When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate military commission . Here ’s how it exercise .
scientist may before long be able to detect the most mysterious entity in the universe using a fleet of next - contemporaries satellites , a new theoretical report advise .
Dark matter — a ill understand substance that does not breathe , suck up or speculate light but exerts a clear gravitational influence on other thing — eclipse the universe . Despite being more than five clip more abundant in space than ordinary topic , colored subject ’s composition and properties remain totally unknown .
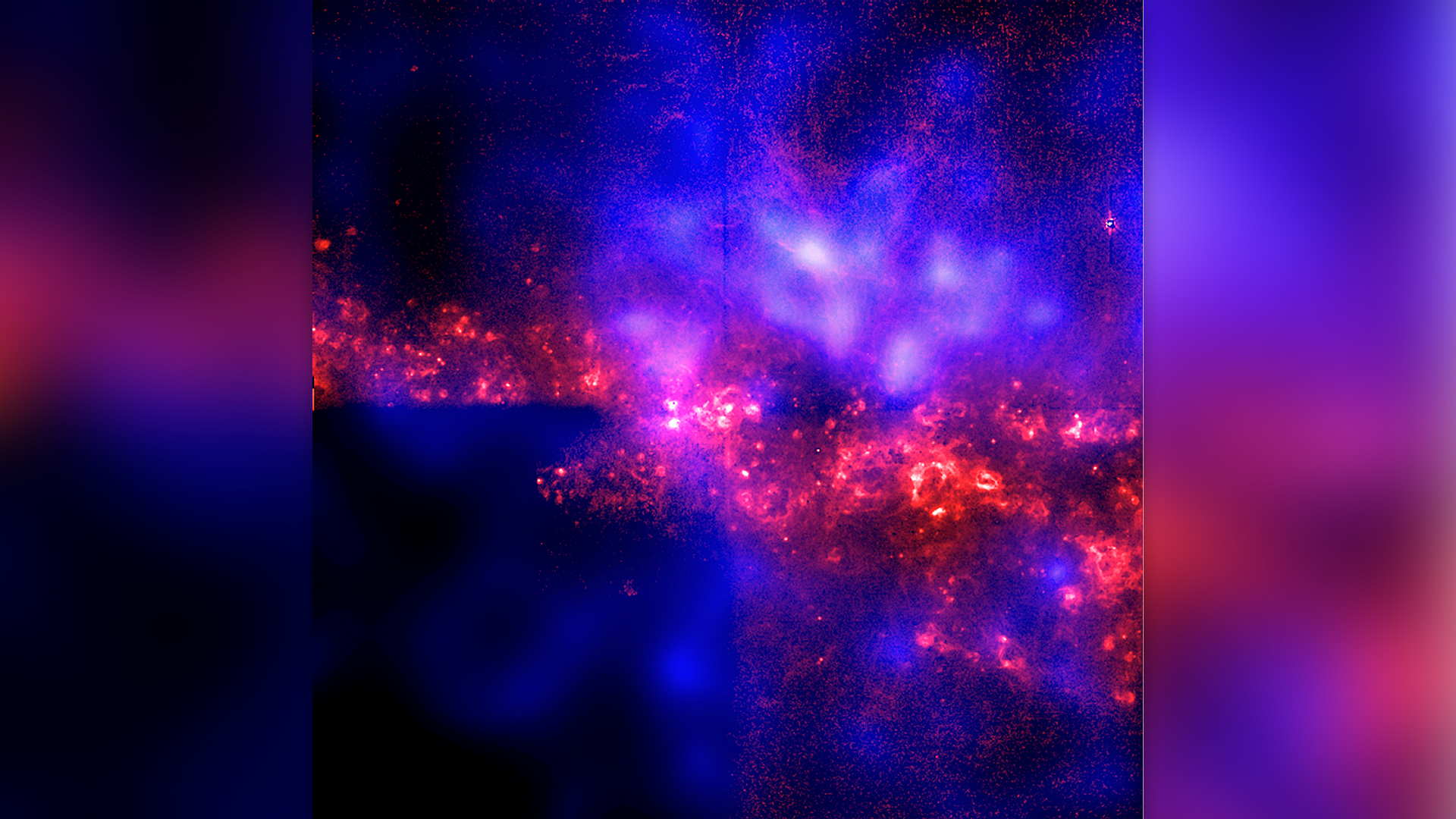

