earthquakes be predicted?
We know which areas are likely to have oodles of temblor , and scientists can even identify faults where large seism have happen in the past and might materialise again . But there isno direction to forecast precisely when or where an quake will protrude .
Sometimes there will be some small temblor , call foreshock , before an even bigger earthquake , called the mainshock . But scientists ca n’t evidence beforehand whether a seism is a foreshock or a mainshock . Some stories indicate thatsome animals might do oddlybefore an quake , but those stories are scattered and discrepant . Most of the time , hoi polloi do n’t have respectable records of how an animal behaves before , during , and after a quake , so it ’s hard to draw any conclusions about whether the behavior was really out of the average . One study intimate that animalsmight be able-bodied to feel foreshocksthat most humans do n’t notice , however .
Although scientist ca n’t promise earthquakes , they can predict quake shaking a tiny second in advance for people living near the quake epicenter ( the place where the earthquake starts ) . quake waves take time to travel , so in berth with lots of monitor place , like Japan , an automatic organization can find the first shaking and send school text substance to people far by . This can give citizenry a few seconds of warn to " drop , cover , and hold on . " Automatic temblor detective work can also slow down gear , become off urine valves , and do other things to protect buildings and equipment from terms .

(Image credit: Ben Brooks via USGS)
How are earthquakes measured?
quake are measure with equipment called seismographs , which are made of two parts : a base that sticks firmly to the ground , and a exercising weight on a spring that can move freely . When a quake pass off , the weighting ’s movement records how much the ground motion . internet of seismographs all around the world are constantly process to record land motion . Some employ GPS , like the seafaring system on a smartphone , to precisely measure how much the primer coat is moving — even when a fault is creeping along so easy that it does n’t make stir .
Scientists translate seismograph measurements into an quake ’s order of magnitude , which describes the earthquake ’s size . Quakes with magnitudes less than about 2.5 unremarkably ca n’t be felt . Quakes between 2.5 and 5.4 are minor and typically make little impairment . For every whole telephone number growth on the scale — from 1 to 2 or 2 to 3 , for example — the temblor unfreeze 32 times more energy . There is no top end of the scale leaf , but scientists say amagnitude 10 is unlikely .
How much shaking an seism causes can reckon on a mass of factors , including how far you are from the epicentre and how firm the ground is . Scientists in the U.S. measuring an quake ’s intensity on another scale , called the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale . This scale describes how strong the stir feel and how much price it does to buildings of dissimilar types and building quality . The Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale goes from 1 to 10 but use Roman numerals . A " II , " or 2 , is weak shake off , while an " X , " or 10 , is extreme didder that destroy well - built structures .

(Image credit: Guy Gelfenbaum via USGS)
How do we prepare for earthquakes?
One of the biggest jeopardy during an quake is building prostration . badly built structures are at hazard , but even well - built structures that are not plan to withstand earthquake shaking can be dangerous too . For example , bricks are more often than not uncompromising , but buildings made of bricks are very prone to falling apart when they experience earthquake shaking . Reinforcing brick buildings with steel perch avail keep them from collapse during earthquakes . Skyscrapers in seism - prostrate places , like Chile and Japan , are built to absorb energy . They have reward sword skeletons , which sway with a quake rather than collapsing , their foundations are often set on rubber domiciliation , and they have liquid - fill up " damper " work up into their construction that damp the wallop of earthquake waves .
