When you purchase through golf links on our website , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
Far few cervical cancer screening tests are coming back overconfident for precancer in the United States thanks to the widespread borrowing of thehuman papillomavirus(HPV ) vaccine , which prevents the main cause of cervical cancer .
Cervical cancer develops in cells of the cervix , whichconnects the womb to the vagina . Each year , around 11,500 peopleare diagnosed with cervical Crab in the U.S. , and 4,000 people die annually from the disease .
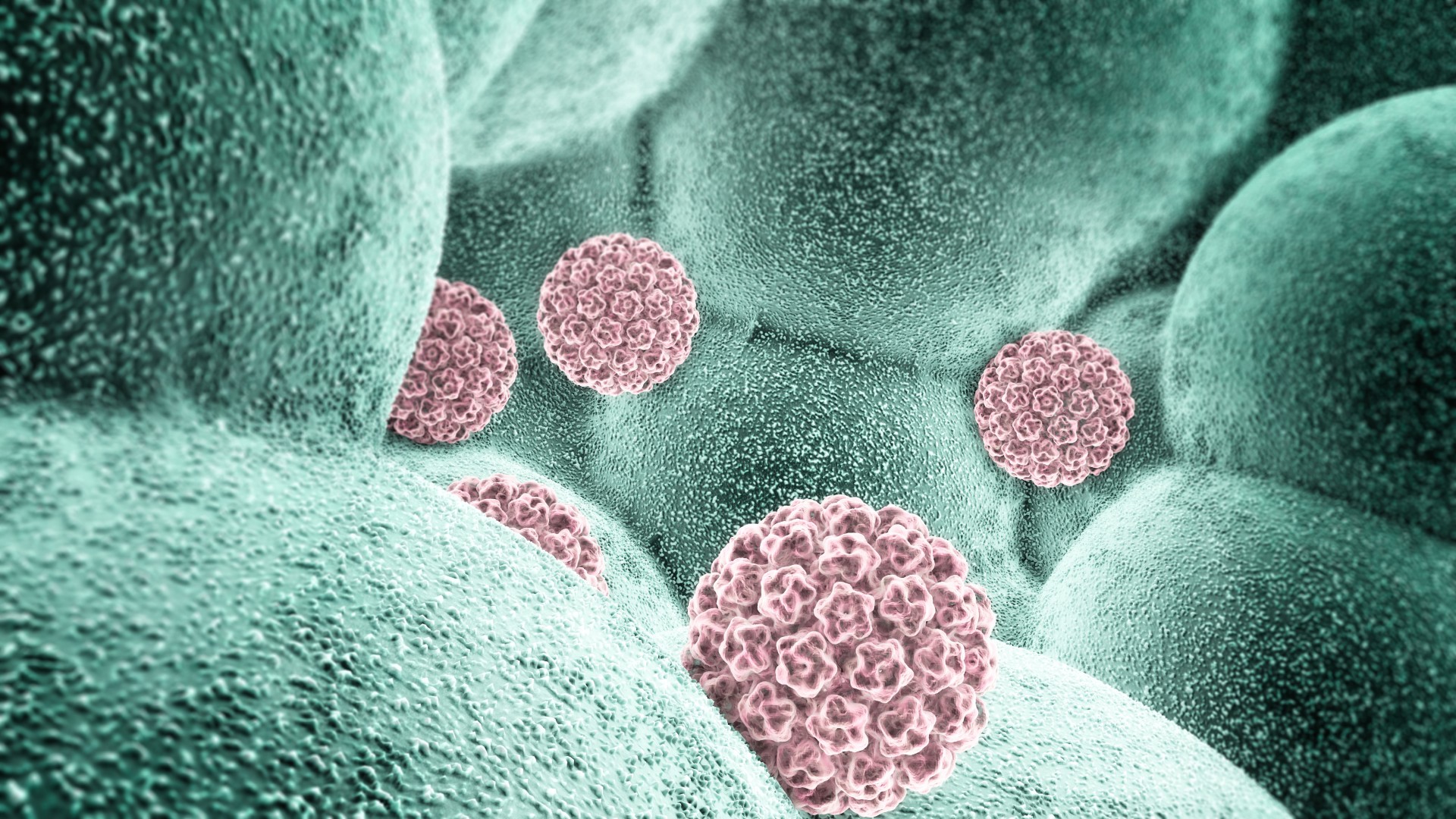
Rates of precancerous lesions that have the potential to become cervical cancer have fallen among young women in the U.S., likely due to widespread adoption of the HPV vaccine.
virtually all cervical cancer sheath — over 90 % — are because of contagion withhigh - risk character of HPV , viruses that canspread from person to person through intimate link . The disease can happen toanyone with a cervix uteri at any age , but it is most ordinarily diagnosed in peopleages 35 to 44 .
The HPV vaccinum , which wasfirst approve for usein the U.S. in 2006 , protects against the HPV infections that cause most cervical malignant neoplastic disease . Since the vaccine ’s introduction in the country , U.S. rates of HPV inoculation have increase steadily , reaching an estimated76.8 % of the eligible universe in 2023 .
