When you purchase through link on our web site , we may make an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work on .
A controversial novel study has spark concern that the ozone yap above Antarctica is not retrieve as tight as we cogitate it was , and may even be getting bigger . However , many experts who were not involved in the study have rejected those call , criticize the quality of the enquiry .
The ozone stratum is a section of Earth ’s atmosphere between 9 and 22 naut mi ( 15 and 35 kilometers ) above the airfoil , where there is a high concentration ofozone — an oxygen particle variant with three molecule alternatively of the usual two . This layer blocks out harmful levels ofultraviolet raysfrom the sun that could otherwise cause serious scathe to life , include humankind .
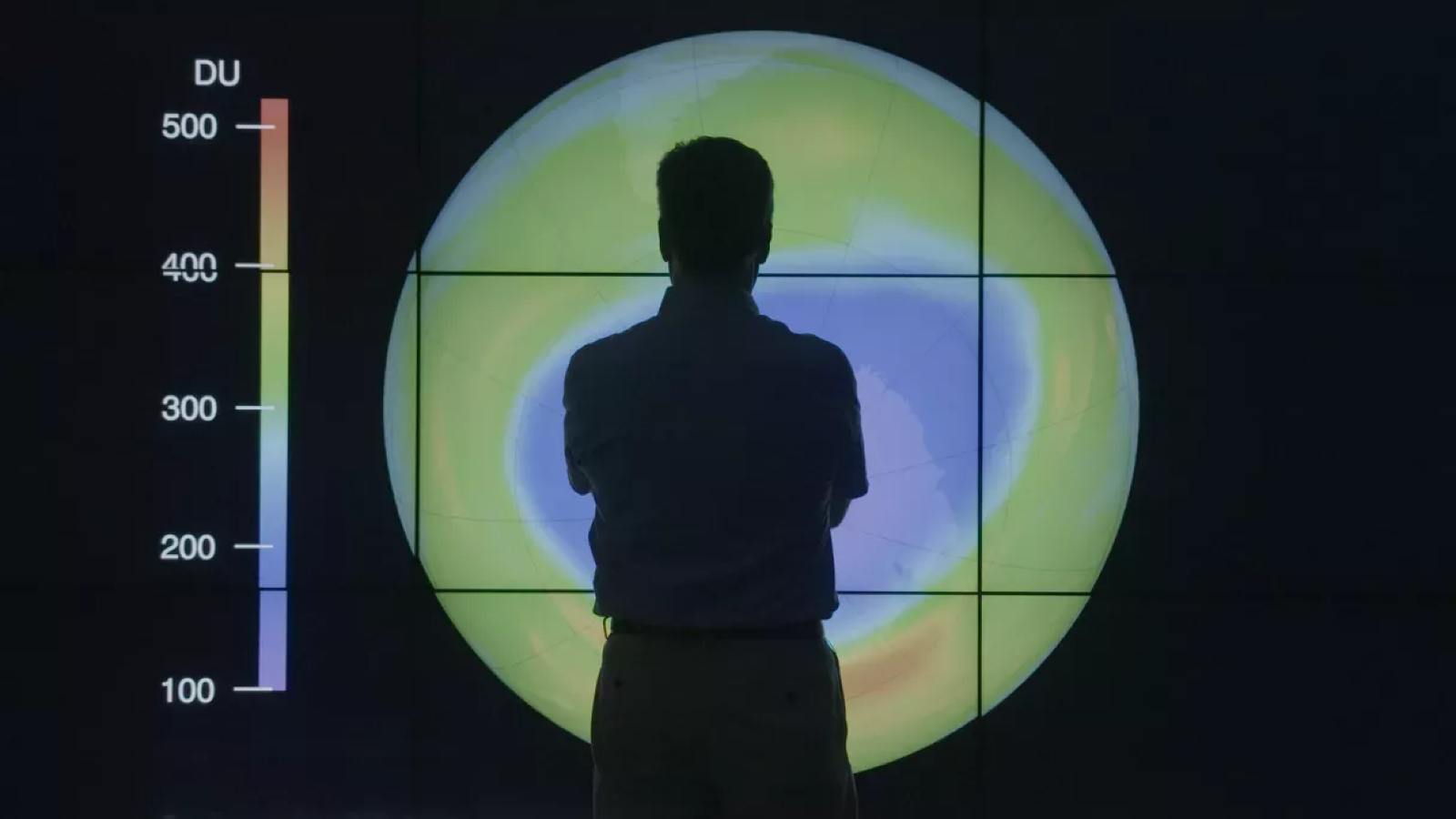

Experts have criticized a new study, which has fueled speculation that the ozone hole above Antarctica may not be recovering as expected.