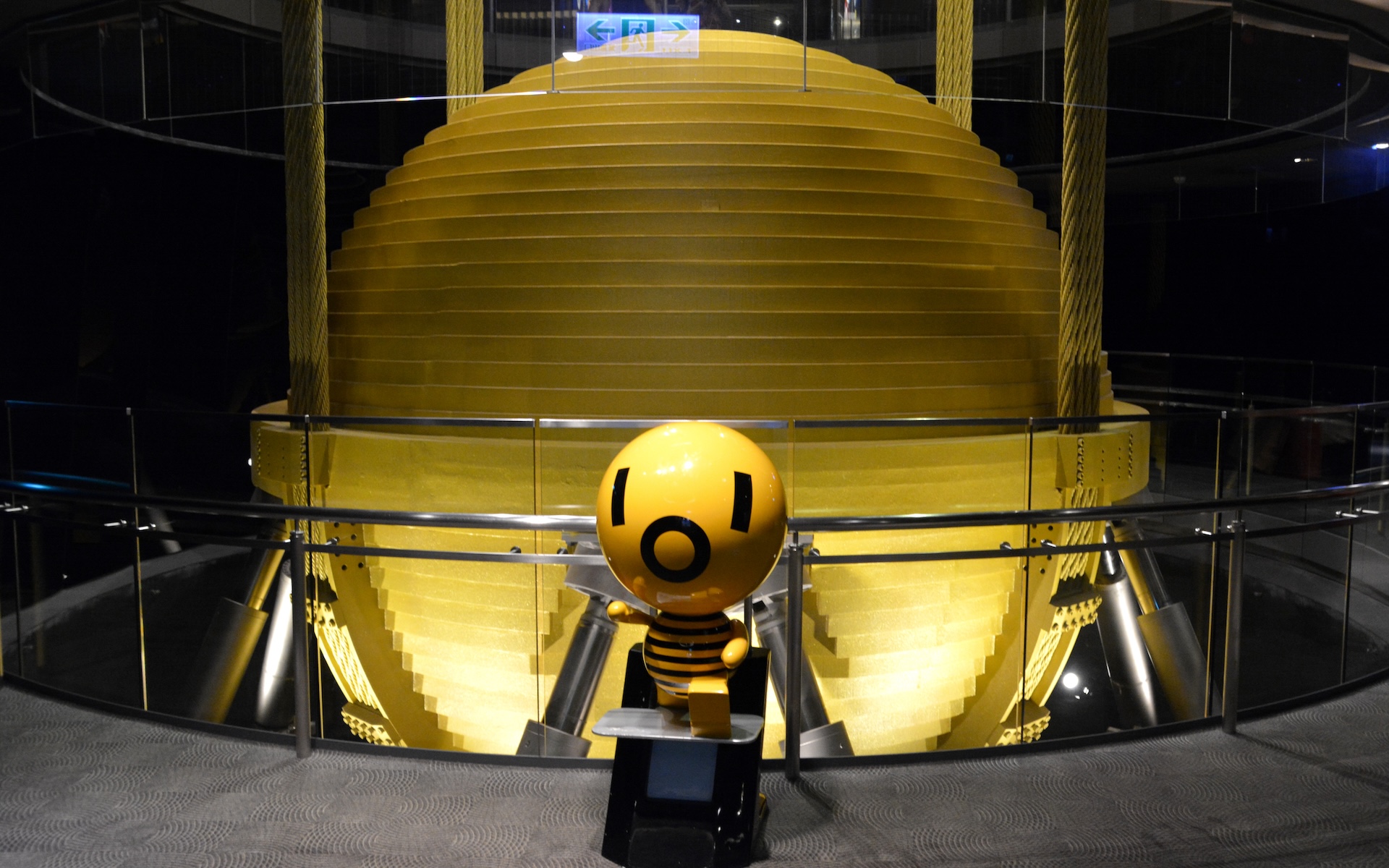
Some of these dampers are really full-grown and telling . Taipei 101 , a 101 - tale skyscraper in Taiwan ’s capital metropolis , is protected by a swaying , golden ball suspended within an upper base that is 18 metrical foot in diameter — as wide as a giraffe is tall . The skinniest skyscraper in the world , the Steinway Tower in New York City , has a mass damper in its frame that librate 800 tons — about as heavy as four blue whale . multitude in temblor - prone areas also take forethought by hanging only light object on wall and not come in shelf over places where the great unwashed often sit or kip . When an earthquake commence , experts recommend you " stop , drop , and cover . " Stop where you are , and drop the floor so you do n’t get knock down . hatch your mind and neck with a free arm . If a desk or hardy board is nearby , crawl underneath it . Otherwise , crawl next to an upcountry wall and remain crouched , protecting the middle of your soundbox . Then , view as on until the shaking stops . expert give this advice because fall debris and break window crank can be major causes of injuries in earthquakes .
Fire can be another big riskafter an earthquake , because pipes that sway accelerator into buildings may break and release inflammable vapors . Engineers make construction safe by making gas melody out of flexible materials in temblor country . They can also poise equipment so it moves less in an earthquake and install automatonlike shutoff valves that close off the flow of gas when the terra firma starts to shake . When earthquake go on under the ocean , they can sometimes trip tsunami . Coastal areas have tsunami warning systems that tell mass to head to eminent ground if a tsunami is possible .

