When you purchase through links on our situation , we may earn an affiliate perpetration . Here ’s how it work .
bacterium present in some the great unwashed ’s guts may help let out down cholesterol , making them less susceptible toheart disease , a young survey suggests .
The link between a high diversity of intestine microbes and a lower chance of cardiovascular disease is well established . premature researchhas shown that masses with heart - related diseases , such asatherosclerosis , persuade different kinds of germ in their guts than people without the consideration . Researchers opine this may be related to a microbe - made enzyme calledIsmAthat breaks down cholesterin .
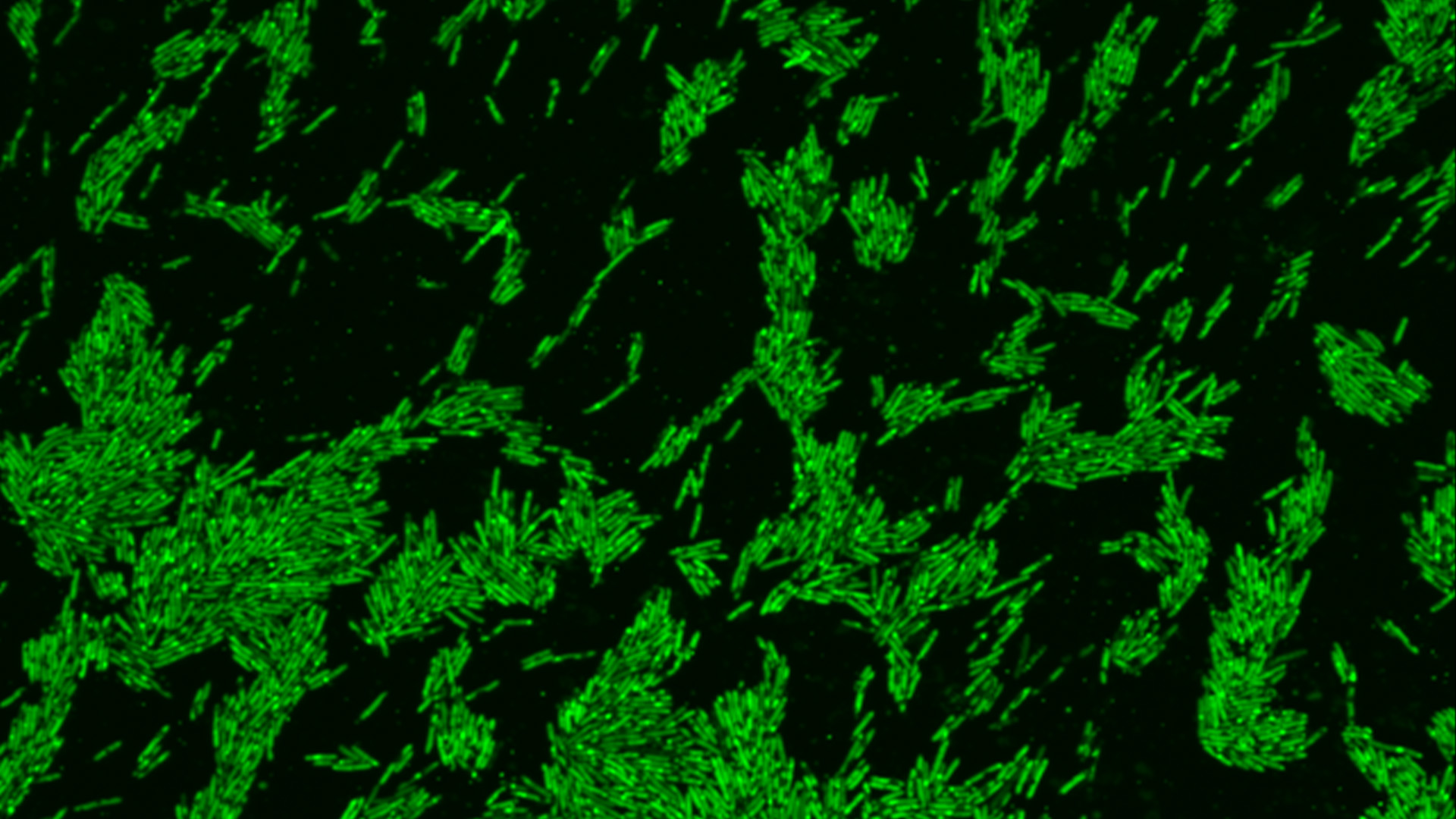
These rod-shaped bacteria were confirmed to gobble up and break down cholesterol (here shown in green).
People whose gut bacteria made IsmA had less cholesterin in their blood than those whose gut bacteriadidn’t make this enzyme . However , the specific species of bacteria that make cholesterol - gobbling enzymes were not known .
Now , a study published April 2 in the journalCellhas show that bacterium in the genusOscillibacterbreak down cholesterol and that people who carry more of those bacteria have lower cholesterol stage than citizenry with few of those microbes .
Related:9 heart disease danger factors , according to experts

