When you purchase through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
" Spacecraft dust " from defunct satellites burning up in Earth ’s atmosphere could soften our satellite ’s magnetic bailiwick , a controversial young paper suggests .
In the worst - guinea pig scenario , the unchecked enlargement of commercial orbiter " megaconstellations " revolve Earth , such asSpaceX’sStarlinknetwork , may give enough magnetized dust to cut our planet ’s protective shield in half , potentially lead to satellite disasters and " atmospheric baring , " the paper ’s author tell Live Science .

A new paper suggests that pollution from falling space junk could irreversibly alter our planet’s magnetic field. But not everyone is convinced.
But is this effect really potential ? Other researchers are skeptical of the paper ’s title , though they all agree on one thing : there ’s an urgent demand to measure the plate of the problem .
Private satellites presently in orbit are arapidly grow cephalalgia for astronomersdue to their tendency tophotobomb cosmic imagesandinterfere with radio telescopes , as well as the increase peril ofcollisions with other spacecraft . But the actual scourge they pose may be what happens to them when they die .
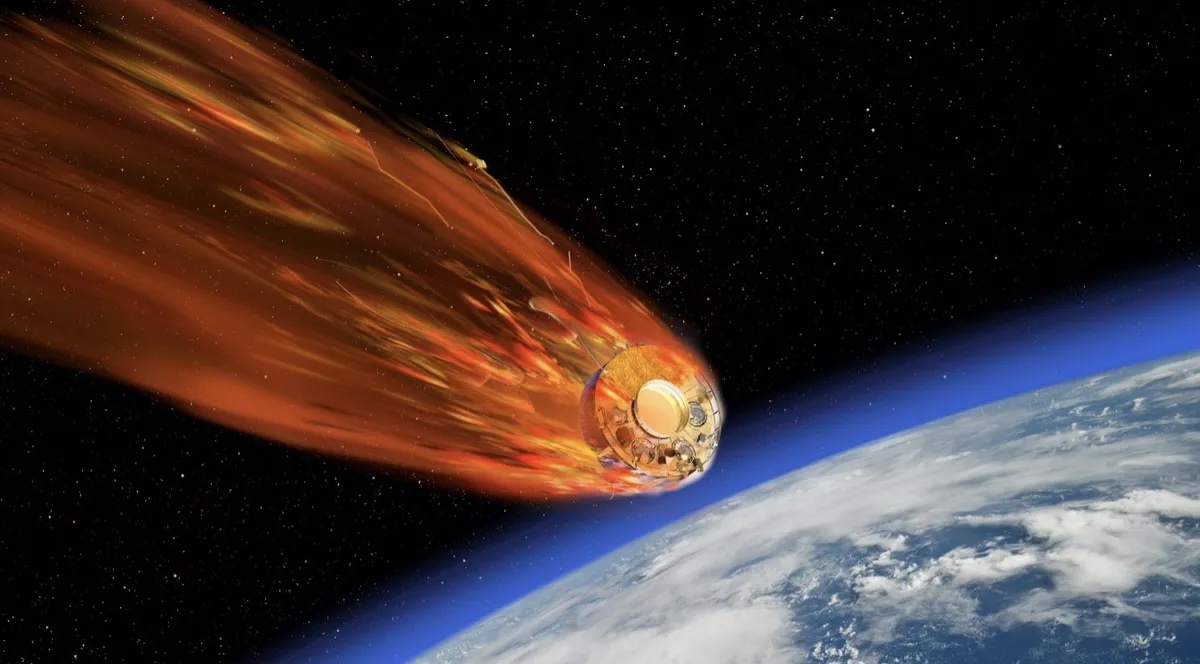
When spacecraft end their missions , most aredeorbited and burned up in Earth ’s atmosphereto minimize the amount ofspace junkcircling our planet . However , as they fall apart in flames , the death spacecraftlitter our upper atmosphere with vaporized metal pollution .