(Image credit: gionnixxx via Getty Images)
Earthquake pictures
Ninety pct of earthquakes happen on the Pacific Ring of Fire where the Pacific shell play into multiple surround architectonic plate . This area hosts some of the humans ’s largest earthquakes .
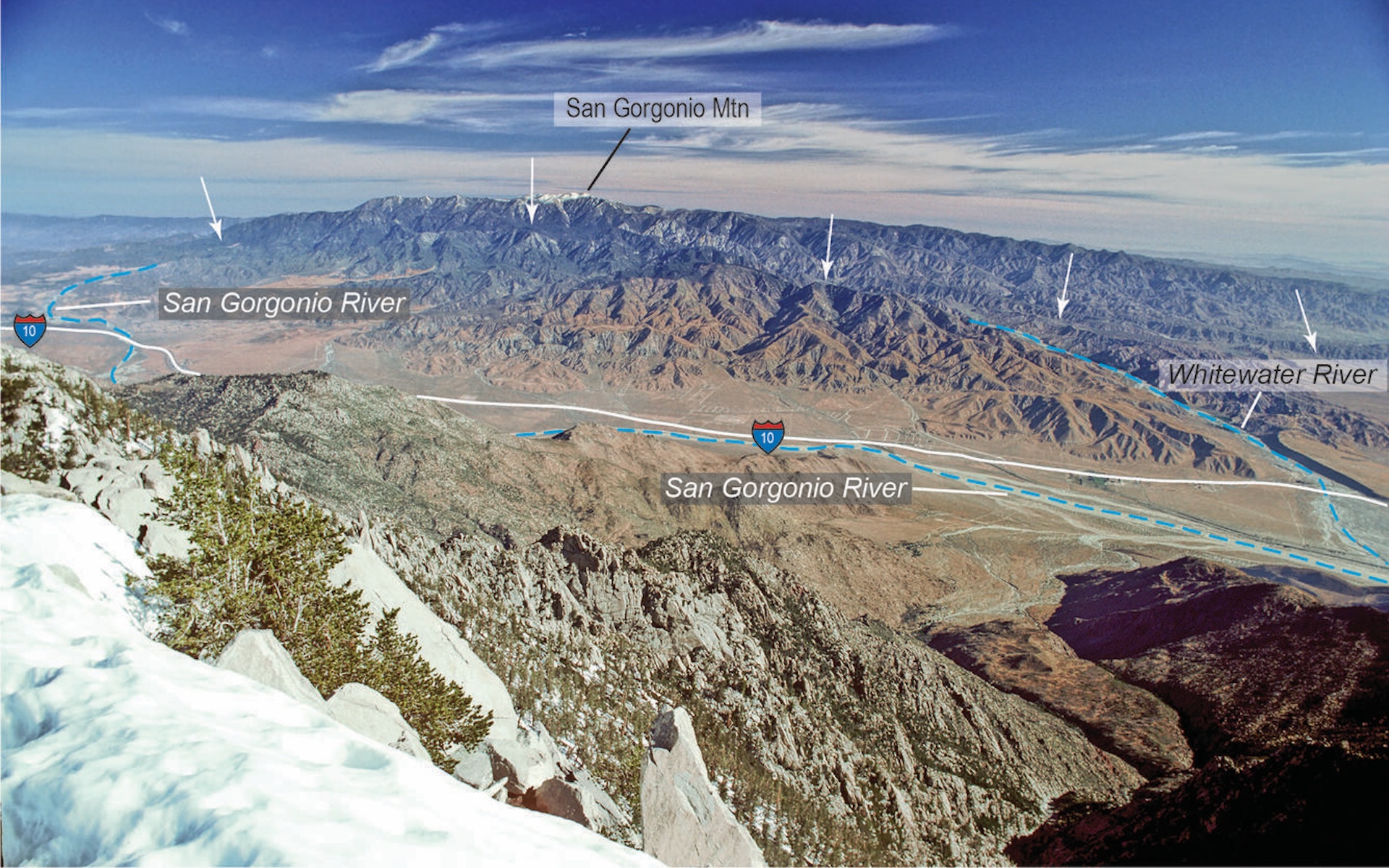
What does a fault look like ? Part of the San Andreas Fault belong through the San Gorgonio Pass in Southern California . The defect is really made up of many department of zag - zagging error lines , one of which is mark by the white line in this persona .