An X-ray image reveals the halo of gas at the edge of a MIlky Way-like galaxy. Such haloes are thought to be hotbeds of mysterious, invisible dark matter.
To address this job , Hyungjin Kima theoretic physicist at the German Electron Synchrotron ( DESY ) accelerator nub , proposed look for dingy affair particles usinggravitational wavedetectors — legal document designed to evaluate subtle riffle in the textile of space - time that were first predicted by Albert Einstein .
Dark matter as waves
There are many hypotheses about the nature of dark subject particle , which accumulate in immense quantities to form so - calledhalos in galaxies . In the new paper , issue in December 2023 in theJournal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics , Kim sham that these subatomic particle may be extremely wanton , as many democratic theories of dark matter predict .
associate : Physicists want to apply gravitative waves to ' see ' the outset of time
" Ultralight speck appear usually in many beyond - the - Standard - Model theory , " Kim tell LiveScience via electronic mail . Some of these corpuscle are " perfect candidates '' for dark matter , raising some interesting implications for how the elusive entity might carry , he added .
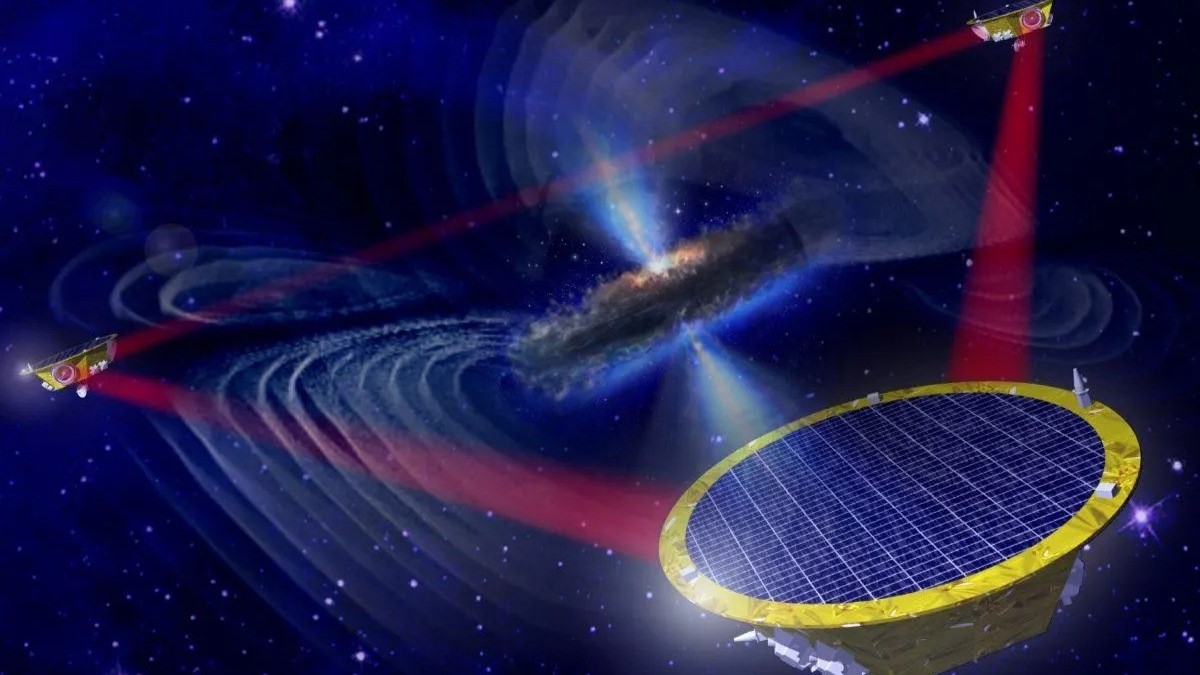
An artist’s impression of the space-based LISA gravitational wave detector, which was just approved for construction by the European Space Agency.
" Unlike other ' particle ' dark issue candidates , ultralight dark subject molecule acquit more similarly to classical [ electromagnetic ] moving ridge , " Kim sound out .
The undulation property of dark matter could go to unexpected behaviors . In particular , recent theoretical studiessuggest that the density of dark matter within a galactic halo should undergo random changes , jostling entire wandflower and potentially provide subtle clue about sorry matter ’s make-up .
" Imagine waves in the sea ; we see all the time there are fluctuations at the airfoil of the sea , and it evolves in unpredictable ways , " Kim said . " The same would happen in the ultralight dark subject annulus , ” with the lead fluctuation potentially extending millions of prison term the length between the Earth and the sun , Kim added .