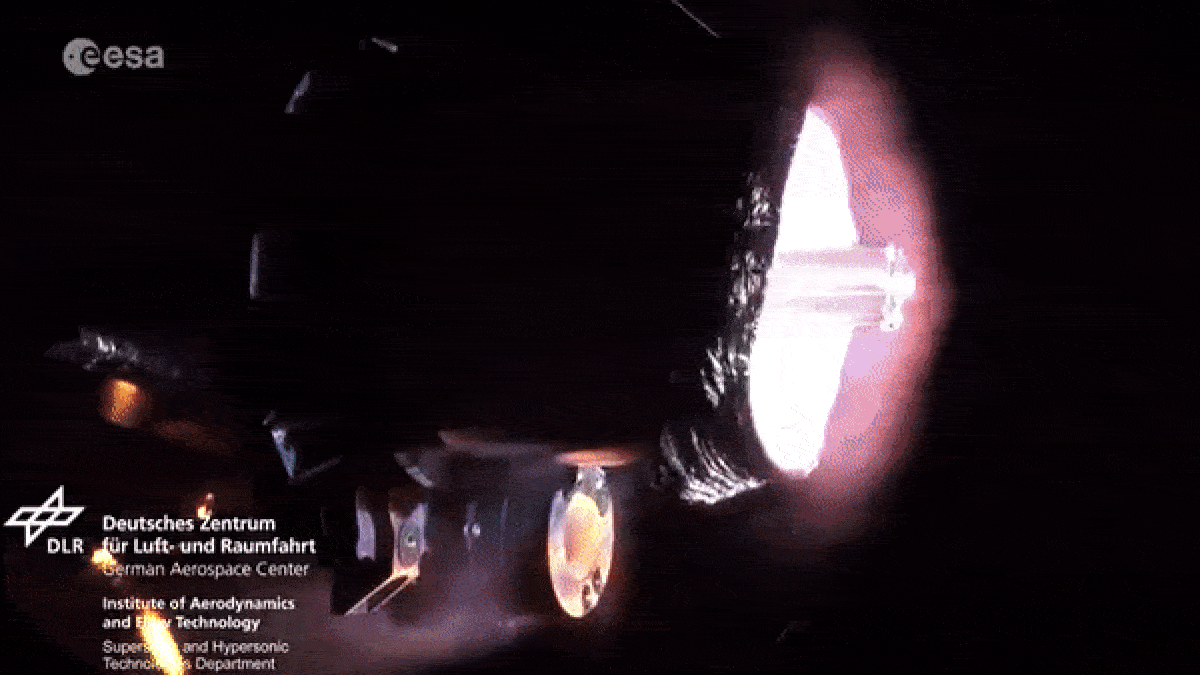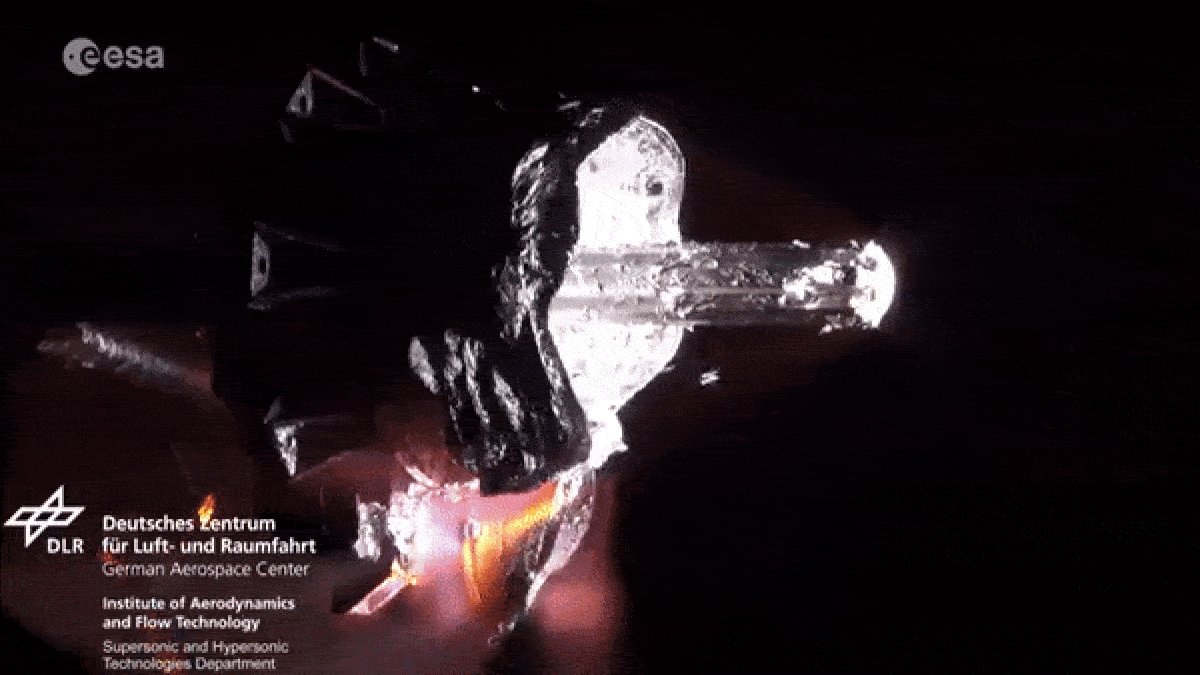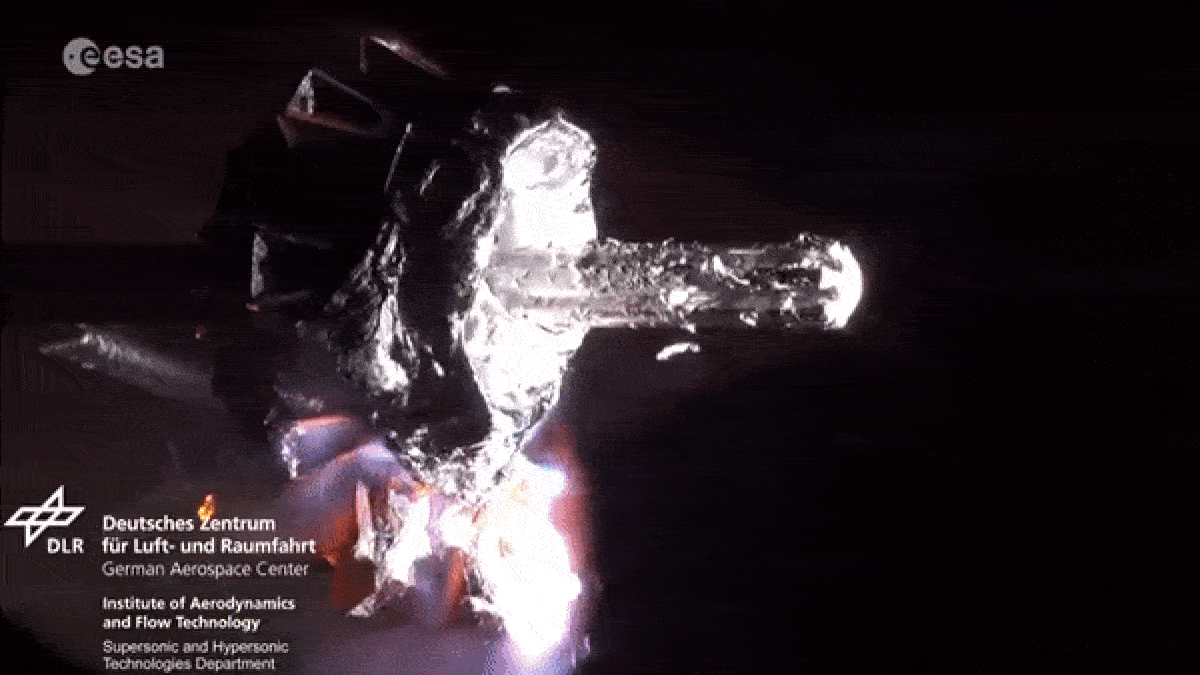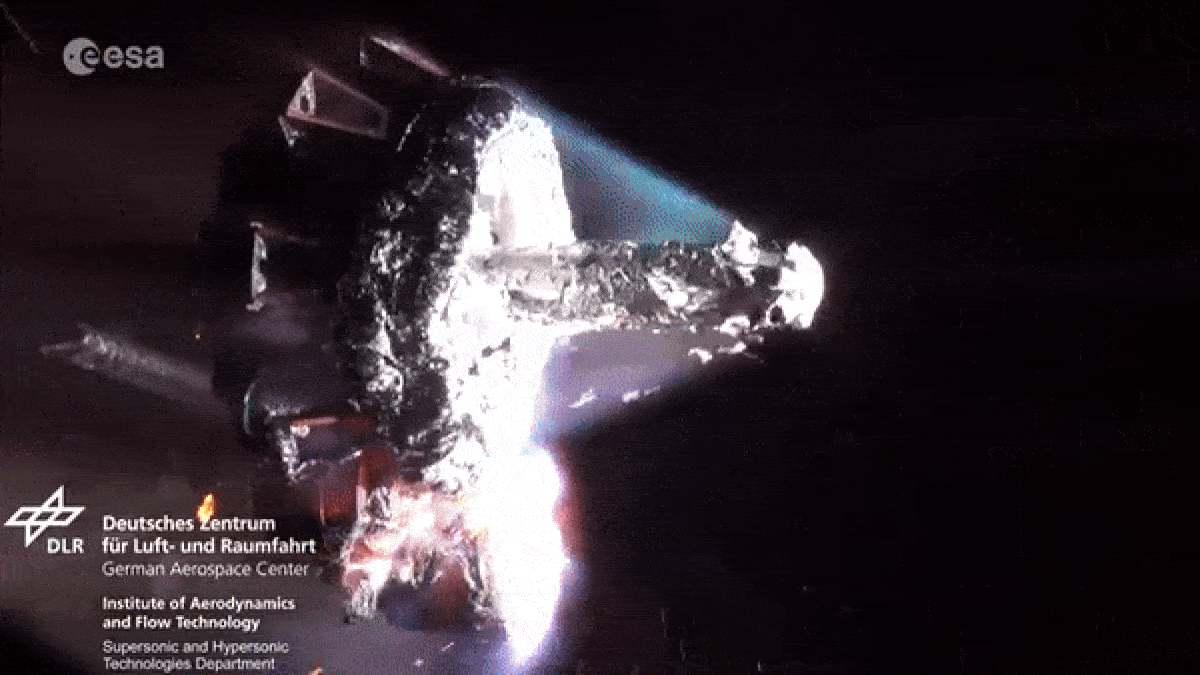
As spacecraft burn up during reentry they release metallic particles into the upper atmosphere.
Related : Sci - fi inspired tractor balance beam are existent , and could solve a major blank junk problem
In the new theoretical paper , uploaded to the pre - print databasearXivin December 2023 but not yet peer - reviewed , Sierra Solter - Hunt , a doctorial candidate at the University of Iceland , proposed that this atmospherical spacecraft dust may compromise the magnetosphere — the part ofEarth ’s magnetic fieldthat expand into blank space and protects the atmosphere from solar radiation .
Solter - Hunt is concerned that if orbiter megaconstellations evolve as planned , the amount of dust they release may create a magnetized shell that could restrict the magnetosphere ’s reach .
