When you buy through links on our land site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
Astronomers have spot one of the most powerful shock wafture ever seen , due to a galaxy slamming into four of its neighbors while traveling at 2 million miles per hour ( 3.2 million km / h ) .
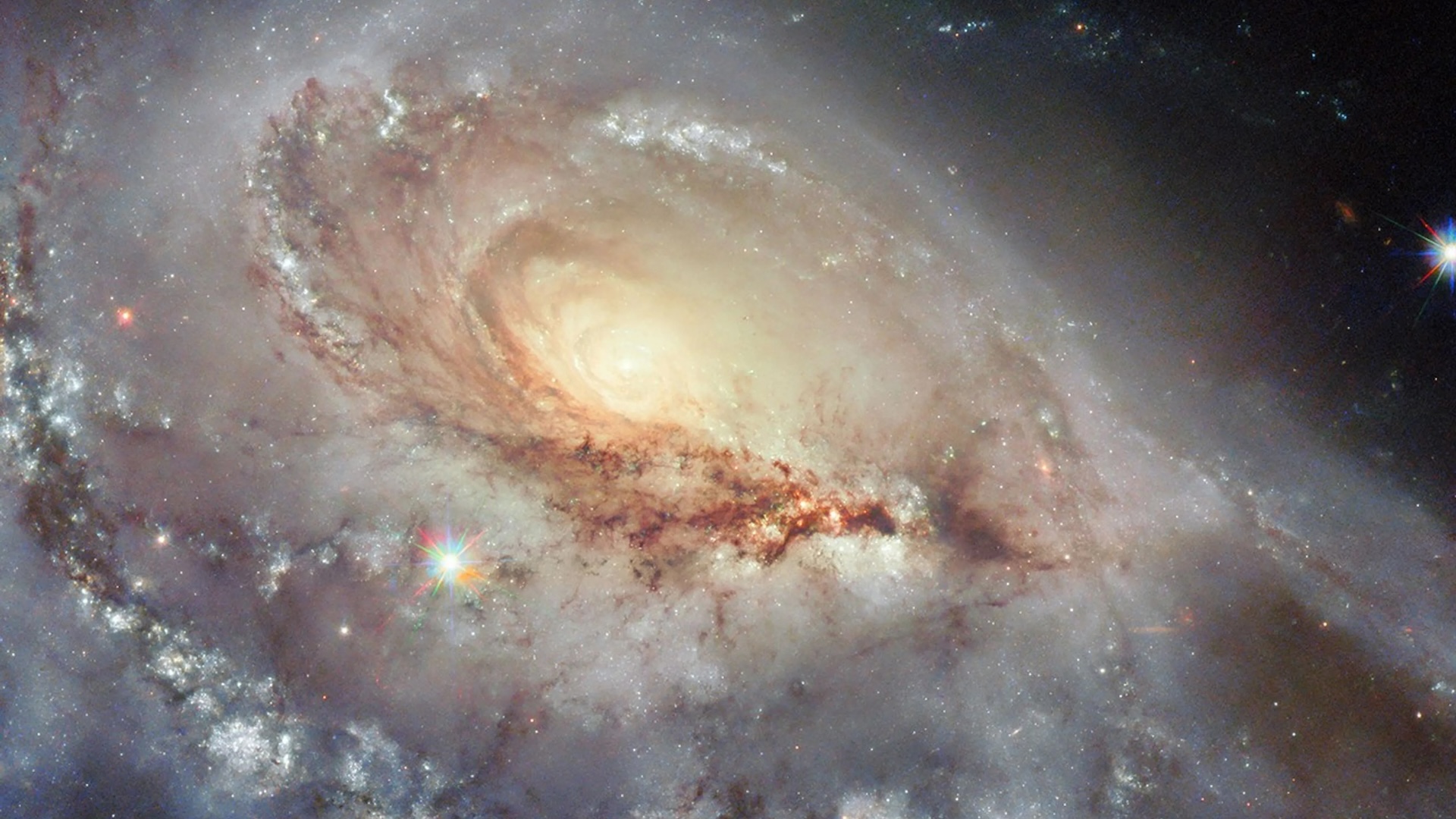
The cosmos - rattling event occurred inStephan ’s Quintet , when one of the scheme ’s five galaxies , hollo NGC 7318b , smashed into the other four .
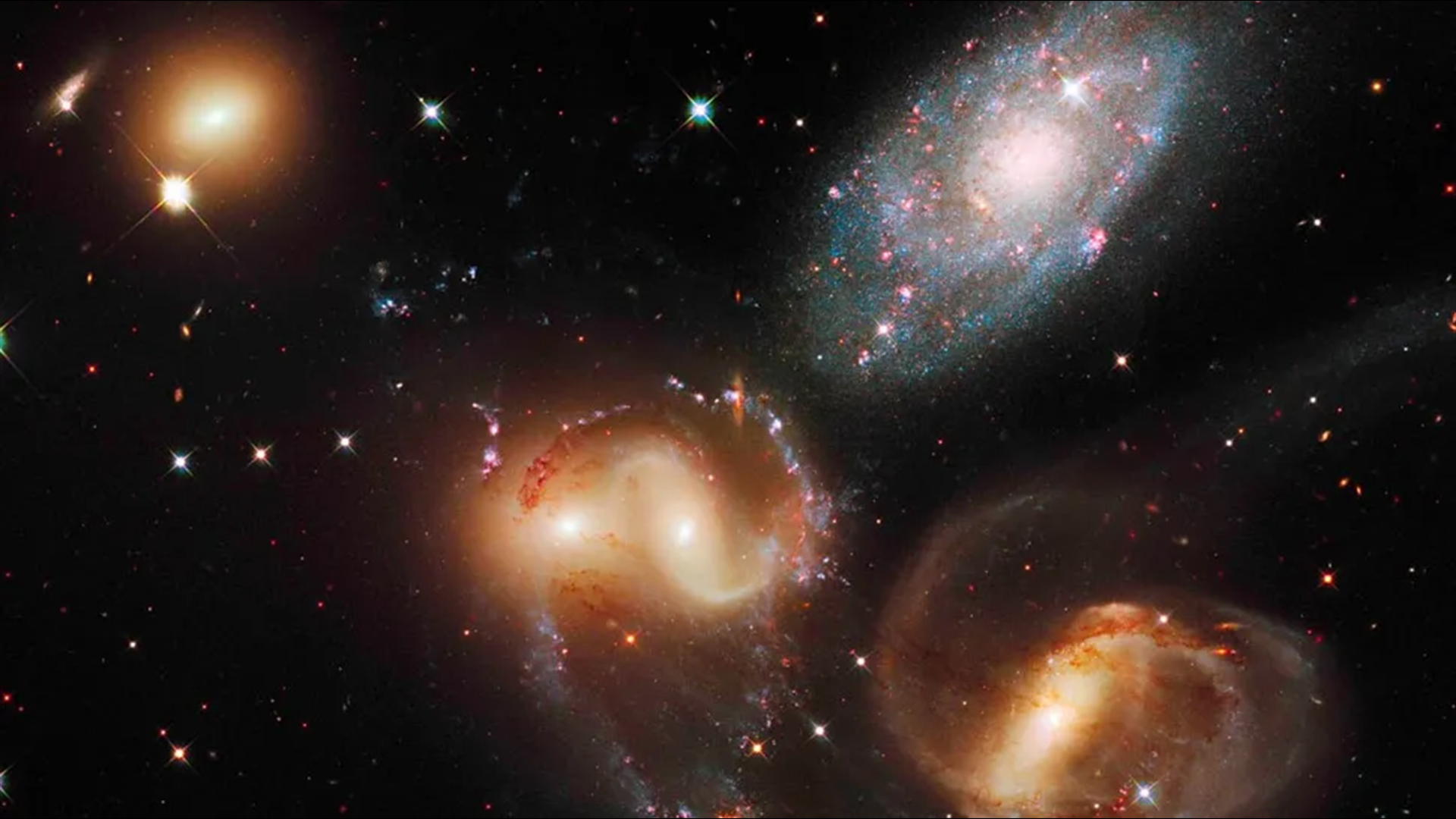

