When you purchase through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
The quondam disease - causing fungus ever found has been discover within a museum ’s fossil assembling .
estimate to be 407 million old age old , the newfound fungous plant life pathogen , namedPotteromyces asteroxylicola , is a thready fungus — a eccentric of fungi commonly affiliate withinfections .
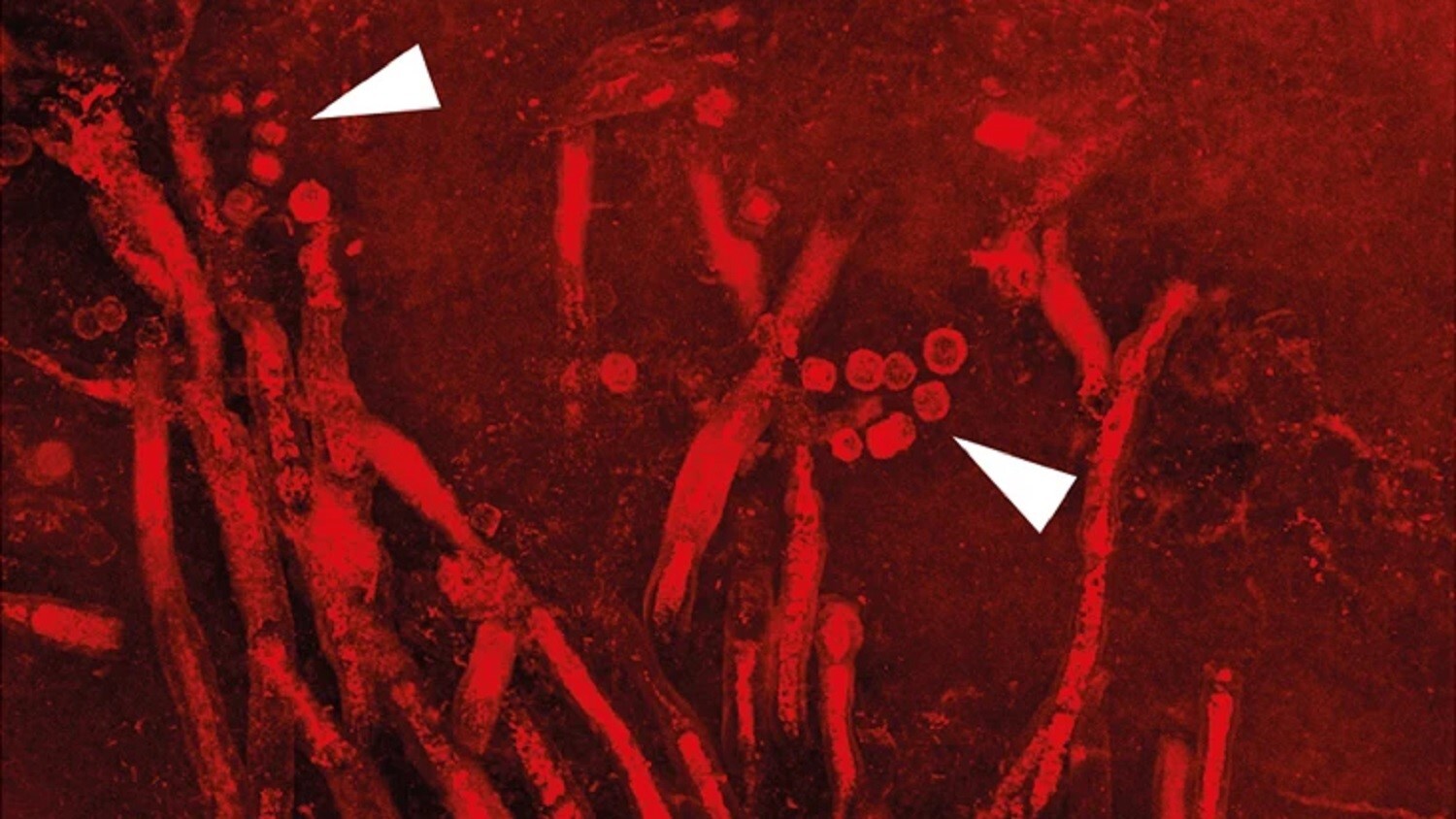
Microscopic image showing the fungus bursting through the walls of the plant.
The parasitic fungus was find growing in an ancient plant calledAsteroxylon mackieiin a specimen held at the Natural History Museum in London . The newfound fungus had burst through the plant ’s verboten bulwark , kill its host ’s cells and take up its nutrients .
The plant appeared to have developed dome - shaped growing in response to the fungus , which research worker enounce point that it was alive while the fungus was assail .
This is the earliest record grounds of a fungous leech causing disease in a plant . The investigator described their finding in a fresh study , published Dec. 1 in the journalNature Communications .
