When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it works .
uranologist have release the percipient image yet of the baby cosmos — and they affirm that the lead possibility of the universe ’s evolution accurately describes its early stage .
The new image capture light that trip for more than 13 billion years to hit the Atacama Cosmology Telescope ( ACT ) in Chile . They show the existence when it was just 380,000 years old — much like seeing babe pictures of our now middle - aged universe .

This is the clearest image yet of the faint afterglow from the Big Bang, known as the cosmic microwave background radiation (half-sky image on the left, closeup on the right). Orange and blue represent varying intensities of radiation, revealing new gas clouds in the universe. The Milky Way appears as a red band in the half-sky view. Analyzing this cosmic microwave background in high definition has allowed researchers to confirm a simple model of the universe and rule out many competing alternatives.
At that clock time , our population give off the cosmic microwave oven background as it emerged from its intensely raging , opaque state following theBig Bang , enabling space to become crystal clear . This faint afterglow nock the first approachable snap of our cosmos ’s infancy .
Rather than just the transition from darkness to light , however , the new images reveal in gamey resolution the geological formation and motions of natural gas clouds of primordial atomic number 1 and helium , which , over millions to zillion of year , flux into the stars and galaxy we see today .
" We can see right back through cosmic chronicle — from our ownMilky Way , out past distant galaxies host immense dark holes and huge galaxy clusters , all the direction to that clip of infancy,“Jo Dunkley , a prof of natural philosophy and astrophysical sciences at Princeton University in New Jersey , who chair the ACT analytic thinking , said in astatement .
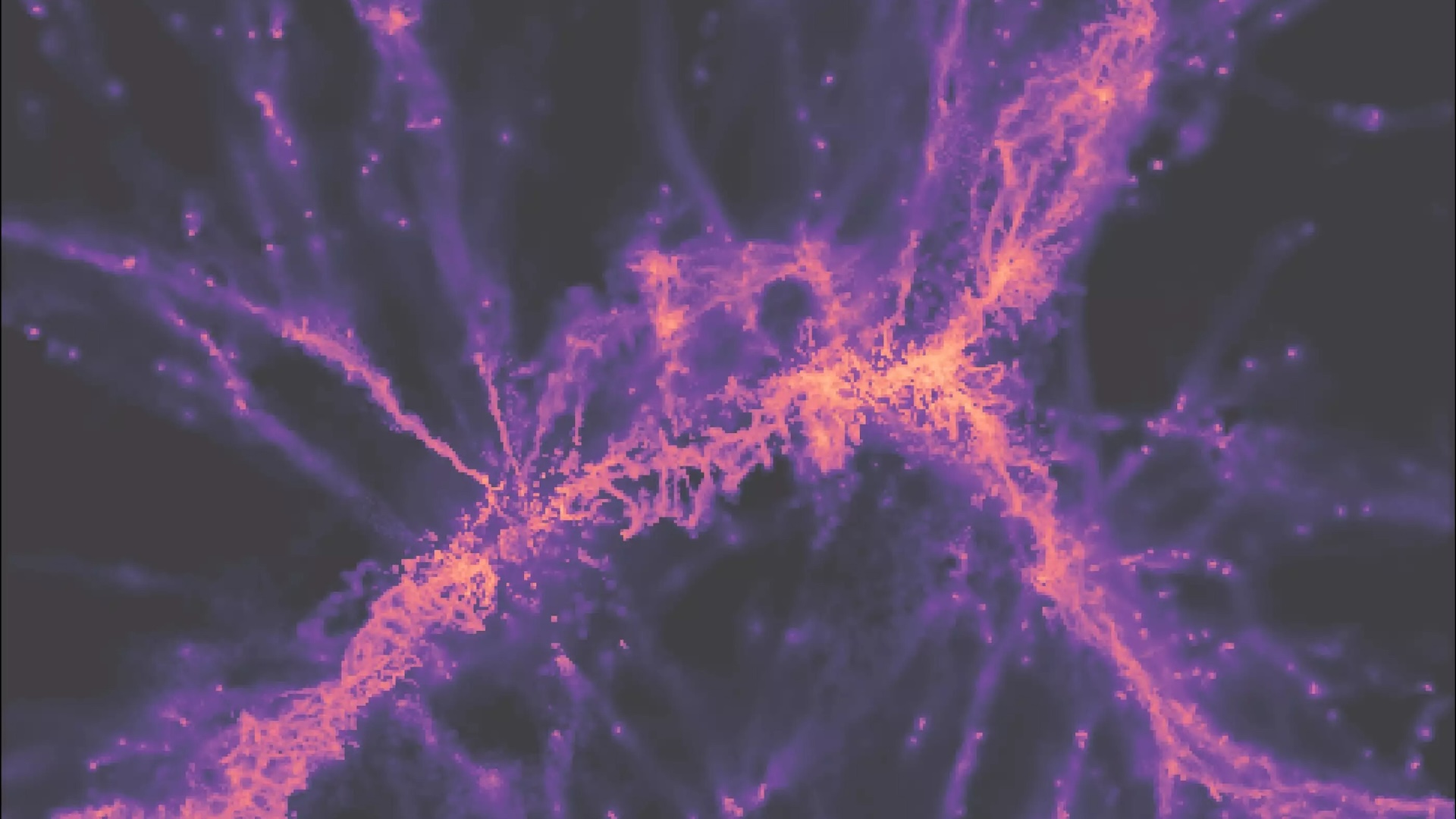