Related : Cervical cancer deaths have plump among young women , US subject area finds
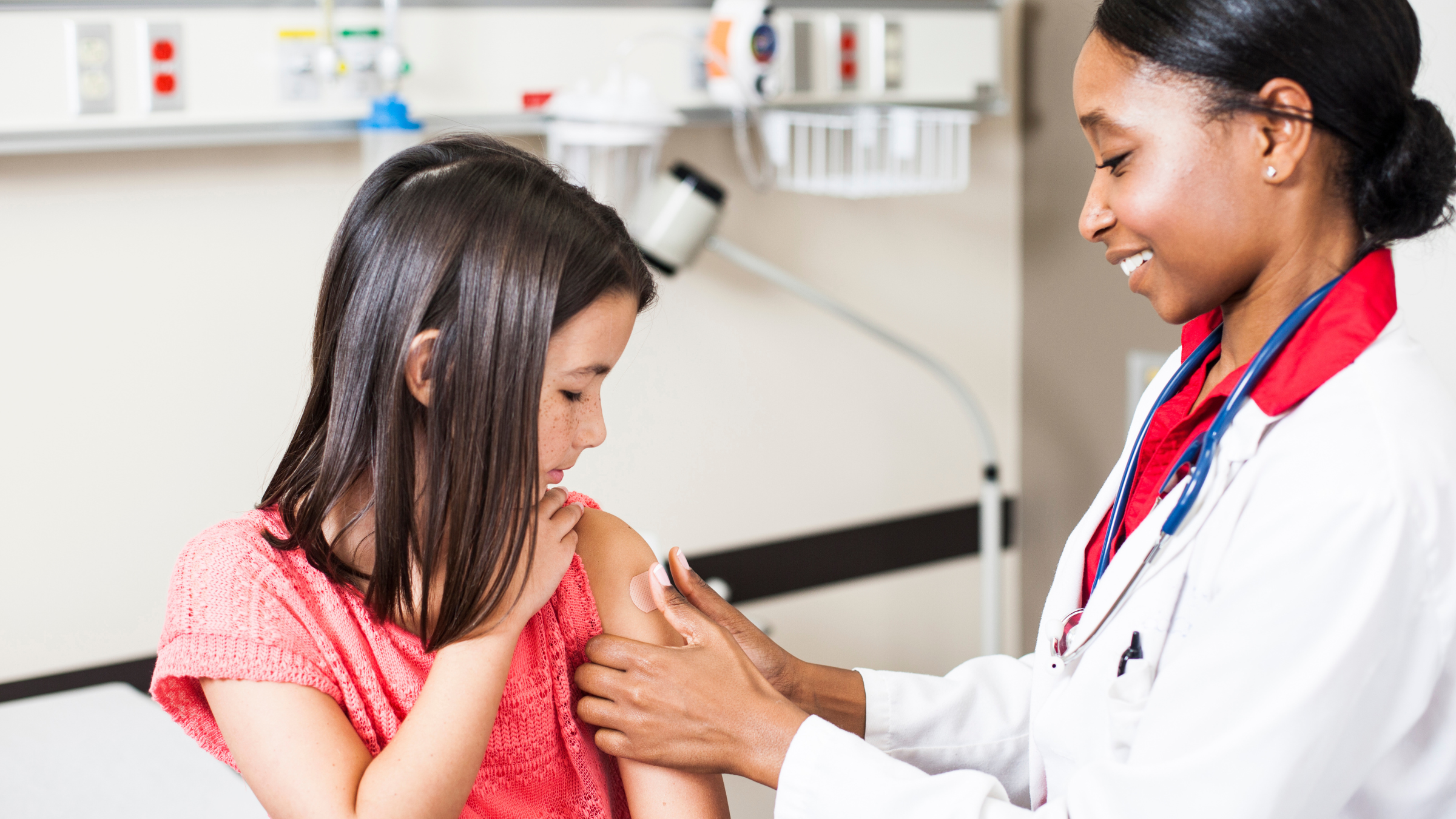
The first dose of the HPV vaccine is recommended at age 11 or 12.
Now , fit in to a newfangled psychoanalysis of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ) data , pace of precancerous lesion detected during cervical cancer masking have fall by about 80 % since 2008 .
The finish of cervical cancer screening , which includes " nipple smears , " is to observe precancerous lesions , mean groups of cell in the cervix that have the potential to become cancerous . If successful , screening detects these cells years before they become tumor , make it well-heeled to treat the precondition . At that early stage of the disease , treatment may involvelaser operating theater or cryotherapy .
To analyze the results of cervical cancer screen through time , the new depth psychology , published Feb. 27 in the CDC’sMorbidity and Mortality Weekly Report(MMWR ) , looked at a mix of secret and public insurance claim and survey data . It focused on woman ages 20 to 24 , the age group that ’s most probable to be vaccinated for HPV , as well as women ages 25 to 29 , who were comparatively less likely to be inoculate .