In the mid-1980s , scientists began to observe that expectant maw in the ozone layer were appearing above the North and South pole as a result of CFC ( CFCs ) , which break down and react with ozone , thus splitting the mote and decreasing ozone levels . In 1987 , world regime link up to sign the Montreal Protocol , which would blackball the use of CFCs that had , until then , been used hard in aerosol container cans , packing materials and refrigerators .
The ozone holes have hang in , particularly aboveAntarctica , due to hover CFC floor and increasingly erratic climate conditions . However , they are diminished than they used to be and scientist have long expected that the hollow will finally to the full recover . In January , aUnited Nations reporton ozone depletion revealed that ozone layer are on track to repay to pre-1980 floor by 2045 in the Arctic and 2066 in Antarctica .
However , the controversial raw study , publish Nov. 21 in the journalNature Communications , suggests that the concentration of ozone in Antarctica ’s ozone mess is fall . The unexampled newspaper sparked a wave of stories from major news outlets claiming that the " ozone hole may not be recover at all " and may even be growing . However , many expert have argue that the study ’s findings are dubious and that the lead coverage is very shoddy .
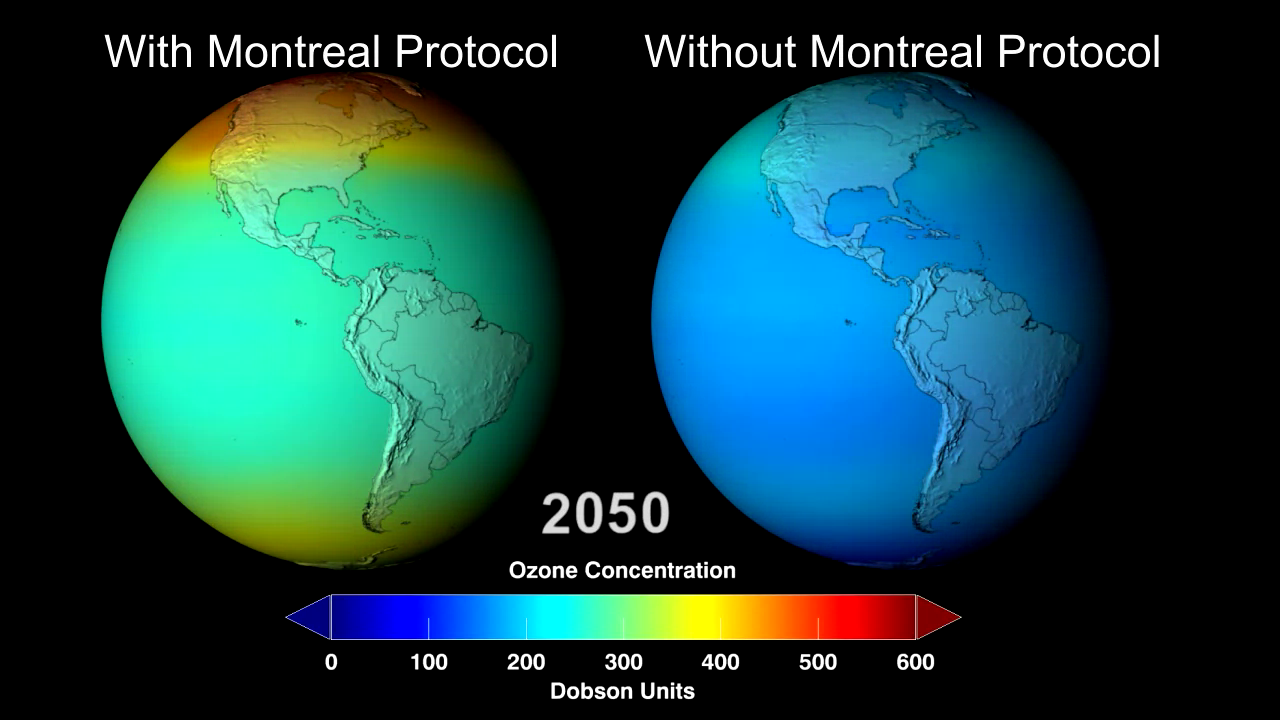
If world governments had never banned CFCs then most of the world’s ozone could have disappeared by 2050.