A Hubble Space Telescope image of Stephan’s Quintet.
NGC 7318b ’s submission into the system make an immensely muscular shock absorber front consanguineal to a " transonic boom from a jet champion , " the investigator read . They trust that by study it they can sympathize more about the crimson and helter-skelter interactions between galaxies . They published their finding Nov. 22 in the journalMonthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society .
" It ’s essentially a huge intergalactic field of debris,“Marina Arnaudova , an astrophysicist at the University of Hertfordshire in the U.K. , told Live Science . " The new intruder NGC7318b has smashed into the debris field , and compressed the blood plasma and gaseous state in it . In doing so it has re - arouse the plasma causing it to shine brightly at receiving set oftenness , and belike trigger off star formation in the process . "
advert after French stargazer Édouard Stephan , who discovered it in the 19th C , Stephan ’s Quintet is a group of five galaxies that are " locked in a cosmic saltation of repeated secretive encounters , " accord toNASA .

Related : James Webb Space Telescope discovers cryptical ' cherry monster ' wandflower so expectant they should n’t be
The Little Phoebe sits around 290 million light - years from Earth and was the first compact galaxy group ever spotted . It has been imaged by numerous scope , let in theHubble Space Telescopeand theJames Webb Space Telescope .
To investigate the quintet ’s behavior and cosmic history , the researchers behind the raw field of study used the William Herschel Telescope Enhanced Area Velocity Explorer ( WEAVE ) , a spectrograph mounted to the William Herschel Telescope on the island of La Palma .

By breaking Christ Within from the arrangement down into its constituent voice , the WEAVE spectrograph go after the debris remnants , the birth of new star and the trail of ionise gas leave alone behind by the force of the hit . All of these component were stirred up by the shock front , which rippled out at hypersonic speeds follow NGC 7318b ’s entranceway into the system .
— 13 billion - twelvemonth - former ' current of stars ' discovered near Milky Way ’s mall may be earliest building block of our Galax urceolata
— Study of ' twinned ' star finds 1 in 12 have drink down and eaten a planet

— new discovered ' fountain of young person ' phenomenon may aid stars delay demise by jillion of days
stargazer consider Stephan ’s Quintet could gain worthful brainstorm into how collisions and mergers stretching back to theBig Bangshaped the galaxies we see today , and what the system may look like in the future , the research worker said .
" This type of Galax urceolata collision in Stephan ’s Quintet is a rare chance to see a complex set of galaxies catch in the act of collide , " Arnaudova say . " As to how it will cease up , well it ’s likely that it will finally merge with one of the grouping member , but not for millions or billions of yr because the sizes and speeds of these things are so vast . "

The observation are the first to be made by WEAVE , but far from the last . The researchers say the spectrograph will also be used to study the reionization of the universe in the backwash of the Big Bang ; cast newfangled light on how stars organize and accrete over time ; and perform a number of " astronomic archaeology " experiments to find oneself how our ownMilky Waygrew over cosmic time .