When you buy through tie on our site , we may earn an affiliate direction . Here ’s how it works .
The colors of the rainbow are all around us , but so are hues that most of us ca n’t see , including ultraviolet light — a wavelength that circumvent many homo but , surprisingly , many animals can perceive .
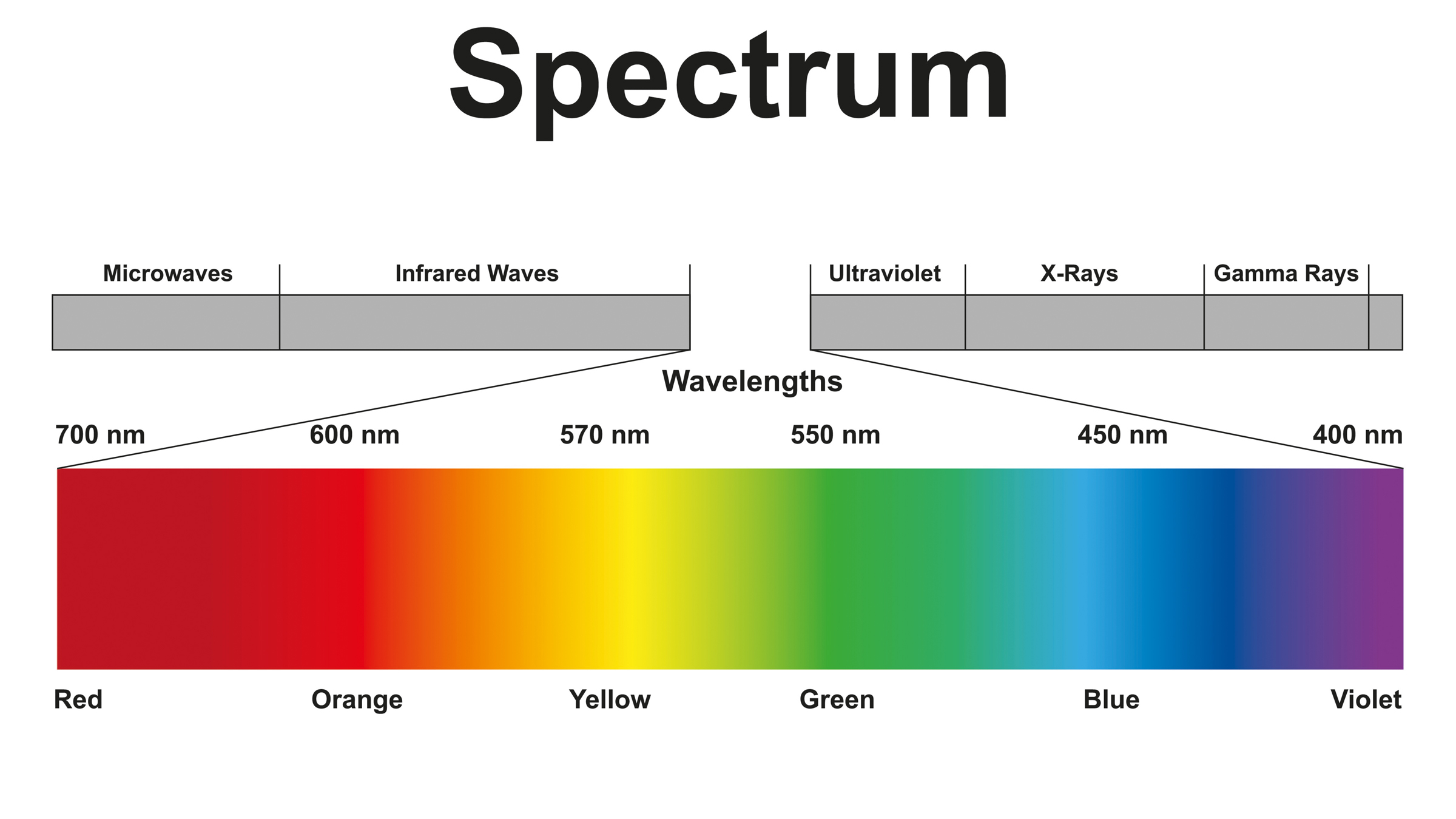
Ultraviolet(UV ) wavelength are small than those on the visible spectrum , but can people see them ? The answer , it turns out , depends on how former you are and whether your eyes contain ultraviolet radiation - filter out lens , expert told Live Science .