Uncovering the bacteria that metabolize cholesterin is " very interesting and exciting,“Daoming Wang , a investigator at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands , tell Live Science in an email . Wang , a bioinformatician who studies the human gut microbiome , was n’t ask in the new study .
To translate how catgut bacterium influenceheart wellness , the researchers examined can and line of descent samples pull in from more than 1,400 people in theFramingham Heart Study , a decades - long study of heart disease peril ingredient .
The team used different techniques to profile the microbial DNA in the fecal matter samples . They also analyzed metabolite — the byproducts allow over when chemicals like cholesterin develop down . For each participant , the squad then correlate these findings with known markers of heart health , like blood - hold cholesterin andtriglyceridelevels .
hoi polloi with lower triglyceride and cholesterol levels had an teemingness ofOscillibacterbacteria in their poop , the squad find . They mark whether this correlation showed up in another , independent readiness of people and found that it did .
To confirm thatOscillibacterindeed metabolized cholesterol , the researchers grow the bacterium in the laboratory and exposed them to cholesterol marked with fluorescent tags . Using microscopy , the squad looked for fluorescence within the bacterial cells , to see if the microbes sucked up the cholesterin — and they did .
The researchers then tracked the fate of the bolt cholesterin and found that different bacterial species broke it down into various steroid hormone . These sex hormone could be absorbed by other gut bacteria , resulting in minify cholesterin levels overall .

To figure out which cistron and protein might helpOscillibacterbreak down cholesterin , the team used amachine - learningalgorithm . The algorithm analyzes features of genes to predict how proteins encoded by these genes will look . This analysis revealed that genes that encode proteins standardized to IsmA were likely responsible for metabolise cholesterol .
These result take us closer to understanding the " dark subject " of the microbiome , signify the big number of gut microbic genes whose functions are n’t yet fuck , Wang say . " This dark matter obstruct us from go out the whole ikon of catgut bacterial functionality . "
— Scientists bring out novel ' heart - on - a - chip '

— scientist may have found the missing link between heart disease and sleep problems
— Gut bacteria yoke to colorectal cancer in young people
In possibility , tweak the gut microbiome to boost cholesterol breakdown could be a strategy to reduce citizenry ’s cholesterin levels , the cogitation author proposed . But before that can be done , we involve follow - up investigations to better interpret on the button how these bacterium discontinue down cholesterol and how this can be used as a therapy , Wang said . We want elaborated written report in lab animals , followed by clinical trials in humans , he said .

Nonetheless , Wang added , " it ’s very exciting to further search the potential of manipulatingOscillibacterspecies as therapeutic interventions for managing cholesterin levels . "
Ever enquire whysome people work up muscle more easily than othersorwhy lentigo derive out in the sun ? Send us your interrogative about how the human body work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the subject business line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your enquiry serve on the website !