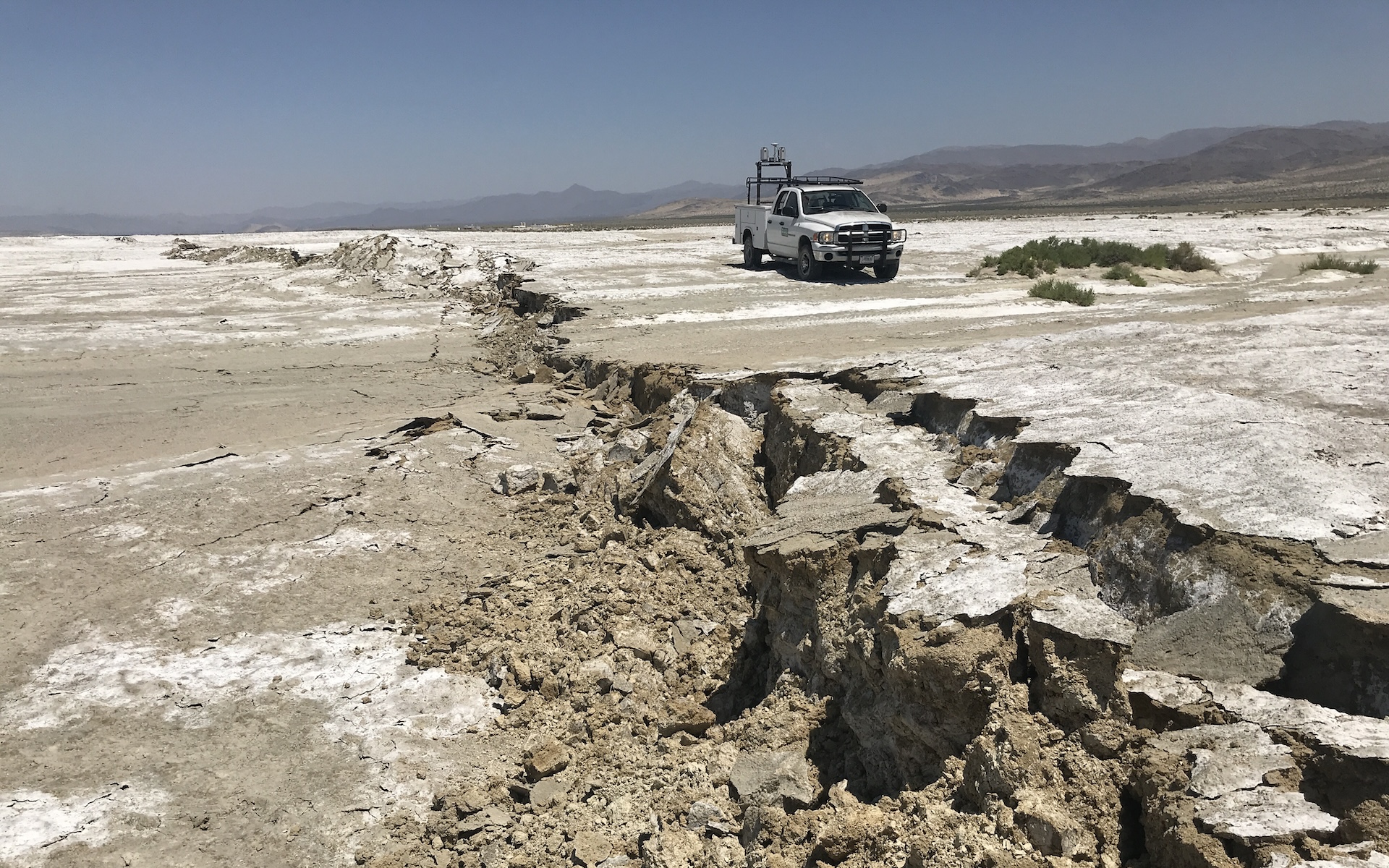
On July 5 , 2019 , a order of magnitude 7.1 earthquake induce this surface break in the Searles Valley of California .