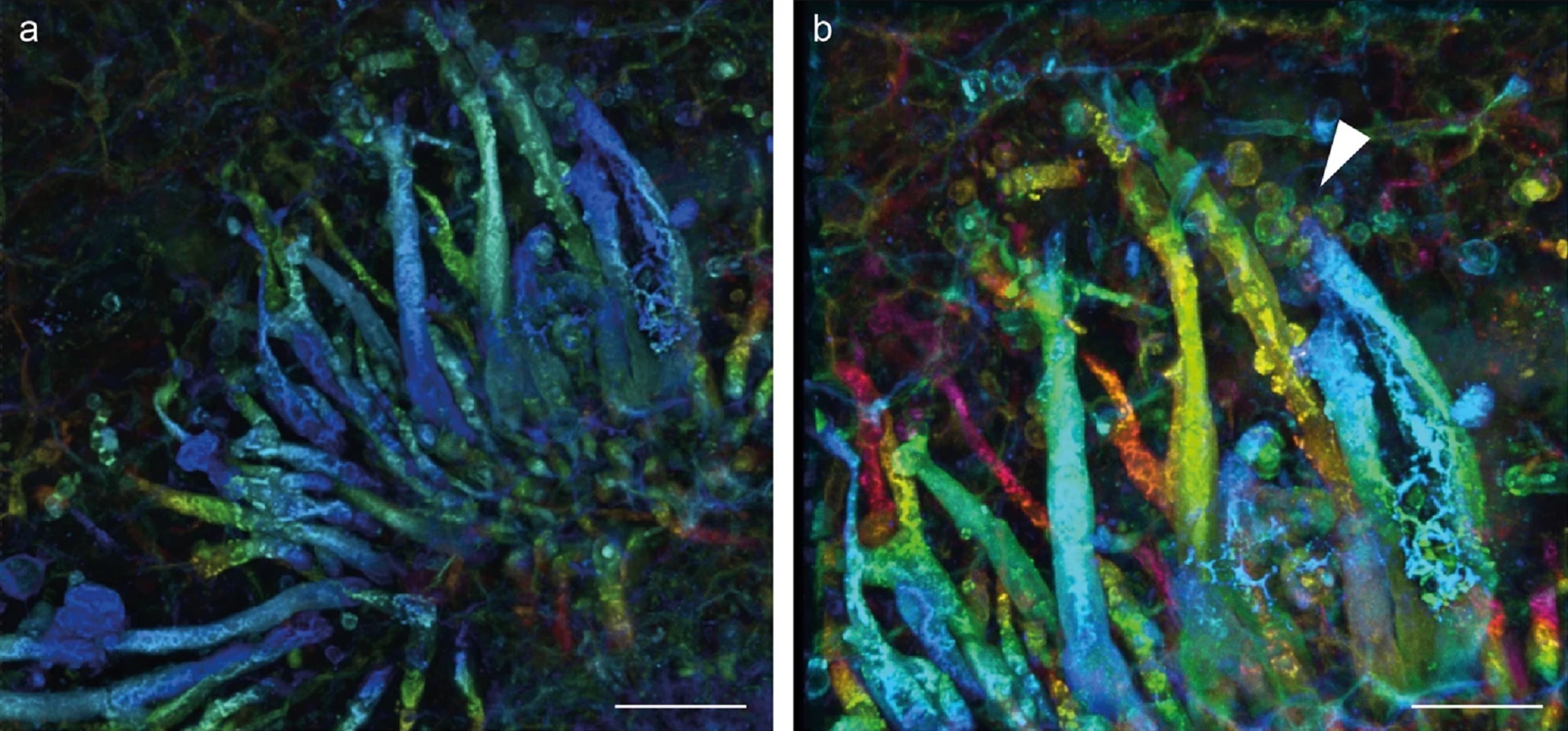
Spores from the parasitic fungusP. asteroxylicola.
While study plant samples under a confocal microscope to make a 3D range , researchers realized one glide at the Natural History Museum London hold back what appeared to be a never - before - seen fungus .
Related : appall photo seizure moment parasitic fungus bursts from vast wanderer ’s body
However , because the appearance of fungi can differ between individuals , it was n’t until another specimen was found that the team was able to confirm it was a young species .