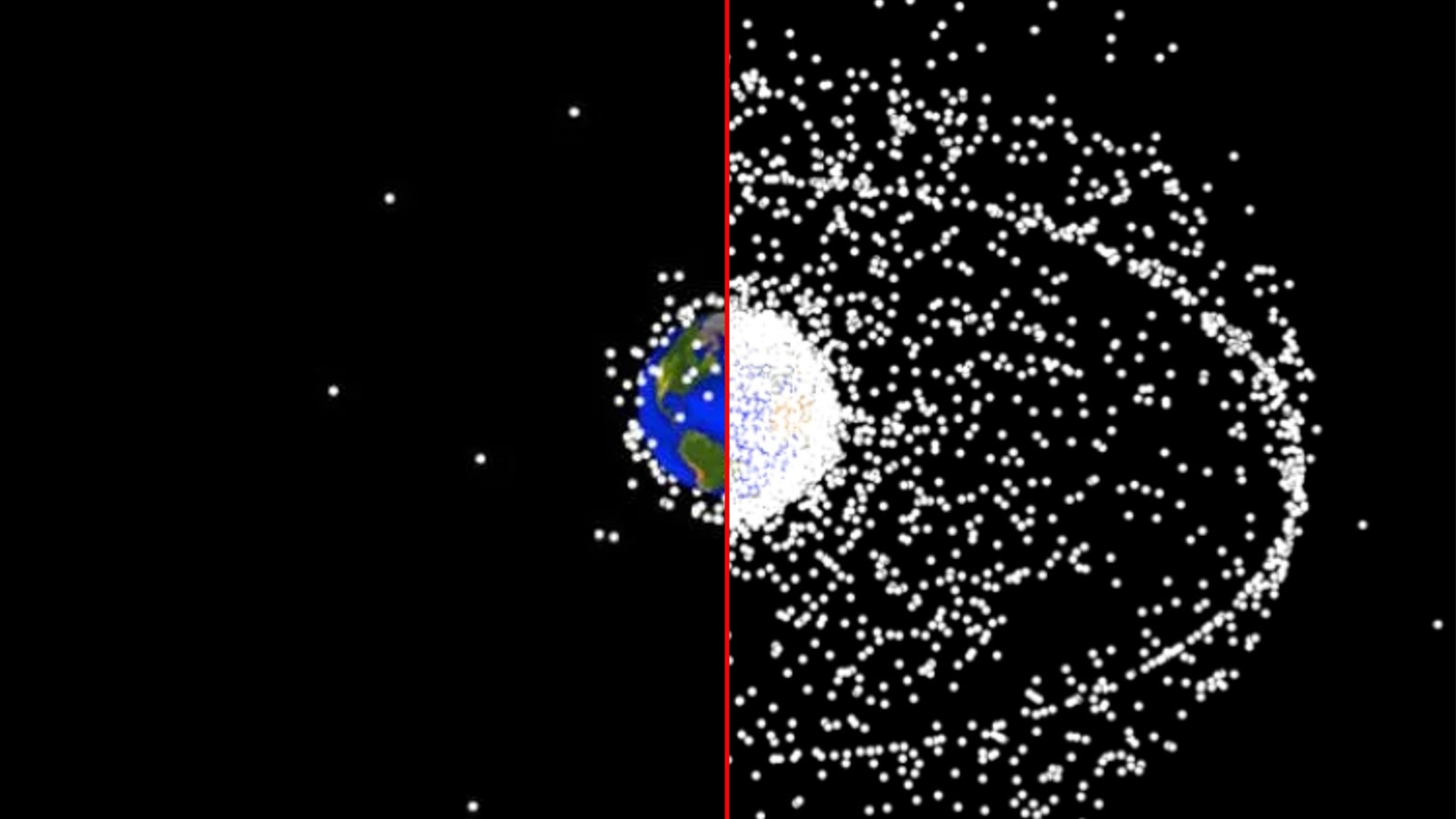

There is much more space junk orbiting Earth today (right) than there was at the dawn the of space age (left).
" I was shocked at everything that I found and that nobody has been studying this , " Solter - Hunt told Live Science . " I think it ’s really , really alarming . "
Accumulating dust
We currently have no agency of monitoring the amount of spacecraft dust in the standard atmosphere , but based on the amount of quad junk that has already burned up on reentry , we could have increase the amount of metal particulate matter in the skies by a million - fold since the start of the distance age , Solter - Hunt said .
And Solter - Hunt figure between 500,000 and 1 million individual satellites could orbit our planet in the coming decade . When all these satellites eventually fall to Earth it could dramatically increase the amount of spacecraft junk in the ambiance to billions of times its current level , she order .
Related : How many satellites revolve Earth ?