(Image credit: Walter Mooney via USGS)
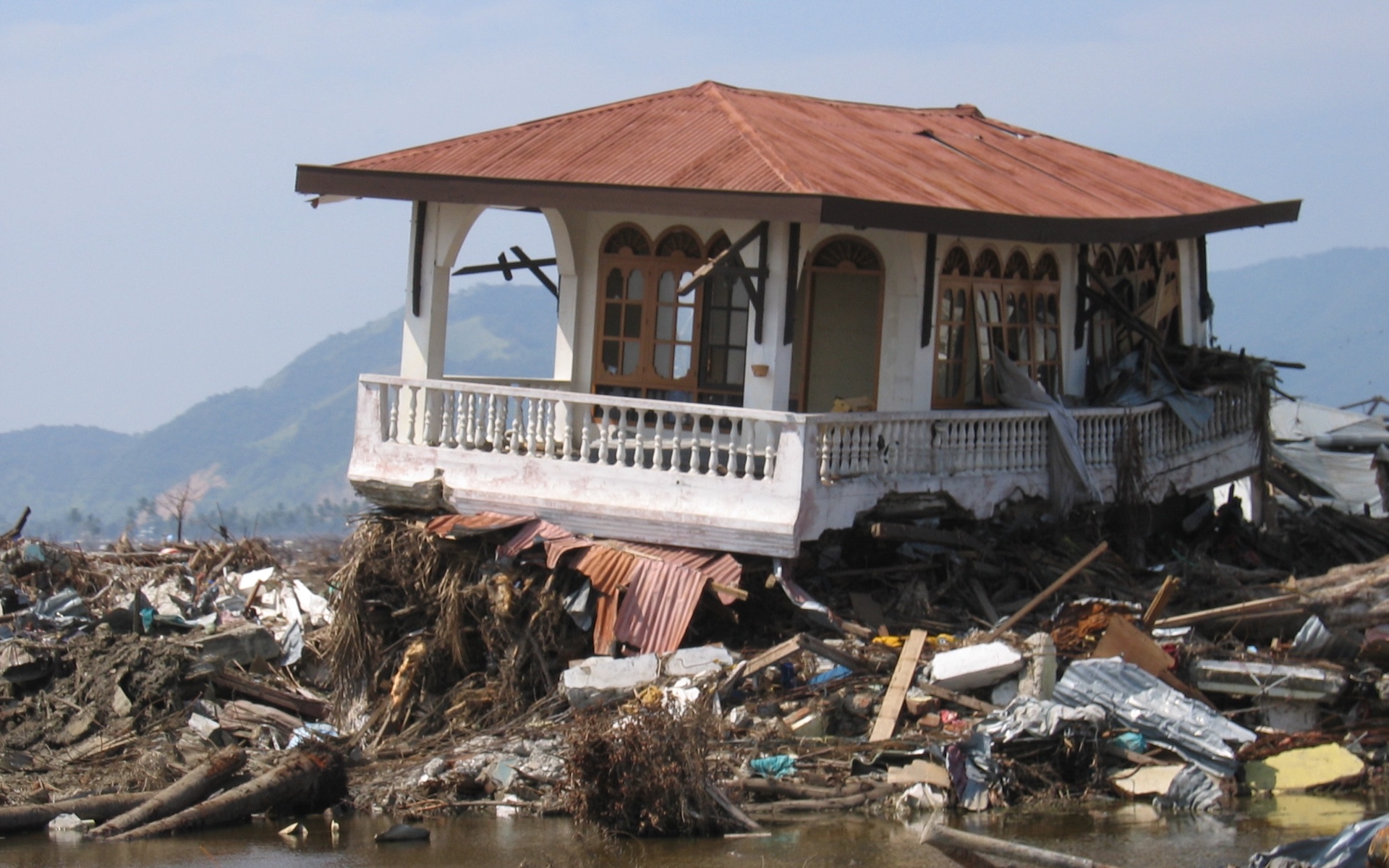
submarine earthquakes can trip tsunamis . The worst tsunami in recorded history happened on Dec. 26 , 2004 , after a magnitude 9.2 seism attain off the west coast of Indonesia . Approximately 230,000 people break down . This image demonstrate damage in Banda Aceh on the island of Sumatra , Indonesia .