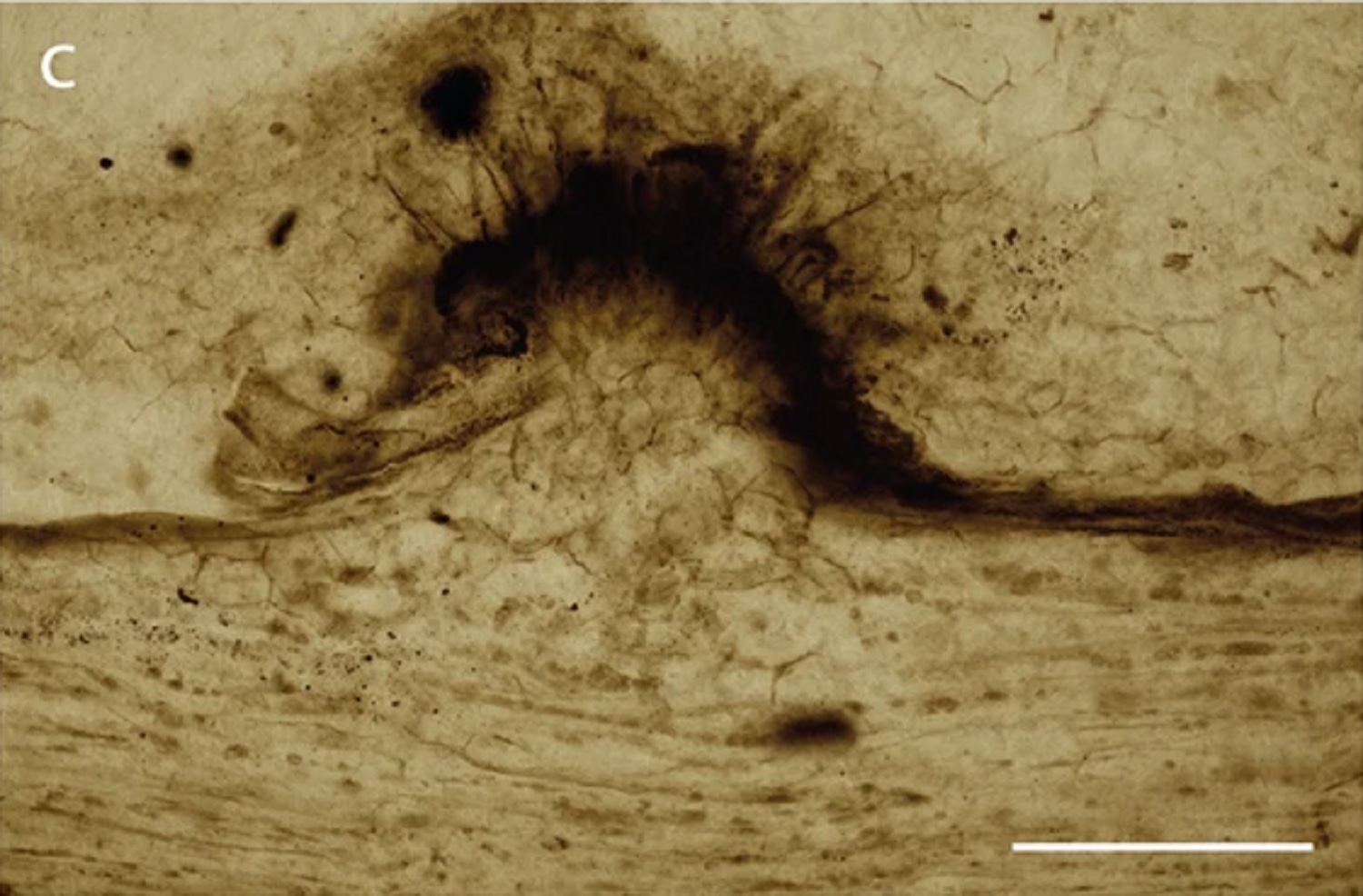
Image showing the plant responding to the parasitic fungus by developing dome-shaped growths.
The second specimen was found in the National Museums Scotland collection . " Working on fogy fungi is not like working on dinosaurs , " lead study authorChristine Strullu - Derrien , a palaeontologist at Natural History Museum London , enunciate in astatement . " When you find a dinosaur , an someone can be described as a fresh species , but for fungi you have to find more than one to be really surefooted you have something alone . I found the first Potteromyces specimen in 2015 , but it took years until I discovered another so that I could trace it . "
Fossil sampling house in both museum were hold from the Rhynie Chert , a layer of rock-and-roll that bear preserved plant , bacterium and fungi , as well as animals from the Early Devonian period ( 419 million to 313 million eld ago ) . The site in Scotland is reckon as vital in see theearly evolution of plantsand associated kingdom Fungi .
— 120 million - year - old ' industrial plant ' ferment out to be radical - rare fossilized child turtles

— ' Once again , innovation and proliferation ended with catastrophe ' : The environmental catastrophe of plants claim over the world
— Mystery of ' living fogey ' tree freeze in time for 66 million years ultimately solved
A divers range of fungous - plant interactions are known to have take place in former mundane ecosystems , and this a la mode evidence further extend what is known about fungous species .

" Although other fungal parasites have been found in this area before , this is the first case of one causing disease in a industrial plant , " Strullu - Derrien said . " What ’s more , Potteromycescan provide a valuable period from which to date the development of different fungus groups , such asAscomycota , the heavy fungous phylum . "
The fungus ' genus is identify after children ’s writer and mycologist Beatrix Potter , who is well know as the author of " The Tale of Peter Rabbit " ( 1901 ) . Potter ’s detailed illustration of fungi and study of their growth were in some event decades ahead of scientific research at the time , according to the statement .