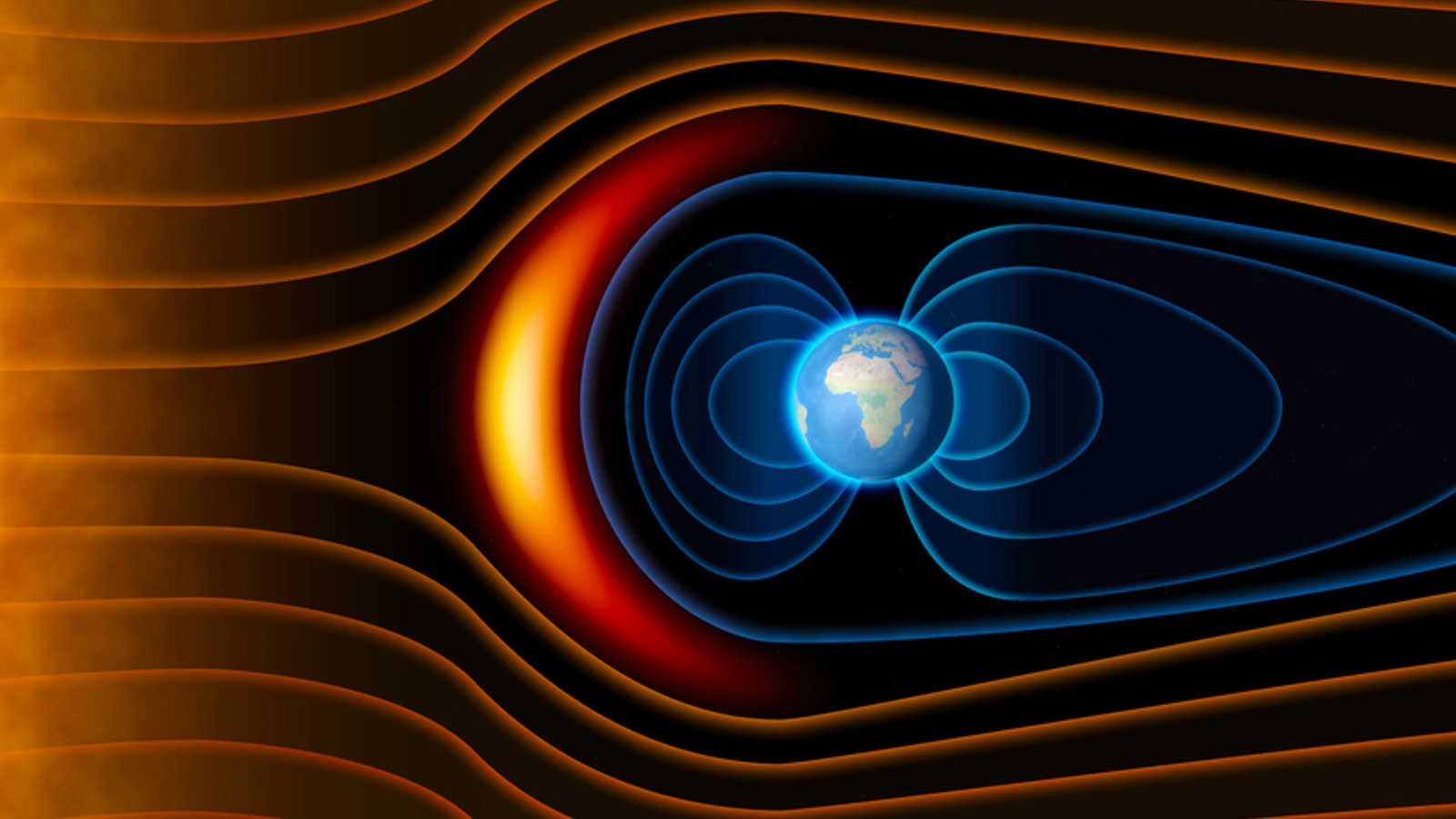
The magnetosphere extends deep into space and protects us from radiation and solar storms.
It is presently unclear where all of this space vehicle dust will eventually end up but Solter - Hunt thinks that it will probably settle in the upper part of the ionosphere — a region of the atmosphere between 50 and 400 miles ( 80 and 644 klick ) above the surface . " And it could just stay there constantly , " she append .
Magnetic shielding
If all these proposed satellites go up in flame , the ensue spacecraft debris could create a " consummate conductive net around our satellite " that could be open of carrying an galvanising charge , Solter - Hunt enounce . If this materialize , the magnetosphere , which unremarkably prolong thousands of international nautical mile into space , would be " distort to stay under the conducting stuff , " fundamentally circumscribe its stretch to the upper ionosphere , she lend .
