When you purchase through golf links on our internet site , we may bring in an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Astronomers using theHubble Space Telescopehave discovered a gigantic " blowlamp - like " green blasting out of a black hole — and it seems to be cause nearby stars to burst forth .
The 3,000 - light - year - tenacious trail of flaming plasma is radiate out from a supermassiveblack holewith a mass 6.5 billion meter that of the sunshine in the centerfield of the galaxy M87 .
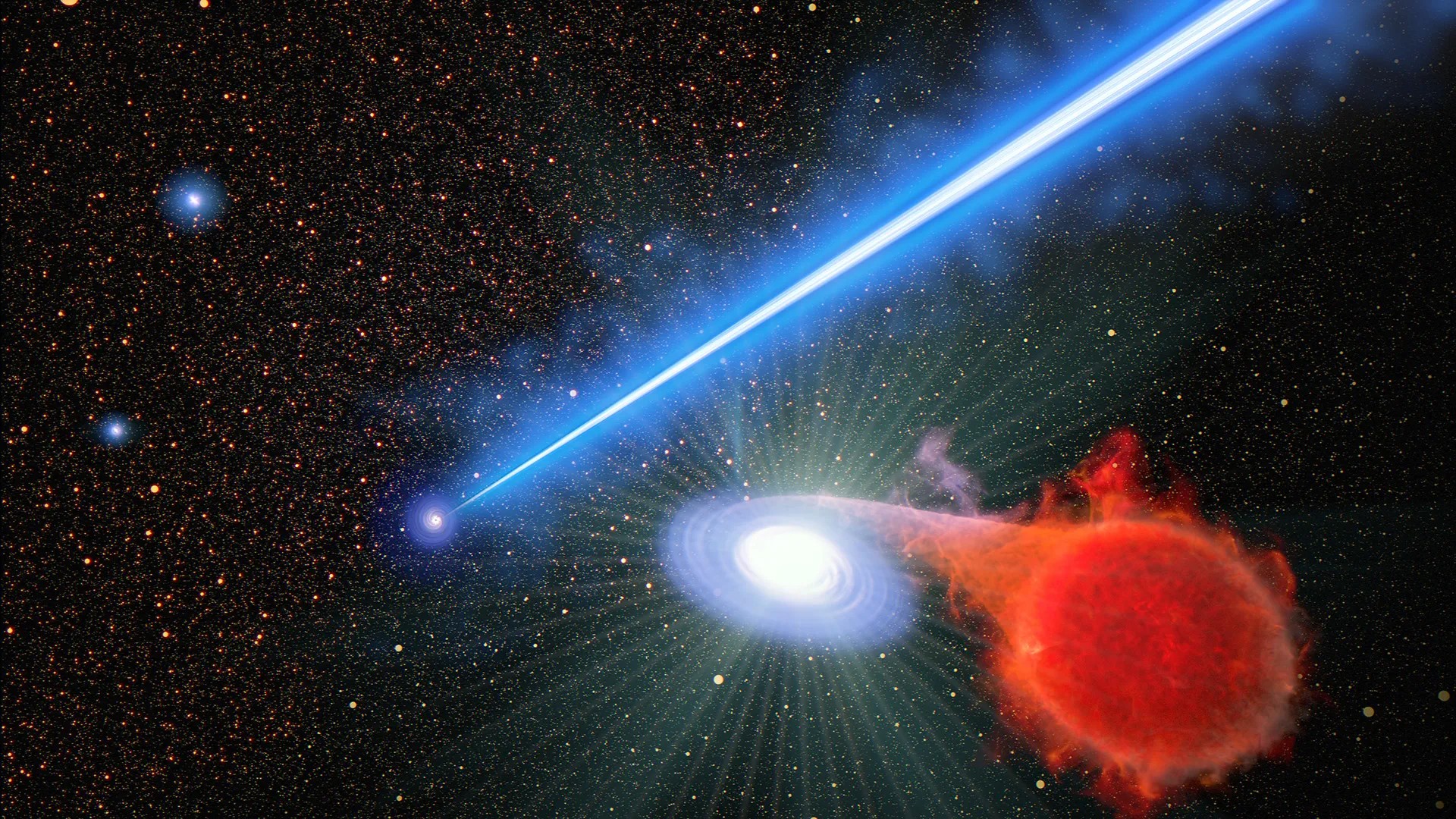
Getting caught in this electron beam would be deadly for any cosmic object , but according to new notice , even being in its neighborhood can be annihilative . The superheated energy beam appear to be cause nearby star system to erupt in blowup called novas . Yet precisely why this is happening remains a mystery .
" We do n’t know what ’s going on , but it ’s just a very exciting determination , " study lead authorAlec Lessing , an astrophysicist at Stanford University , enunciate in a NASA statement . " This mean there ’s something missing from our understanding of how disastrous muddle jet interact with their environment . "
The researchers published their finding Aug. 14 on the pre - print serverarXiv , so it has yet to be peer - refresh .
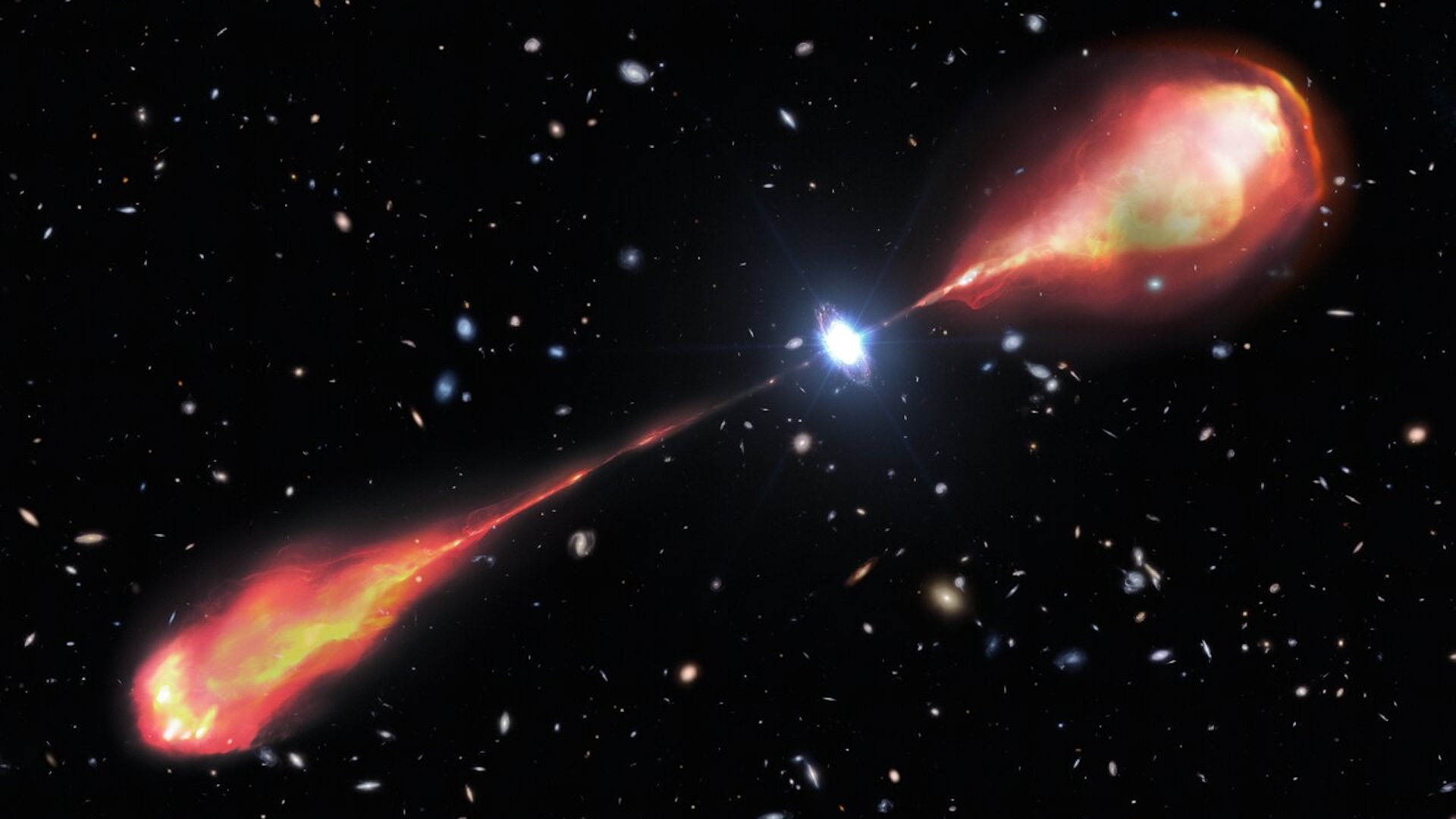