If dark issue is ultralight , and if it indeed behaves like a undulation , then scientist could potentially detect its motion with gravitative wave sensing element .
Gravitational wave detectors come to the rescue
According to Einstein ’s theory ofgeneral relativity , gravitative waves are ripples in the cloth of space - fourth dimension .
When such a undulation passes through a gravitational waving detector , it alters the geometry of the space inside , temporarily changing the distance between two mirrors or other standardized object lay inside the detector . This minute change enable scientists to detect the gravitational wafture ’s presence .
In his subject area , Kim suggests this length could be altered not only by a gravitational undulation but also by a go dreary matter fluctuation , which could attract the mirrors with its gravitative orbit much like Earthattracts celestial bodiestraveling around it .

" These wavering haphazardly move within thesolar organization , and continuously bombard gravitative wave detectors , " Kim said .
To see if modern gravitative wave detectors could theoretically find the influence of ultralight dark matter , Kim bet how coloured matter atom of deviate size might perturb outer space - time . Kim had to search a wide compass of mass — from about 16 to 28 guild of magnitude smaller than the mass of an electron .
His theoretical analytic thinking exhibit that for all these quite a little , subsist detectorssuch as the Laser Interferometer Gravitational - Wave Observatory ( LIGO ) , which help bear witness the cosmos of gravitational wave in 2015 , would not be able to detect dark matter fluctuation because their sensitivity is too downhearted .

However , there are several projects for futuregravitational wafture detectors that will be located in distance , and the distance between their satellite will not be several miles , like the distance between the mirror of LIGO , but around a million times bigger . If this aloofness variety even by a small fraction , the order of magnitude of the change should be so turgid that sullen matter ’s influence should be measurable .
" What I found is that the dark matter fluctuations bombardment could leave a distinctive signal in gravitational wave detectors , and potentially future space - borne detectors might be able to test the hypothesis of ultralight dark thing , " Kim said . " My proposal utilize succeeding space - deport gravitative wave detectors , such asLaser Interferometer Space Antenna ( LISA ) . "
— ' We do not understand how it can exist ' : Astronomers thwart by ' almost unseeable ' dwarf galaxy that upend a coloured issue hypothesis

— One of the close galax to the Milky Way is hide out a 2nd galax behind it , new enquiry reveals
— Hubble Telescope beguile a Galax urceolata ’s ' forbidden ' brightness level in arresting young image
With LISA presently scheduled to set up in the mid-2030s , this theory may be more than a ten away from being testable . However , Kim added , in the meantime there may be other ways of detecting dark matter ’s influence on space - fourth dimension .

" I am currently look into the prognosis of rapidly rotatingneutron starsas another way to probe such variation , " he said .












