When you purchase through links on our land site , we may pull in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Extreme mood change associated with Alzheimer ’s disease may be partly driven by braininflammation , new research suggests .
Historically , the prevailing theory for what causesAlzheimer ’s diseasewas that a gradual buildup of unnatural protein calledamyloid - genus Beta and tauin the brain triggers a cascade of events , lead to nerve damage , the death of mentality cells , and symptom of cognitive decline and mood problems .
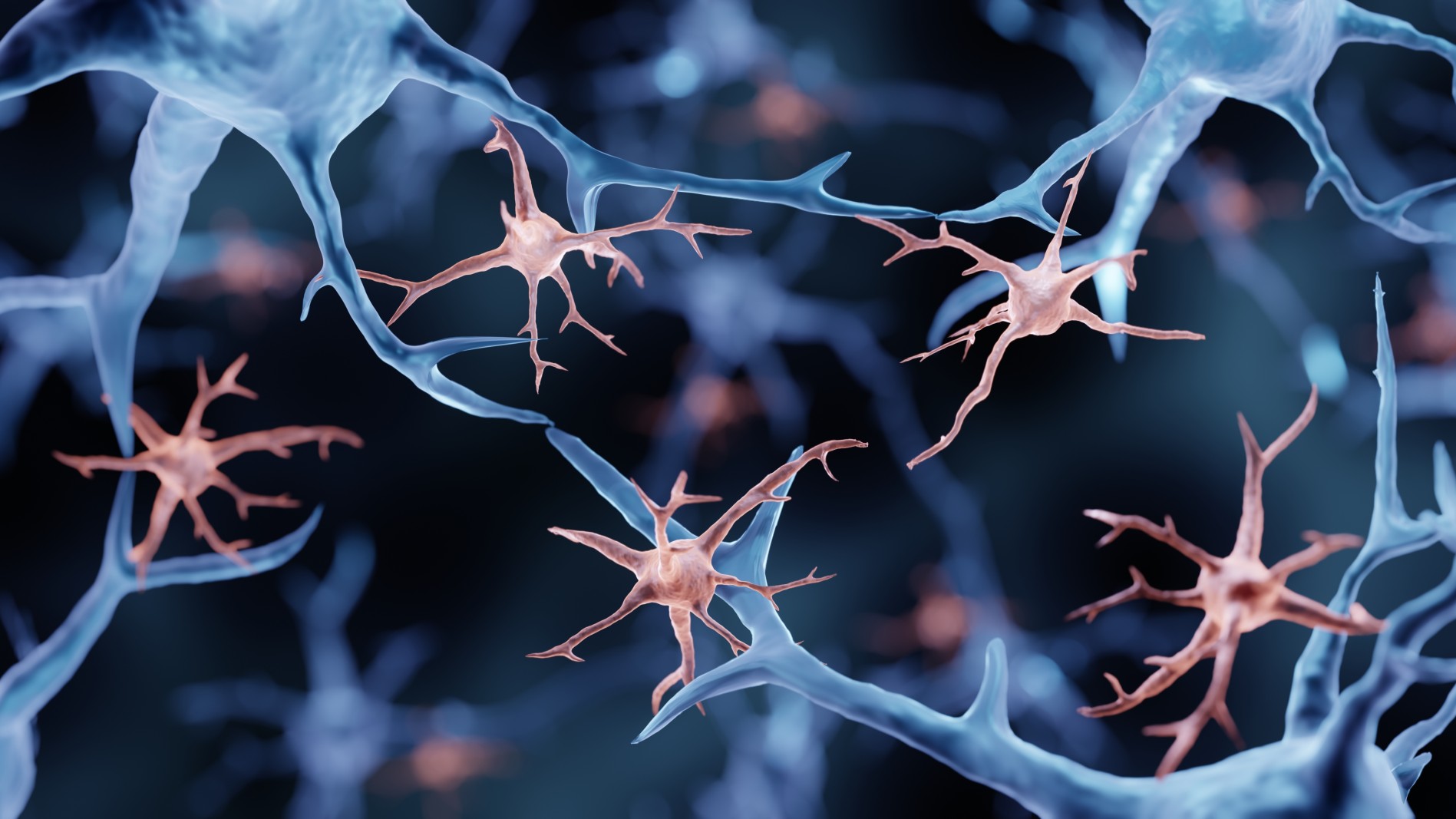
Microglia (in pink) are immune cells that trigger inflammation in the central nervous system in response to tissue injury or infection.
However , emerging evidence suggests thatinflammation in the brainmay also be involve in the development of the disease . Specific culprits include immune electric cell calledmicroglia , which normallypromote inflammationin response to wound or disease . Activated microglia have been found to interact with amyloid - beta and tau protein andmay influence the forward motion of Alzheimer ’s disease .
And now , in a study published Nov. 27 in the journalJAMA web Open , scientist have leave what they say is the first strong evidence that the neuropsychiatric symptom of Alzheimer ’s are directly relate with microglia activating .
best understanding the role inflammation plays in the maturation of Alzheimer ’s could take us one step closer to developing more targeted treatments for the disease , the researchers say .

Related : Gene discrepancy carried by 1 in 5 masses may guard against Alzheimer ’s and Parkinson ’s , massive study finds
" Neuropsychiatric symptom such as irritability , agitation , anxiousness and depression are among the most difficult symptom to treat in affected role with Alzheimer’s,“Dr . Cristiano Aguzzoli , the field of study ’s lead author and a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Pittsburgh , said in astatement .
" Here , we show for the first clip that head excitement may be to blame for these symptoms , " he said .

In the new study , the authors inscribe 70 masses who had no symptom of cognitive decline and 39 who were cognitively impaired , either display early sign of memory loss have sex asmild cognitive impairmentor dementedness cause by Alzheimer ’s . The participants browse from age 38 to 87 .
The writer assessed whether the participants displayed any of the mood problems that are characteristic of Alzheimer ’s . The researchers also scanned the participants ' brains to look for signs of microglial activating , as well as the accumulation of amyloid - beta and tau protein .
People with cognitive impairment were more likely to have amyloid - beta and tau protein in their brains . For example , amyloid - genus Beta was found in 79 % of those with cognitive damage equate to 30 % without .

However , even after learn these factors into account , the participants with more serious neuropsychiatric symptom had a outstanding stratum of microglial activation and more substantial signs of inflammation than the player with milder symptoms . This inflammation specifically affected three regions of the outer layer of the brain . Of the mood symptoms , temper was most powerfully assort with microglial activating , follow by nighttime flutter and tempestuousness .
The authors did n’t directly compare whether participant ' protein buildup was more or less powerfully associated with modality problems than their ignition levels . So they could n’t determine whether one broker is more influential than the other . However , the researchers guess it ’s potential that both are recreate a role .
In summation to conducting these tests , the investigator expect the health care provider of the patients with cognitive decline to fill out a questionnaire about their experience . They establish that the caregiver were more potential to report distress when looking after player with greater layer of brain inflammation , particularly when it was linked to symptom of irritability . Caregivers were also more likely to cover that patients experience speedy temper swings when the patient had mellow inflammation level .

Going forward , the author desire to direct more study with orotund groups of patients , including those who are at late stages of the disease and receive more extreme neuropsychiatric symptom , such ashallucinations or delusion . This would assess whether the team ’s determination are more generalizable to the wider population of people with Alzheimer ’s .
— Could vaccines prevent and deal Alzheimer ’s disease ?
— A man ’s rare gene variant may have shielded him from annihilating form of early Alzheimer ’s

— learning ability training probably wo n’t reduce Alzheimer ’s hazard — here ’s why
In the meantime , they hope this inquiry will act as a springboard for developing fresh therapies for Alzheimer ’s and possibly other types of dementedness .
" Since both neuroinflammation and neuropsychological abnormalities are found in several other type of dementia , includingParkinson’sdementia , we are collaborating with scientists around the existence to expatiate these finding to these other diseases,“Dr . Tharick Pascoal , co - aged cogitation author and an associate professor of psychological medicine and clinical neurology at the University of Pittsburgh , said in the program line .

This article is for informational purposes only and is not meant to offer medical advice .
Ever wonder whysome hoi polloi build muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckles hail out in the sunshine ? Send us your query about how the human body work tocommunity@livescience.comwith the open line " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your question respond on the internet site !