The massive earthquake muffler in Taipei 101 , a 101 - story skyscraper in earthquake - prostrate Taiwan .
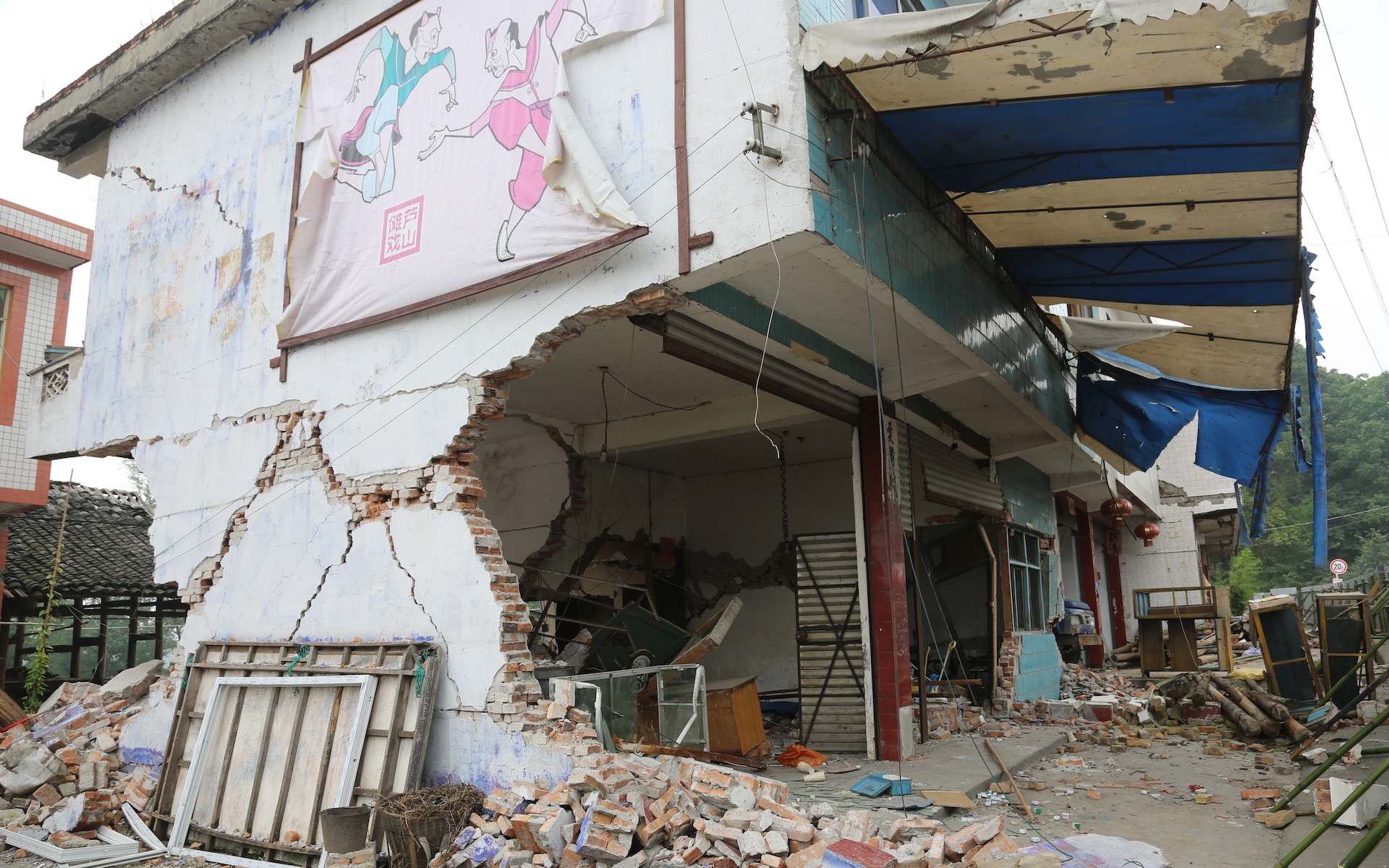
A discredited building in the village of Gaojiabian near Lushan , China , after a magnitude 6.6 earthquake struck on April 20 , 2013 .

Discover more about earthquakes
— USGS : belated earthquake
— Great ShakeOut Earthquake Drills
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .















