When you purchase through links on our website , we may earn an affiliate commissioning . Here ’s how it works .
Climate modification intensify thecatastrophic floodsthat swept through several U.S. United States Department of State at the kickoff of April , a new report has found .
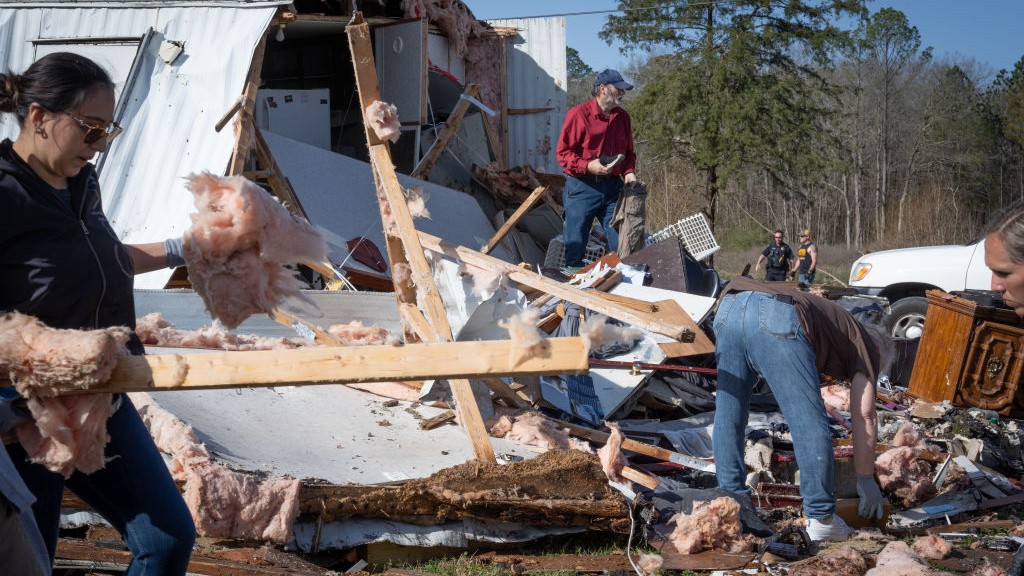
At least 15 people have died as a result of the flooding , which devastated states like Tennessee , Arkansas and Kentucky between April 2 and 6 . The southerly Midwest and parts of the southeastern U.S. also get multiple rung of twister at the same time , whichkilled at least 9 hoi polloi .

Severe flooding hit several states in April. This image was taken in Hopkinsville, Kentucky, on April 4.
Now , research worker have studied how climate change may have wager a role in the historical flooding and extreme weather . They estimated that homo - causedclimate changeincreased the likeliness of the flooding by about 40 % and increased their volume by about 9 % , according to areportby World Weather Attribution ( WWA ) , which study how climate change determine uttermost weather outcome .
However , it ’s still hard for scientists to measure our impact on global weather , and the researchers noted their estimates were conservative due to discrepancies between different clime models . The report also highlight that an in force emergency reception prevented what could have been an even larger catastrophe .
link up : Kids born today are going to grow up in a hellscape , grim climate study find

The historical flooding came in the wake of uttermost rain . These rains get when a high - pressure system over the East Coast and southeastern U.S. clash with a dispirited - press organisation to the west , and the limit between these two systems stalled , so the rain kept off the same orbit . At the same time , the jet flow stockpile moisture into the area from the eastern Pacific as surface wet came in from the Gulf of Mexico .
To estimate the stage to which climate modification increased the likelihood and vividness of the flooding , the research worker psychoanalyze historical datum in the key Mississippi River valley alongside the rain information from April . The team found that both regional weather condition trends and enhanced sea surface temperatures led to more wet being useable when the rains fell , according to the report .
For exercise , the report highlighted the function of climate modification in the increase wet coming in from the Gulf of Mexico . Sea surface temperatures are increase with globose warming , and the squad institute that higher temperature lead to higher rate of evaporation in the Gulf of Mexico , which increased the amount of moisture available when the rains fell over the U.S.

Scientists are still teasing out the degree to which human activity has regulate any given extreme conditions event , but it ’s clear we ’re causing the planet to hot up up throughburning fogy fuelsand other activities . When the researcher just bet at overall warming , they concluded that an extreme rain event like the one in April is expect to pass every 90 to 240 year , based on current conditions , but it would be much rarer if the climate were 2.3 degrees Fahrenheit ( 1.3 degrees Celsius ) cooler . This amount of warming made the event between two and five time more probable with 13 % to 26 % more intensity , ground on the report figure .
— ' The Big One ' could rock the Pacific Northwest and fuel sea - tier rise and monumental implosion therapy
— mood war are draw near — and they will redefine global difference
— touch forests are grow as sea levels go up
macrocosm drawing card signed theParis Agreementin 2015 , which was an outside treaty that promise to throttle global heating to preferably below 2.7 F ( 1.5 century ) and well below 3.6 F ( 2 deoxycytidine monophosphate ) . Earth is now consistently above that target , with April representing the 21st out of the last 22 months to breach the preferred 2.7 degree Fahrenheit limit point , according to the European Union’sCopernicus Climate Change Service .
The authors of the report discourage that we ’re heading for 4.7 F ( 2.6 atomic number 6 ) by the end of the current hundred . Climate modelspredictthat extreme rain will become more frequent and intense in sure region as the creation continues to warm up .
At those grade of warming , such extreme rain events will likely double in oftenness and be 7 % more acute , concord to the report .
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompt to enrol your display name .