The CDC recommend the HPV vaccine toall tyke ages 11 to 12 . However , the vaccination series can be started as early as age 9 , as well as later in life , for those who were n’t immunize as tyke . People usually receive two or three doses of the vaccinum , spaced one to 12 month apart .
Meanwhile , the American Cancer Society recommends that people shouldstart cervical cancer screenings at age 25 .
The new MMWR paint a picture that HPV inoculation crusade have been successful at drive down precancer rates . Notably , precancer comes in several forms , includingmoderateandsevere , and the latter is more likely to twist cancerous . The rate of both types of precancer fell over the study period .

Specifically , the incidence of moderate precancer fall by 79 % in woman eld 20 to 24 , while the more serious lesion decreased by 80 % during the same clip period , the scientists found . rate of the dangerous lesions also declined by 37 % among cleaning woman ages 25 to 29 .
" This report published in MMWR adds more evidence usher the effectualness of HPV inoculation for prevention of pre - cancers of the cervix,“Heather Brandt , director of the HPV Cancer Prevention Program at St. Jude Children ’s Research Hospital in Tennessee , who was not imply in the research , told Live Science in an email .
The novel report did n’t forthwith measure whether HPV vaccination make the drop-off in precancerous lesions . However , numerousother studieshave shown that the vaccine slashes cervical cancer rates .

— New ego - swab HPV test is an choice to Pap smears . Here ’s how it works .
— Can virus cause cancer ?
— 2 infants inhaled Crab cells from mothers during parturition

The report speak to the importance of having at least one dose of the HPV vaccine before age 15,Dr . Diane Harper , a family Dr. and clinical research expert in HPV - associated disease who was not involved in the research , told Live Science in an email .
Harper said she hopes that , shortly , children as young as 4 to 6 years old could be offer the HPV vaccinum , when they have theirsecond dose of the morbilli , mumps and rubella ( MMR ) vaccinum , she told Live Science in an email . This would ideally simplify things and encourage more multitude to be vaccinate against HPV , she advise .
This article is for informational use only and is not think of to offer medical advice .

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to insert your display name .
Parasitic dirt ball raises risk of cervical cancer , subject area encounter
Crab : fact about the diseases that cause out - of - ascendency cell emergence

What ’s hiding under Antarctica ’s ice ?