bear on : Claims of raw ' tropic ozone golf hole ' raise disceptation
The subject analyzed the tightness of ozone at the center of Antarctica ’s ozone hole between 2001 and 2022 and found that the engrossment of ozone at the heart of the gob had decreased by an norm of 26 % during this time .
However , other ozone expert are not at all convert by the final result or the methods used to get them .
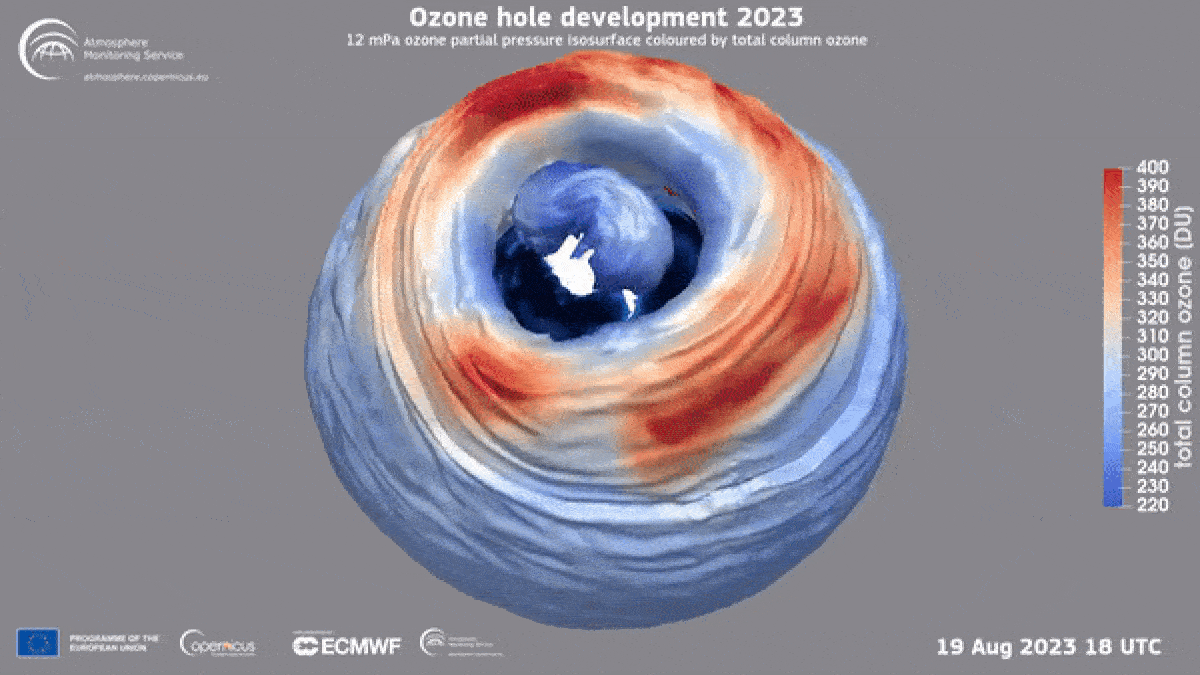