Related : adult black hole jets ever seen are as long as 140 Milky Ways
Supermassiveblack holestypically sit at the center of galaxies , suckle in thing from their surround before spitting it out at uttermost speeds , thus make a feedback unconscious process that shapes how galaxies evolve . As material approach a ignominious hole ’s " mouth , " clash make it to heat up and emit light trillions of metre more luminous than the bright wizard that can be observe by scope . at times , fighting black holes funnel this infalling issue into gargantuan energy jet that eruct into space , sometimesspanning integral galaxies .
However , how these jets affect their surroundings is mostly unknown . By target Hubble near the M87 jet , the investigator found that twice as many nova were erupting in star system near the special K than in the wide beetleweed .

Novas typically occur in binary star systems after a white dwarf — the smoldering straw of a dead star — steals H fuel from its normal star cooperator , get the white gnome to explode like a giantnuclear bomb . It seems the black muddle honey oil is causing the same thing to happen to these nova system , but the exact mechanism has not been observed .
" There ’s something that the jet is doing to the principal system that wander into the surrounding vicinity , " Lessing said . " Maybe the jet somehow snowplows hydrogen fuel onto the bloodless gnome , cause them to erupt more oftentimes .
— James Webb telescope come upon the oldest , most aloof pitch-black hole in the universe

— smuggled hole may be swallow invisible thing that slow down the movement of stars
— What ’s the big black maw in the universe ?
" But it ’s not clean-cut that it ’s a forcible push , " he lend . " It could be the upshot of the pressure of the swooning emanating from the jet . When you deliver hydrogen faster , you get eruptions quicker . Something might be duplicate the mass transfer rate onto the white midget near the jet . "

Another opening , the researchers say , is that the jet material was somehow being captured by the regular companion stars , causing them to pour forth onto their white dwarf counterparts .
To discover the answers , astronomers will need to appear for direct observations of star eruptions occurring around cosmic jets . This is far from easy , but render that one nova erupts in M87 every sidereal day , it is n’t inconceivable .












