When you purchase through link on our website , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
A newfangled immune cell - based treatment forglioblastoma , the most aggressive type of brain Cancer the Crab , has show hope in shrinking tumour in the inadequate - terminal figure , allot to two early clinical trials .
The trials test the safety and effectivity of a personalized therapy calledchimeric antigen receptor ( CAR ) T - cell therapy . This involves drawing out and genetically falsify patients ' immune cells , known as metric ton cell , to more effectively recognize and attack tumors once they ’re reintroduced into the body .
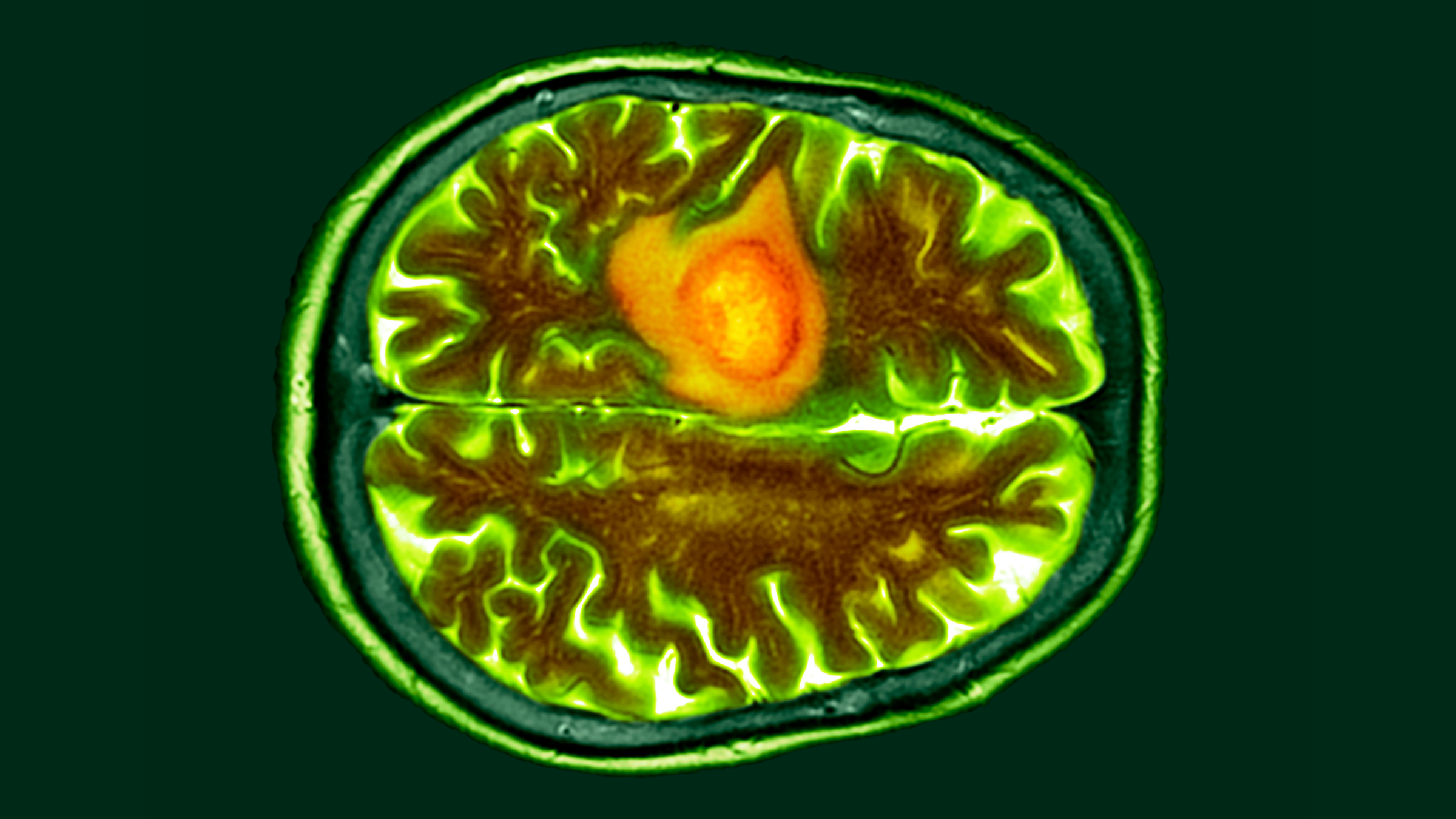
Glioblastomas are the most aggressive form of brain cancer. An example of one of these tumors is shown in the colored brain scan image above in orange.
