When you purchase through link on our site , we may clear an affiliate mission . Here ’s how it works .
DNA ’s 3D human body — its twisted ladder complexly curl up into roll and loops — and other features beyond its genetic computer code may influence where " hotspots " of cancer - induce mutations amass .
That ’s agree to a new study of how " genomic topography " impact Crab mutation . Genomic topography broadly refers to elements of the genome beyond the sequence of molecules that make up deoxyribonucleic acid . That include variations in how tightly our DNA is wound and which factor are " activated " in different cells .
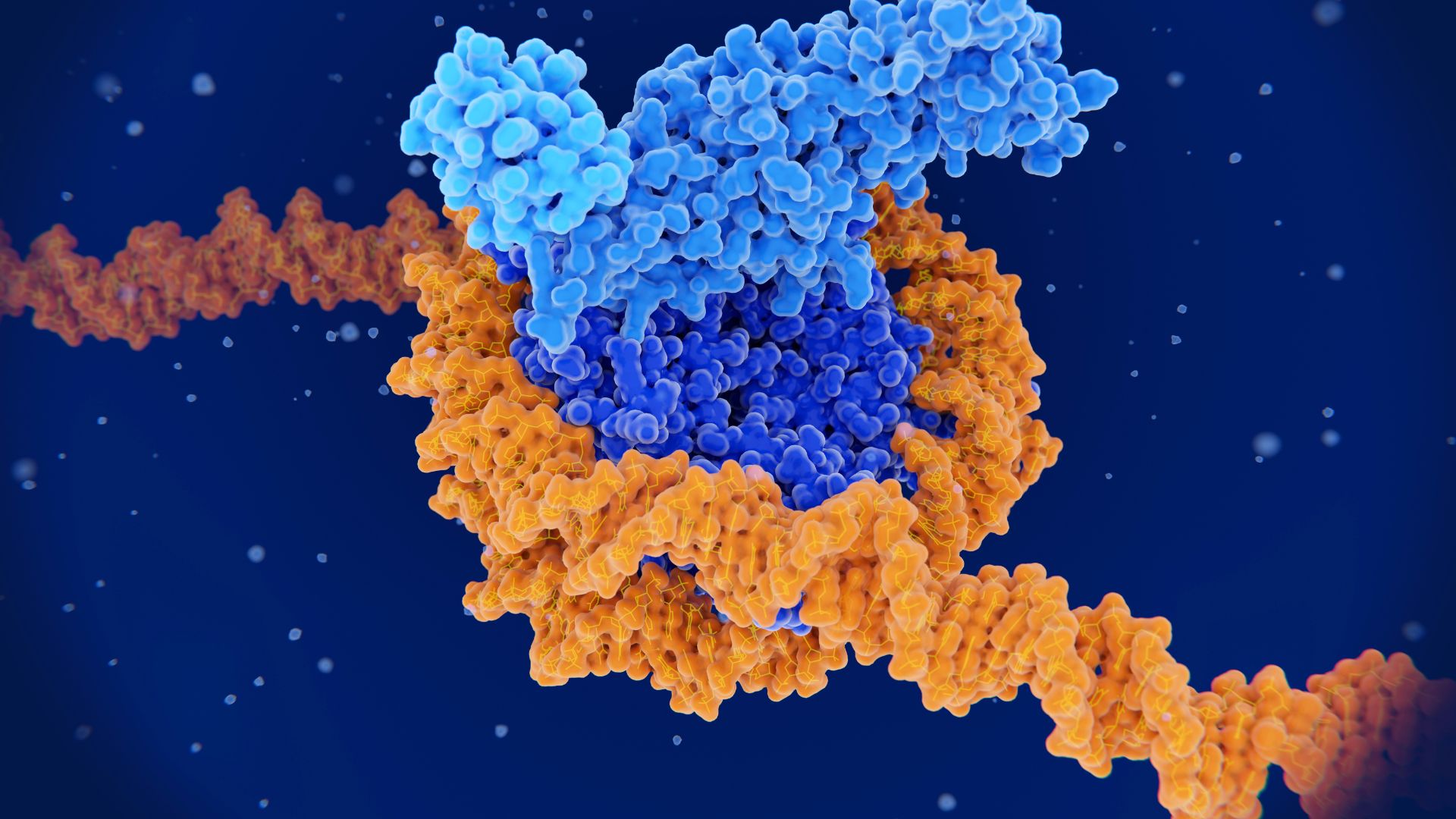
Here, DNA (orange) is shown condensed and tightly wrapped around a histone (blue), a protein that helps keep DNA neatly packaged inside cells.
The cogitation , published in August in the journalCell Reports , catalogs connection between topographical features of DNA and known patterns of cancer - causing mutations across several type of cancer . This granted the investigator new insight into some alcohol - related cancers , and in the futurity , the vast trove of data point could facilitate scientists prevent , realize and treat many different form of cancer .
" It ’s the next level of cataloging of the cancer - specific mutations , " saidDr . Katerina Gurova , an associate prof of oncology at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Institute who was not involved in the study . " But we still do n’t interpret for the bulk [ of the genetic mutation ] why DNA topography plays this persona or that role . "
Related : Bizarre knotty DNA structures linked to cancer in mouse
The subject reckon at mutations embedded within the complete genome sequences of more than 5,000 tumors across 40 Crab types . The team analyzed the influence of 516 topographic features over where these variation cropped up in the genome .
Some of these features link up to when and where sport appear during written text , the mental process of translating DNA intoRNA , which carry genetic information from DNA out into the cell . Others relate to proteins called histones , which deoxyribonucleic acid molecules thread around like a bobbin , and the bodily structure of that wounding - up DNA . Another feature is related to a protein name CTCF , which regulates the 3D bodily structure of chromatin , the complex formed by DNA and histone . CTCF enables DNA to form into highly thickset chromatin loops .
It ’s like " we have a library in every mobile phone , but this program library is machinate in dissimilar manners , " Gurova said , supply that these unlike type of organisational methods are what the researchers mean when they say " topographic " feature film .
The chief goal of the study was to catalog association between different mutation patterns and these DNA features , but the researchers made some interesting observation about specific Cancer .
For example , they discovered that several variation pattern colligate to alcohol consumption seem ahead of time in the process of electric cell comeback , rather than later as most variation do . This mutational pattern was see in mind and neck , esophageal and liver cancer cells . They also get hold that , when looking at a type of resistant cell cancer , some mutations that result in the same changes to DNA ’s " missive " can however be linked to very unlike topographical features , advise they arise for different reason .
— ' Doughnut - form ' desoxyribonucleic acid makes cancer more aggressive
— Does it matter what time of day you get malignant neoplastic disease treatment ?
— CRISPR used to ' reprogram ' cancer cubicle into intelligent muscle in the lab
The researchers made their data point freely useable through a database call in COSMIC , which Gurova say might be useful for developing cancer treatments targeted to specific mutant .

That order , the subject does have some limitations , including that the data on the topographical characteristic were collected from a different set of patient than the data on the mutations in cancer cells , she say . So it ’s potential that the results would be moderately dissimilar if data hardening were collected from the same cellphone .
Future research might take the same coming to link other genetic term to topographic features of DNA , saidFulai Jin , an associate professor of genetics at Case Western Reserve University . And in the realm of cancer , Jin said future employment could further look at patients of different sexual activity or patient role who were exposed to dissimilar surround to see how these factors interact with cancer - causing mutations and DNA ’s topography .
And a major end of succeeding research will be to determine why the investigator found these particular associations , Gurova say . This would deal the question of why and how DNA ’s soma influences how cancer arise .