Festival-goers take part in a UV paint fight at the Glastonbury Festival in England. But can people normally see ultraviolet light?
First , it ’s important to understandhow sight works . In the back of the eye , the retina has photoreceptors that sense visible radiation and send off sign about the wavelengths they detect through the optic nerve to the brain , which interpret them as color .
In fact , our blue - detection cones can discover some ultraviolet light twinkle . However , the lense — the clear , curving bodily structure in the eye that focalize igniter onto the retina to serve us see more clearly — filters out ultraviolet light , so the high - vim wavelength never really reaches the strobilus , Michael Bok , a life scientist who studies vision at Lund University in Sweden , told Live Science .
associate : Why does n’t your visual modality ' go blue ' when you blink ?
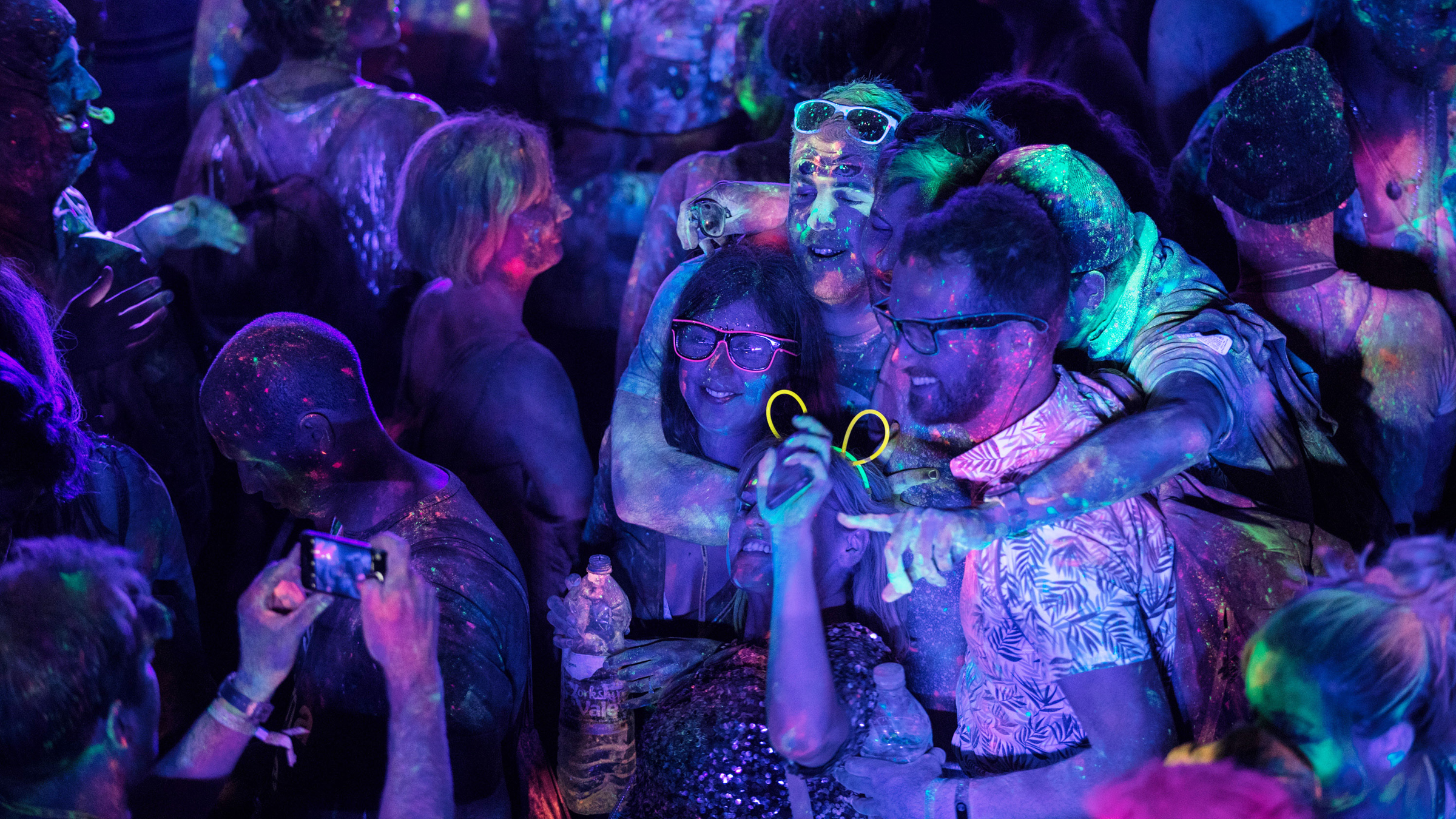

Festival-goers take part in a UV paint fight at the Glastonbury Festival in England. But can people normally see ultraviolet light?