One of the trials , described in a theme publish Wednesday ( March 13 ) in theNew England Journal of Medicine(NEJM ) , include three affected role with repeated glioblastoma , intend theircancerhad returned following standard radiation and chemotherapy . MT cells from these patients were genetically modify to target two versions of a sensory receptor calledepidermal growth element receptor(EGFR ) on the Earth’s surface of tumor cells .
In the second trial run , published the same day in the journalNature Medicine , researchers used CAR thymine cells to target EGFR and an extra tumor - related receptor , calledinterleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 , in six patient with recurrent glioblastoma .
Related : In a 1st , scientists habituate intriguer immune cells to send an autoimmune disease into remitment
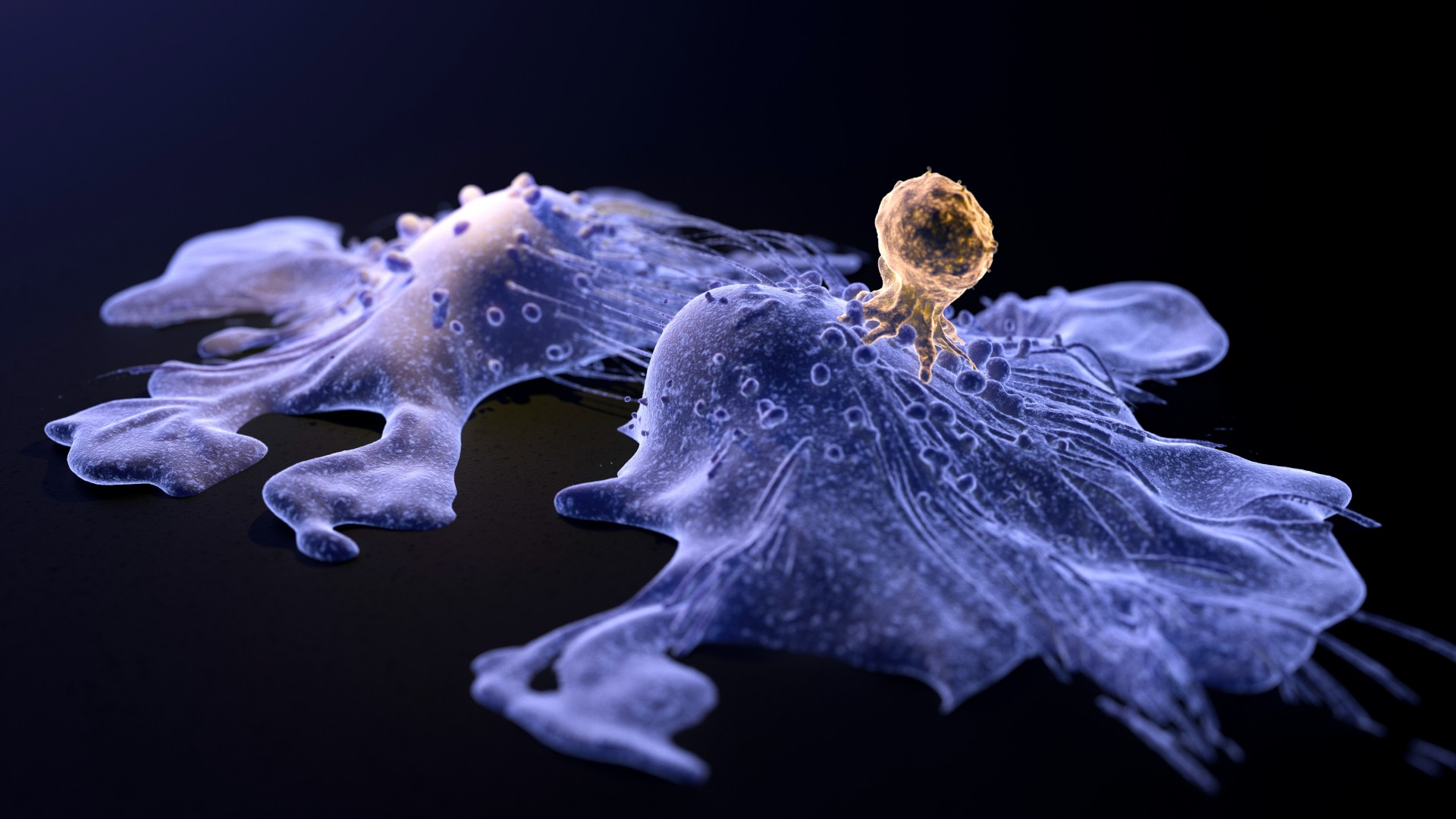
CAR-T therapy is an immunotherapy which involves reprogramming T cells to better attack tumors. In the illustration above, a T cell, in brown, can be seen attacking cancer cells, in purple.