" By reckon back to that time when things were much mere , we can piece together the story of how our universe develop to the rich and complex place we incur ourselves in today , " she added in anotherstatement .
These determination were submitted to the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics and acquaint at the American Physical Society meeting in California on Wednesday ( March 19 ) .
About 1,900 “zetta-suns”
An analytic thinking of these new images revealed that the observable universe extends almost 50 billion sluttish - years in all directions from Earth . While the world is estimate to be 13.8 billion long time quondam , it has alsoexpanded in that clip , turn over light and matter more room to circulate out .
The termination also suggest that the universe contains as much mass as 1,900 " zetta - Lord’s Day , " which is tantamount to almost 2 trillion trillion sunlight . Of this , only 100 zetta - sun hail from normal matter — the kind we can see and measuring stick , which is dominated by H , followed closely by helium .
Of the continue 1,800 zetta - suns of material , 500 zetta - suns aredark matter , the inconspicuous center penetrate the creation that is yet to be directly detected , while a whopping 1,300 zetta - suns come from the density ofdark energy , a similarly occult phenomenon causing the macrocosm to spread out at an speed up rate .

Related:‘The cosmos has thrown us a curveball ' : Largest - ever mathematical function of space reveals we might have gotten dark energy totally wrong
The high - definition observation allow for scientists with a way to check how well the simple , prevailing model of the universe ’s evolution — known as the Lambda dusty benighted affair ( Lambda CDM ) — line the early existence . The data reveals no signs of new particles or unusual physics in the early universe , the scientist said .
" Our standard example ofcosmologyhas just undergone its most stringent set of test . The results are in and it looks very healthy , " study co - authorDavid Spergel , a theoretical astrophysicist and emeritus professor of astrophysical sciences at Princeton University , say in the assertion . " We have tested it for new physics in many unlike ways and do n’t see evidence for any novelties . "

The later observation also provided extra measurements that reinforce previous findings , let in a precise estimation of the universe ’s age and its rate of expansion , which is 67 to 68 kilometers per 2nd per megaparsec ( 1 megaparsec is equivalent to about 3.2 million light - age ) . This data is among thefinal resultsfrom the now - decommission ACT , which fill in its notice in 2022 .
— ' We had less than a 2 % opportunity to encounter this ' : James Webb telescope uncovers baffling ' Big Wheel ' , one of the most massive galaxies in the early universe
— ' I was astonished ' : Ancient galaxy unwrap by James Webb telescope control the oldest oxygen scientists have ever seen
— Could the universe ever stop expanding ? newfangled theory proposes a cosmic ' off switch '
" It is great to see ACT go to sleep with this display of results,“Erminia Calabrese , who is the theatre director of enquiry at Cardiff University ’s School of Physics and Astronomy and a atomic number 82 author of one of the new study , said in anotherstatement . " The circle bear on to close around our standard model of cosmology , with these in style issue weighing in powerfully on what universes are no longer possible , " she added .
Meanwhile , the ACT ’s successor , the Simons Observatory , began operationsearlier this hebdomad and captured the first of what astronomer trust will be many even more detailed images of the early universe .

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .












