When you buy through link on our site , we may take in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
investigator have detected one of the most powerful cosmic rays ever seen slamming into Earth — but they have no idea what caused it or where it came from . The extremely gumptious particle , which has been named after a Nipponese goddess , make it from the instruction of a void in the universe where almost nothing is have it away to live , harmonise to new research .
Cosmic raysare highly energetic corpuscle , mainly consist of proton or He nuclei , that are invariably raining through every square inch of the universe ( including our bodies ) . But a small subsection of cosmic ray , which run into Earth roughly once per straightforward mile every year , are speed to even greater Department of Energy levels by some of the existence ’s most intense phenomena .
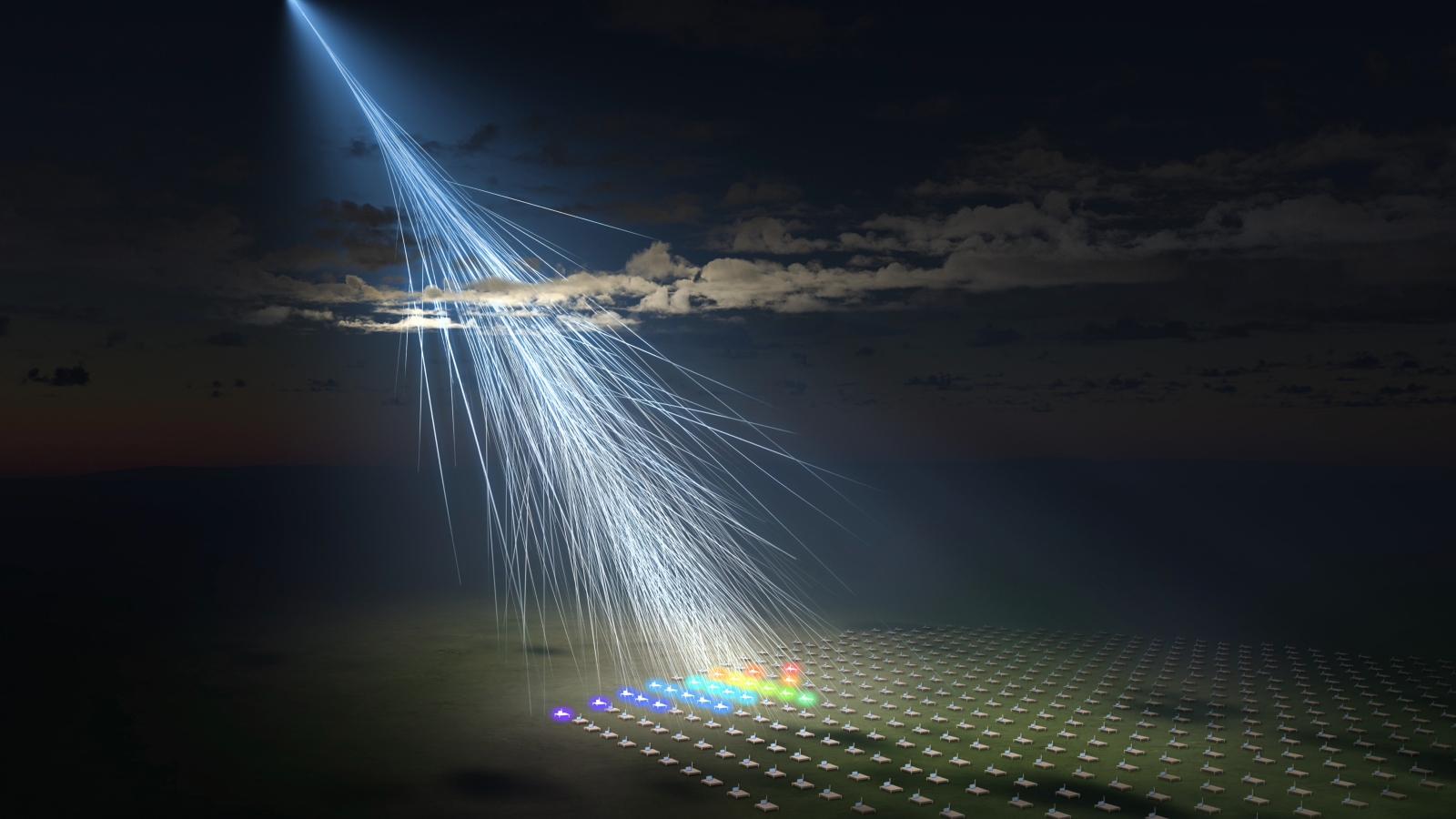
When powerful cosmic rays hit gas molecules in Earth’s atmosphere they create a cascade of energetic particles that are detected on the ground. By tracing back these particles to their source, researchers can estimate how powerful the original cosmic ray was.
These extra - up-and-coming particle , love as " radical - in high spirits - energy cosmic rays , " have at least one exa - electron V ( EeV ) , or 1 quintillion ( 1 succeed by 18 zeros ) electron volts , of vigour , which is around a million time more gumptious than the fastest particles from human - made corpuscle accelerators .
On May 21 , 2021 , researchers detect one of these supercharge cosmic rays with theTelescope Array project — a detector made of individual substations covering more than 270 square stat mi ( 700 square kilometers ) in Utah . This particular subatomic particle had a humongous 244 EeV of energy , which makes it the most energetic cosmic ray since the"Oh My God " ( OMG ) particlein 1991 — the most powerful cosmic ray ever detected , which had an zip of 320 EeV and traveled at more than 99.9 % thespeed of brightness level .
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University ( OMU ) draw the recent cosmic ray in a newfangled subject area that will be write in the journal Science on Nov. 24 . They named the occult speck " Amaterasu " after the sun goddess from the Shinto religion who is believe to have help create Japan .

Cosmic rays from the sun and elsewhere in the universe create colorful “airglow” when they smash into Earth’s atmosphere.
connect : brilliant gamma - electron beam burst ever detected dare account
" When I first discovered this radical - gamy - vigor ( UHE ) cosmic ray , I thought there must have been a mistake , as it showed an vim level unprecedented in the last 3 decennium , " study steer authorToshihiro Fujii , an astrophysicist at OMU , said in astatement .
The scientists are unsure exactly where the UHE ray get from . " Its reaching counselling point back to a void in thelarge - scale structure of the Universe , " the researcher write in Science . This realm has no known coltsfoot , nebulas or other cosmic structures .

It is possible that the cosmic ray originated somewhere else and was bend toward us by magnetic fields besiege a wizard or other monumental object . However , UHE cosmic rays are less potential to be deflected than less - gumptious counterparts , the researchers wrote .
It is also unclear what could have produced such a potent cosmic light beam . The researchers have suggested several potential sources , including supernova explosions , opprobrious holemergers and pulsar .
— Astronomers strike enormous ' roadblock ' carve up the center of the Milky Way from the cosmic ray ocean

— China is building the world ’s large subaquatic telescope to hunt for tough ' touch speck '
— Astronomers identify new class of cosmic explosion brighter than 100 billion suns
But the particle could also fall from an " unknown astronomic phenomenon and novel strong-arm root beyond the Standard Model [ of physics ] , " Fujii said .

Researchers are also still unsure what caused the OMG speck in 1991 .
The team hopes that next - generation observatory will be able to trace the origins of these UHE particles and help reveal what causes them .













