When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
uranologist have spotted the wreckage left by a monolithic collision between two immense icy planet around a distant , sunlike adept .
Using aNASAspacecraft that monitors the sky for asteroid , the scientist also detected the bright afterglow get by the planetary smash - up and the resulting dust cloud that crossed the face of the system ’s parent star , dimming it significantly .
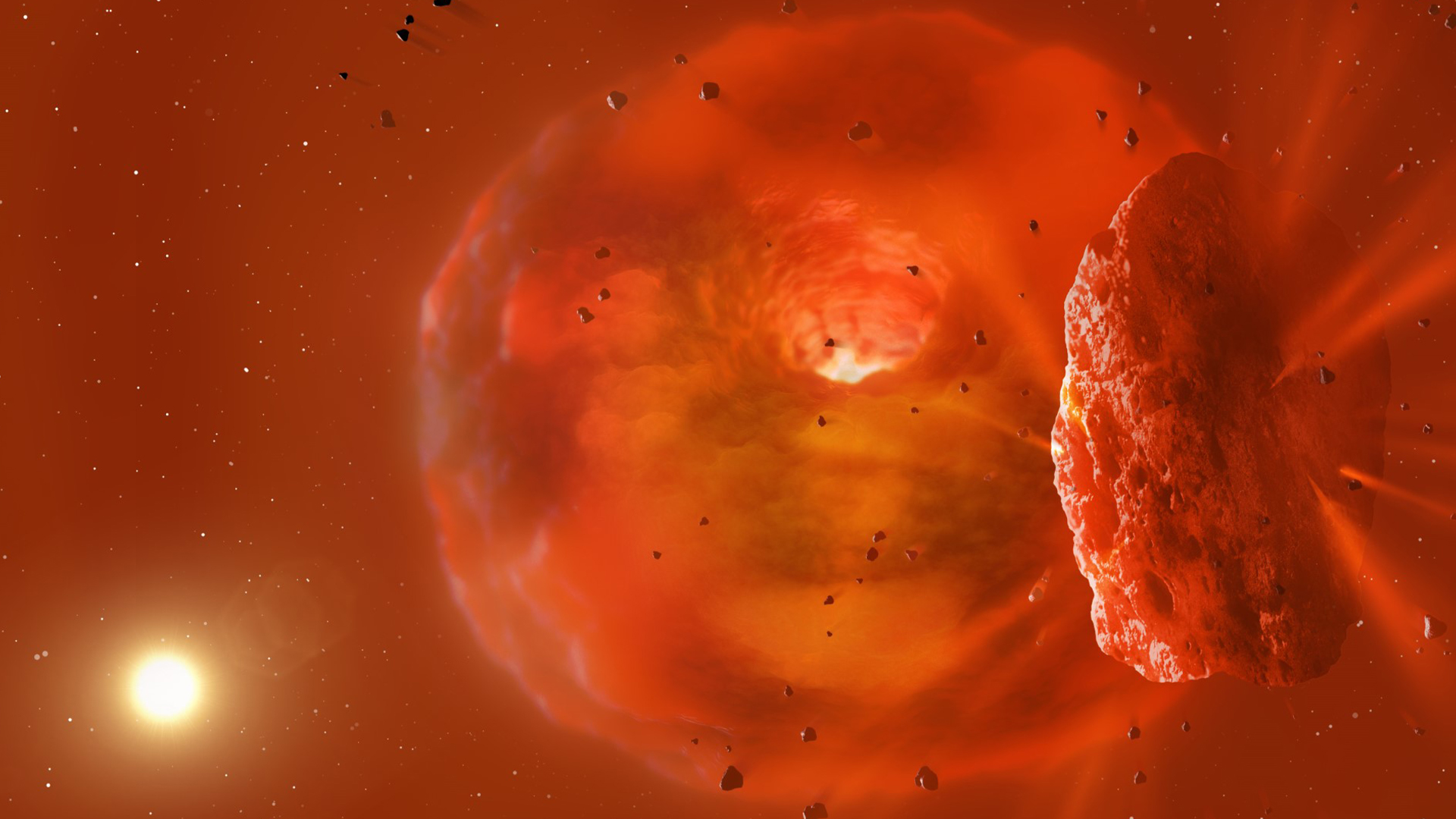
An illustration of the wreckage of a collision between two massive icy planets.
A odd astronomer tipped the team off about the collision after spotting that the star — doom ASASSN-21qj and located around 3,600 light - year from Earth — had a strange light output that doubled in intensity ininfraredlight before fading in visible light three years later .
" An astronomer on societal media pointed out that the star brightened up in the infrared over a thousand days before the optical attenuation . I knew then this was an strange event,“Matthew Kenworthy , cogitation co - lead and a research worker at Leiden University , said in astatement . " To be honorable , this observance was a complete surprisal to me . "
Related:‘Impossible ' new annulus organisation give away at the bound of the solar scheme , and scientists are cross

The researchers continue to study ASASSN-21qj for two years , see how its luminosity changed over time . They publish their determination on Oct. 11 in the journalNature .
The team found that the collision of two ice heavyweight belike stimulate the system to double in brightness at infrared wavelength three years before ASASSN-21qj get to fade in visible twinkle .
Simulating a cool collision
The researchers conducted a simulation of how such a hit would proceed , simulate the initial encroachment and then the diffusion of particles fling out by the clash . This revealed that the ASASSN-21qj planets likely collate into a individual consistence after the collision .
The simulation activate the squad to find how the debris cloud would have expanded outwards from the hit site , taking three years to travel far enough to address ASASSN-21qj as seen from Earth , make it to dim in seeable visible light .
" Our calculations and computer models indicate the temperature and size of the shine material , as well as the amount of time the glow has lasted , is coherent with the collision of two icing giant exoplanets , " co - lead authorSimon Lock , a investigator at the University of Bristol , explained .

Determining the temperature of this planetary wreckage also help the team to derive what the infrared freshness created by this tearing event would see like . An emission matching this visibility had been detected by NASA ’s Near - Earth Object Wide - field Infrared Survey Explorer ( NEOWISE ) spacecraft , which hunts for asteroid and comet within oursolar organization .
— Star organisation with Galax urceolata - corresponding ' weapons system ' may be carry a secret major planet
— 2 pairs of mammoth runaway black hole spotted on hit course , and they ’re bringing four intact galaxies with them

— A single monumental architectonic collision ? That ’s not how the Himalayas came to be , scientists say
The scientist are n’t finished observing ASASSN-21qj and its planetary wreckage just yet . They will watch the arrangement over the coming years , and they expect that the debris cloud will broadcast out along the scope of the destroyed planet . The research worker may essay to catch light spread off this detritus cloud using ground - base observatories and space - found telescopes like theJames Webb Space Telescope .
" It will be enthralling to maintain further developments . at long last , the mass of material around the end may concentrate to form a retinue ofmoonsthat will revolve around this fresh major planet , " field of study carbon monoxide - authorZoë Leinhardt , an associate prof of Astrophysics at the University of Bristol , tell .

NASA Mars satellite uncovers grading ' wish paint dripping down a wall ' on Martian Earth’s surface
uranologist name first ' unspoilt ' prospect for controversial Planet Nine inscrutable in our solar arrangement
The constant surveillance of modern aliveness could worsen our brain use in ways we do n’t fully understand , disturbing studies hint