A reduced charismatic field could scupper satellites to high spirit level of irradiation and solar storms , which couldknock them out of the sky , Solter - Hunt said . " It ’s a real Catch-22 for satellite party , " she added . " They could be soften the magnetosphere with what they ’re doing , which in act puts themselves at risk . "
But even if the magnetosphere does n’t recoil , the increased levels of spacecraft dust could still make it heavily for rockets to launch new satellites and other spacecraft into place , Solter - Hunt said . This is because the magnetic particles could interfere with onboard electronics , she sum up .
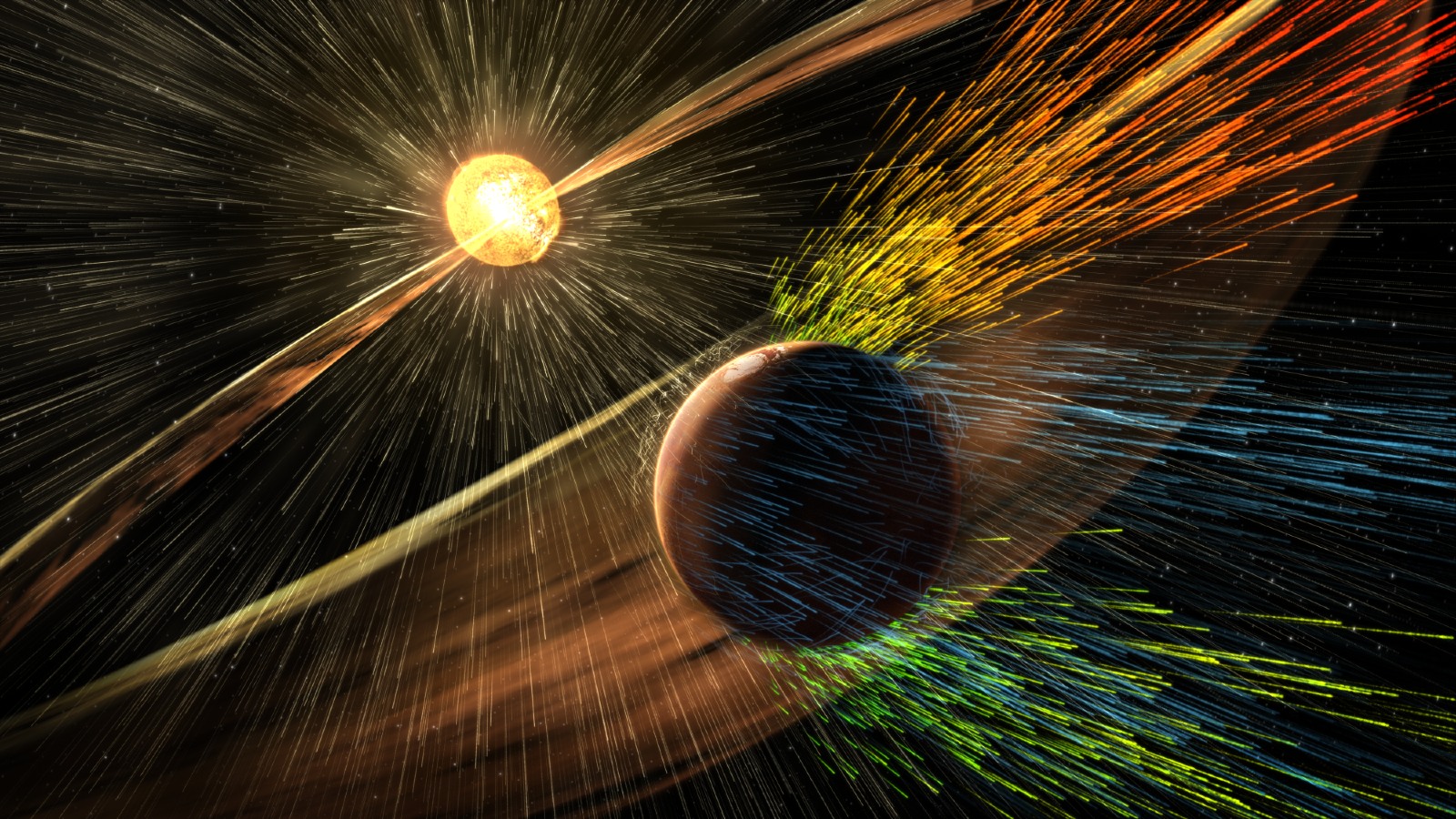
Mars' atmosphere has been almost completely stripped away by solar wind.