Or at least the lens filtrate out most ultraviolet illumination wavelength , for most people . Despite the lens system ' ability to filter out most UV light — to protect our eyes from ultraviolet damage , which canage structures in the eyeand gain the peril of Crab — most young people can perceive some amount of it . In a small 2018 subject published in the journalPLOS One , all of the college - age participants at the University of Georgia could see ultraviolet radiation Light Within at some 315 nanometers . ( The full kitchen range of UV light is about 10 to 380 nm , with reddish blue beginning at the latter . ) During the experiment , " our subjects consistently account that the Christ Within appeared a desaturated violet - blue angel , " the researchers wrote in the study . But this ability appears to drop off around age 30 , indicating that senescence reduces the power to see ultraviolet light wavelengths .
Some people can see much more of the ultraviolet illumination light spectrum , however . Up until the 1980s , cataract operation involve removing the cloudy lens from the centre and not implanting a replacement , so people who had the operation could see UV light . For these people and those born without a lens , UV light looks like a pale sorry or pale reddish blue , Bok said . In a noted case , impressionist painterClaude Monetsaw more blue and purple overtones in water lily after having cataract surgery in 1923 and mull this difference in his former house painting .
But while most adults ca n’t see UV light , that ’s not the suit in the animal existence . Many mammals — include frump , computerized tomography , ferret and reindeer — can see some UV wavelengths throughout their lifetime , agree to a 2014 study published in the journalProceedings of the Royal Society B. The report also noted that the ability to see UV light is widespread in invertebrates , fish , birds , reptile and amphibians , which often have cones specifically for detect ultraviolet brightness — and lenses that let it through .
Ultraviolet wavelengths, which range from 10 to 380 nanometers, are smaller and more energetic than those on the visible light spectrum.
So why can so many animals see in the ultraviolet illumination ambit ? " For any color imaginativeness , the utility is to be capable to improve contrast for detecting object or of import thing in your surround , " Bok explained .
— How do our eyes move in perfect synchronicity ?
— Why do baby rub their centre when they ’re tired ?

— Can carrot give you night vision ?
There are many way UV helps creature do this . For illustration , many predatory sea creatures use ultraviolet radiation light to help see the silhouettes of prey , like plankton and fish larvae , because there ’s a lot of UV light in shallow H2O , saidThomas Cronin , a life scientist who meditate visual bionomics at the University of Maryland , Baltimore County . Manyinsects employ this type of vision to sense figure on flowers , and someuse polarized UV lightin the sky to help them sail . Many birdssignal to each other via their plumagein colors in the ultraviolet illumination range and apply it tofind right Berry .
" The more we look into it , the more it seems quite cleared that it ’s fairly common , " Bok tot .

In fact , the ancestor of craniate could see ultraviolet light and had a photoreceptor specifically for it , according to a 2003 study in the journalPNAS . But somewhere in humans’evolutionaryhistory , that photoreceptor shift more toward detecting violet than ultraviolet wavelength . Perhaps we could n’t afford the damage to our eyes because we are a long - lived species , or maybe it was because UV igniter come at the toll of blurrier vision , Cronin state .