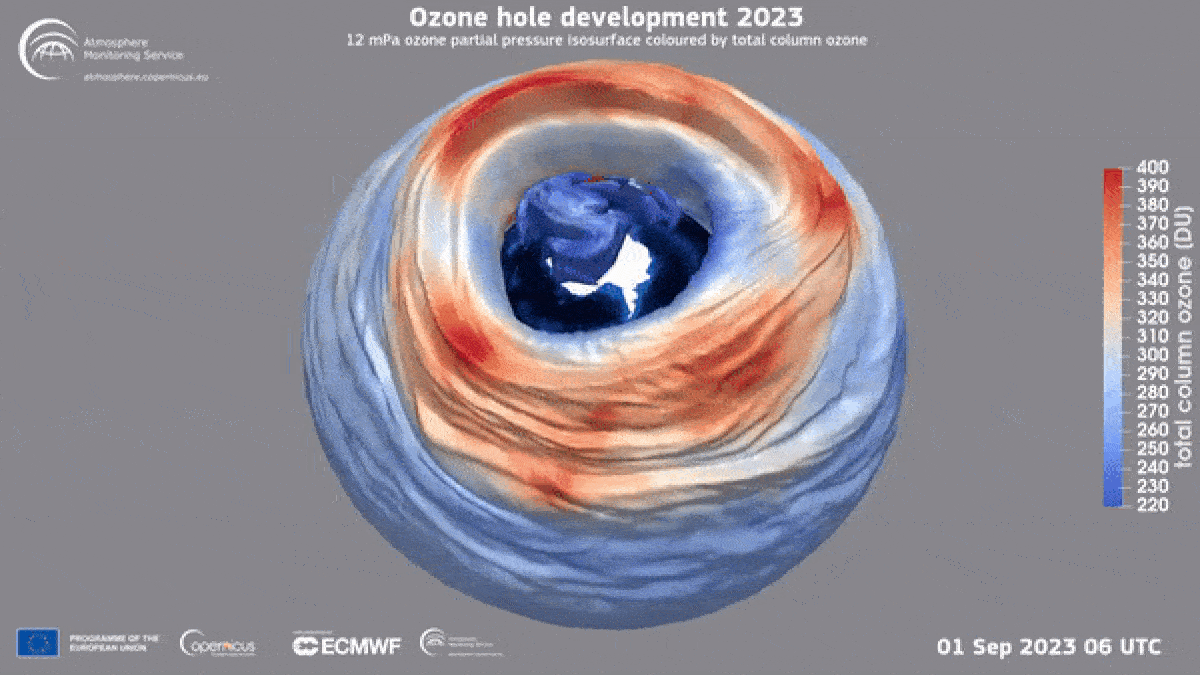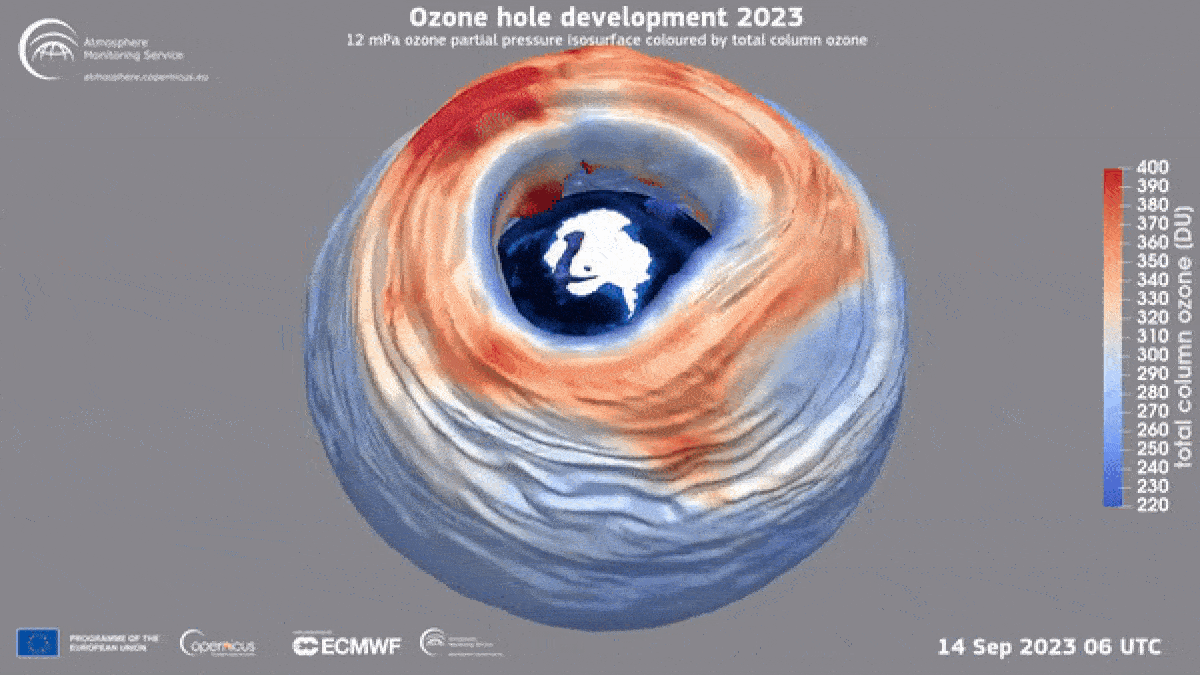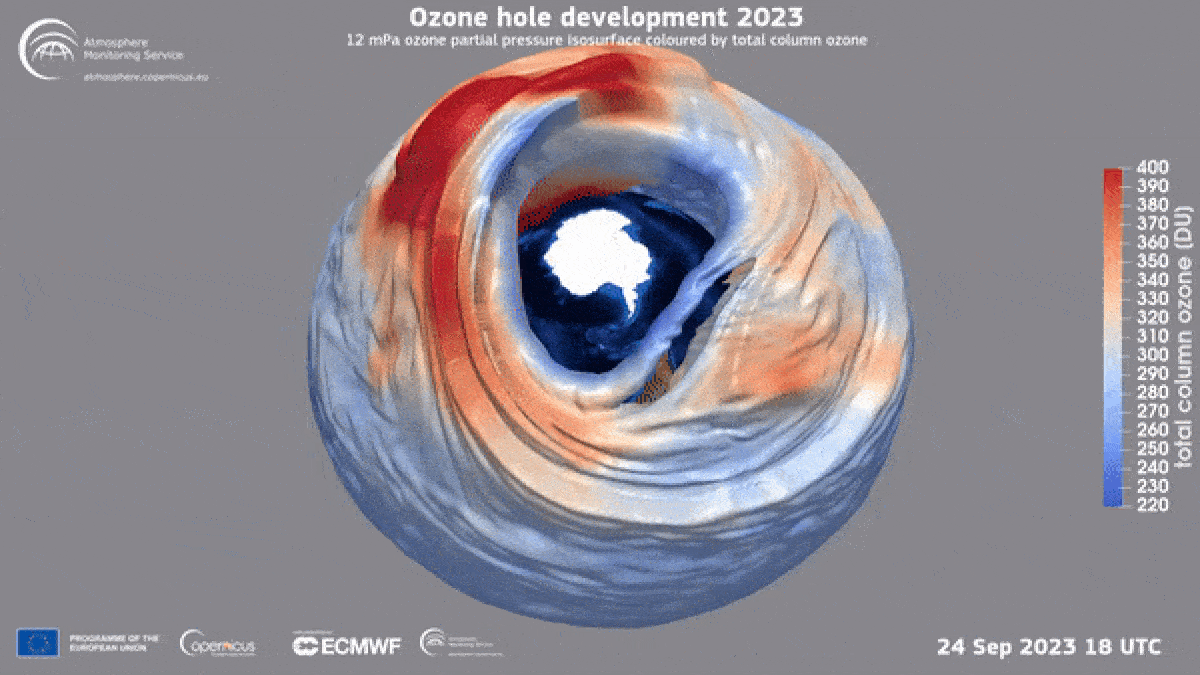
This year’s ozone hole was unusually large but that does not mean that ozone hole recovery has stalled, experts say.