Worst-case scenario
In Solter - Hunt ’s big - case scenario , increased levels of radiation therapy pelt the upper ionosphere could begin to blow away the out edges of our atm — a phenomenon known as " atmospheric stripping , " which has of course occurred on planets likeMarsandMercury .
But this would be the " most extreme case " and may take centuries , if not millennia , to occur , she added .
Related : NASA and Japan to launch humanity ’s 1st wooden satellite as soon as 2024 . Why ?

Researchers are already concerned about how private megaconstellations, such as SpaceX’s Starlink network, will impact astronomy.
But even if the atm remains integral , spacecraft detritus could still damage it .
Past studies have suggested that some of this pollution , peculiarly alumina ( aluminum oxide),could deplete atmospheric ozone , potentially increasing the size of the ozone holes above Earth ’s polar regions .
The magnetosphere is also undergoing somenatural weakeningas the Earth ’s core grows and solidifies , and nobody knows if space vehicle debris could accelerate this process or not .

‘Important first step’
Some research worker praise the new paper for highlight hidden potential publication of spacecraft dust .
" This piece of work is a really important first step " and highlight the " terrifying " amount of spacecraft rubble that could be deposited in the air , Samantha Lawler , an uranologist at the University of Regina in Canada , say Live Science in an email . " The consequences [ of this contamination ] could also be on a totally dissimilar graduated table than we ’re used to thinking about , " she added .
touch on : SpaceX Eruca sativa keep buck parentage - red ' atmospheric holes ' in the sky , and scientist are occupy

However , other experts think that the scenario laid out by Solter - Hunt are too speculative or based on blemished assumptions .
" Even at the densities [ of ballistic capsule dust ] discourse , a continuous conductive shell like a true magnetized shield is unlikely,“John Tarduno , a planetary scientist and magnetosphere expert at the University of Rochester in New York , told Live Science in an electronic mail . Some of the assumption in the newspaper publisher are also " too simple and unlikely to be correct , " he add .
In particular , no one has modeled how space vehicle dust will adjudicate in the atmosphere , how long it will last or how conductive it will be , meaning there is no proof that magnetic shielding is potential , José Ferreira , a doctorial nominee at the University of Southern California who is also studying space dust pollution , told Live Science in an email .

The number of potential satellites orb Earth in the future also " seems exaggerated , " as many vaunt satellite launch never occur , Fionagh Thompson , a research fellow at Durham University in England who specializes in space ethics , told Live Science in an e-mail .
The paper is an " interesting thought experiment , " Thompson added . But without clearly adumbrate just how ballistic capsule dust will have these problems , " it should n’t be passed off as ' this is what is go to materialize ' , " she order .
Solter - Hunt understands the research worker ' unfavorable judgment . However , due to the impending rise in artificial satellite launches , she wanted to divvy up her hypothesis with the scientific community . " I put it there so everyone can see it and talk about it , " she said .

— Weird dent in Earth ’s magnetised theatre is mess up with daybreak in the Southern Hemisphere
— Hidden lunar time period in Earth ’s magnetospheric ' plasma sea ' revealed in new study
— Eerie sounds triggered by blood plasma waves hit Earth ’s charismatic line of business captured in unexampled NASA strait clip

And , despite their reservation about this paper , the expert all agree that more research is desperately needed to study the possible effects of metal contamination in the ambience .
" This is not an publication to be ignored , " Thompson said . " There is a motivation to step back and look at this [ space debris pollution ] as a completely Modern phenomenon . "
" There ’s a heroic need to study this as fast as potential , " Lawler add . " Honestly , I do n’t think anyone knows what could happen . "