Both run obtain that pushcart - cadre therapy was safe and reduced tumor size in all nine patients . In the Nature Medicine survey , patients saw these decrease within one or two sidereal day , while in the NEJM study they saw them after one to five days . One NEJM patient ’s neoplasm almost totally regressed five sidereal day after a single treatment , while another somebody ’s tumor decreased in sizing by 60.7 % after 69 daylight .
However , these effects did n’t of necessity last . Tumors returned for two patients in the NEJM study , within either 72 days or a calendar month after the initial infusion . The other patient showed no signs of neoplasm recurrence more than 150 day after treatment , although this was the last assessment period of the sketch so it is changeable whether this happen afterward . Some of the reduction seen in the Nature Medicine study have also been sustain for several month , for example up to seven month in one patient role .
Glioblastomas are notoriously difficult to treat , unremarkably relying onsurgery to polish off themas well as chemotherapy and radiation to vote down the cancerous cubicle . Each year , more than 10,000 masses in the U.S.are diagnosed with glioblastoma . Only 6.9 % of them survive beyond five long time after diagnosis and most live for only another eight month .

The new CAR T - cell therapy is still in its early days , with no data yet usable on the long - condition survival rates of these patients . Nevertheless , scientist conceive there is reason for optimism .
The research " lends credence to the possible exponent of CAR - T cells to make a difference in solid tumors , especially the brain,“Dr . Bryan Choi , lead writer of the NEJM field of study and a brain - neoplasm surgeon at Massachusetts General Hospital , toldNature . " It adds to the excitement that we might be capable to move the phonograph needle . "
CART - electric cell therapy has been approve in the U.S. to care for blood cancers , such aslymphomas , some forms of leukaemia and multiple myeloma . However , scientists have struggled to develop the therapy for solid tumors , such as spongioblastoma , as the cells within them often vary in their characteristic , meaning they have more way of fudge theimmune system .

— A teenager ’s Crab is in remission after she received unexampled cadre edited with CRISPR
— Doctors are trying to use CRISPR to crusade malignant neoplastic disease . The 1st trial suggests it ’s safe .
— How close are we , really , to curing cancer with CRISPR ?

The new treatments target receptor that are commonly express by spongioblastoma cells , thus singling them out for death . The NEJM discipline also manufactured T cells that can produce antibody against these sensory receptor , give them a second manner of attack . More datum is required to appraise the foresightful term effect of these new treatments , and trials will need to be conducted in larger , more diverse groups of patients to determine their broader relevance .
" These results are exciting , but they are also just the beginning — they tell us that we are on the right track in pursue a therapy that has the potential to change the mentality for this intractable disease,“Dr . Marcela Maus , co - senior author of the NEJM study and director of the Cellular Immunology Program at the Mass General Cancer Center in Massachusetts , say in astatement .
Ever question whysome hoi polloi build muscle more easily than othersorwhy freckles come out in the sun ? institutionalise us your question about how the human body works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject business line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your motion answered on the website !

Scientists just let out a single corpuscle that may treat rare , devastating mitochondrial disease
Acne vaccine : data-based shooting for unwashed pelt condition reach clinical trial . Here ’s what you need to know .
The perpetual surveillance of advanced living could aggravate our wit function in means we do n’t fully understand , disturbing subject field intimate