division of the paper are " terribly unclear " and " wildly speculative , " and despite the researchers ' title , the study " recite us nothing new,“Susan Solomon , an atmospheric scientist at MIT who was part of the squad that first connect ozone hole to CFCs in 1986 , told Live Science .
The biggest job with the new paper is that it does not properly answer for for why ozone concentrations have lessen in late years , Solomon said .
Since 2020 , the size of the ozone hole hasincreased year over year , with thelargest opening occurring this yr . These outstandingly great holes are the consequence of a telephone number of roll in the hay factors , includingthree consecutive years of La Niña from 2020 to 2022 , which created colder air around Antarctica , making it voiceless for ozone to form ; and themassive wildfires in Australia during 2020 , which released particulate that run through ozone . This twelvemonth ’s extremely large hole has also been attribute towater vapor injected into the upper atm from Tonga ’s underwater eruptionin January 2022 .

The ozone hole was unusually small in 2002 but this data was omitted from the new analysis, which has helped to skew results.
But the authors do not explicate why the " past few years have been quite unusual , " which makes it seem like there is some unknown factor that is confine ozone recovery when , in reality , there is not , Solomon said . " This is a large , big bargain " and is " very disappointing , " she added .
The researcher also select to omit datum from 2002 , when ozone levels were unusually gamy , and 2019 , which hadone of the small ozone holes on record . The research worker argue that these anomalousness would below the belt skew the upshot , but other scientist have criticized this determination , specially debate that the late anomalous years were still included .
" It is questionable how the authors can remove 2002 and 2019 from the record but not 2020 - 22 , given that all of these geezerhood have been shown to be dominated by very special and rare events,“Martin Jucker , an atmospherical scientist at the University of New South Wales in Australia , enjoin in aScimex assertion . " Including those events would probably have nullified any foresighted - terminal figure negative trend in ozone tightness . "

Both Solomon and Jucker also believe that the metre period analyzed in the Modern study is too short , which has given too much weighting to late years and produced unrealistic resultant role .
pertain : Ozone - destroy CFCs could make late-21st - century return
In addition , the new study also focuses only on the ozone concentration at the heart of the ozone hole and not on wide ozone concentration levels , which do not severalize the whole story , Solomon say . Without providing any model for how these central concentrations affect wider ozone absorption , the study provide little information that other researchers can follow up on , she added .

— Massive ' proton aurora ' boom a 250 - mile - wide-cut hole in Earth ’s ozone bed
— SpaceX garden rocket keep tearing blood - red ' atmospherical holes ' in the sky , and scientist are concerned
— Falling metal blank junk is change Earth ’s upper atmosphere in ways we do n’t fully understand

The metre of year the ozone golf hole data comes from is also problematical , Solomon said . The researcher focused on data from October and November , when ozone holes reach their maximal size , which is tempt by a chain of mountains of factors . If the team wanted to meditate ozone recovery , then using data point from September would have been a good point of comparison , Solomon say .
As a outcome of these oversights and skip , the paper can not be relied upon to infer much about global ozone convalescence trends , Solomon said .













