When you buy through tie-in on our website , we may earn an affiliate charge . Here ’s how it work .
Astronomers think the Perseus cluster was a massive - but - stable grouping of galaxies , until they find hints of a collision with another cluster — but no one had key out a cosmic intruder . Now , using a method acting called weak gravitational lensing , scientist think they ’ve finally obtain the out of sight intruder .
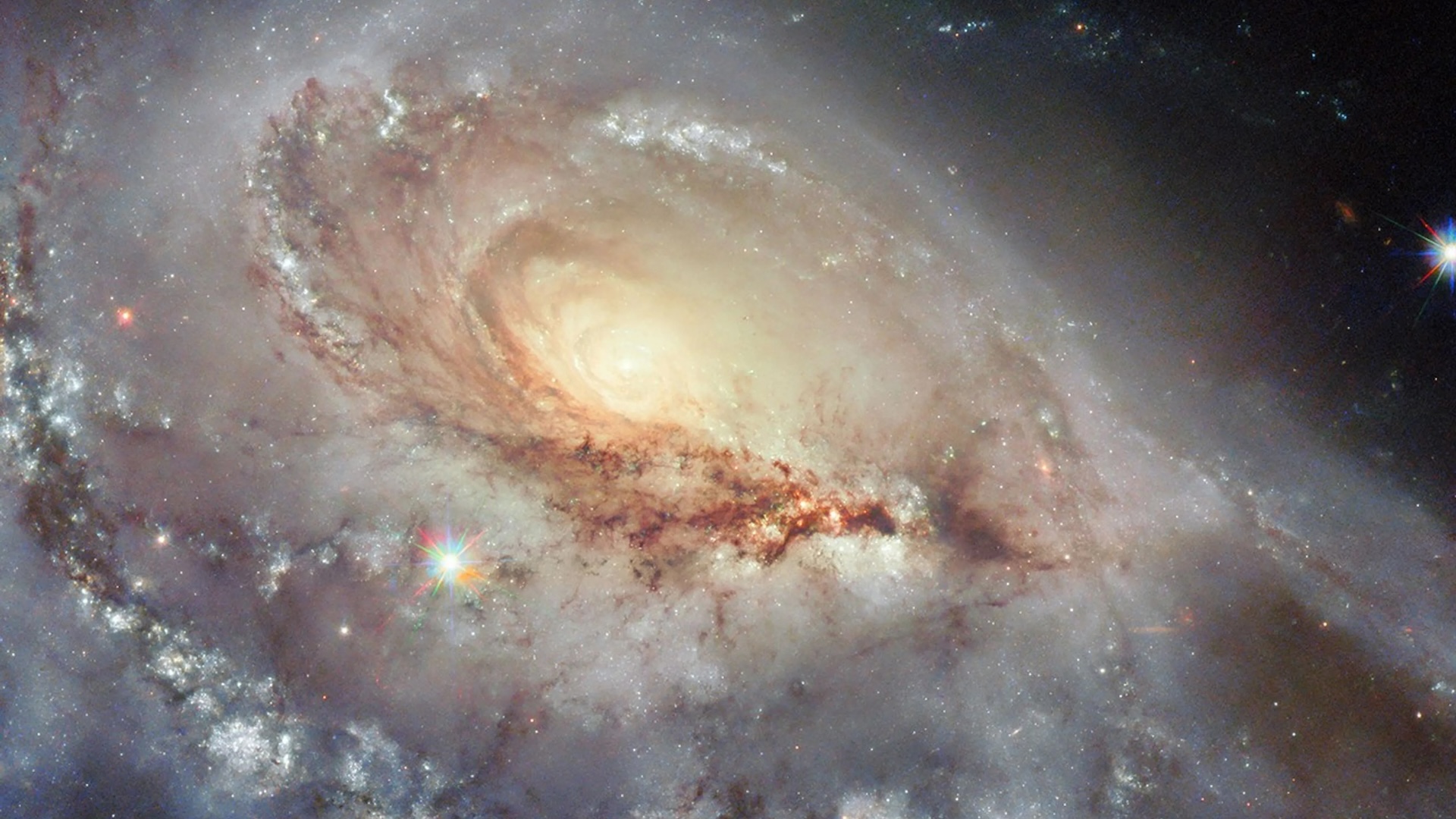
The Perseus galaxy clustering is one of the most massive structures in the known universe . tolerate the name of its host constellation , it ’s a vast grouping of thousands of Galax urceolata diffuse across 11.6 million light years , roughly 100 meter the diameter of theMilky Way .

The Perseus galaxy cluster taken by the Subaru Telescope at the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii. The newly discovered subcluster is on the right. Overlaid in blue is the inferred distribution of dark matter.
At 250 million swooning - geezerhood from Earth , it ’s relatively nearby , though it ’s moving away at 3,335 mil per 2d ( 5,366 kilometers per second ) due to theexpansion of the universe .
A ‘relaxed’ galaxy?
uranologist call tranquil and stable galax clusters " relaxed , " which means they have n’t collide with other clusters in the late story of the universe . For years , the Perseus cluster served as a prime deterrent example of a relaxed cluster .
Steady flows of hot gas move between its component galaxies and mislay warmth as the gas sump toward the cluster ’s center . There ’s also a faint glow of radio waves , called a wireless " mini - halo , " surround the cardinal wandflower . Both are house of a stable cosmic environment .
Yet astronomers noticed that instead of being spherical like an undisturbed clump should be , it was lopsided in an east - west counsel , hint that something was amiss .

This can produce magnified images of distant objects and ‘Einstein rings’.
pertain : Could the universe ever stop expanding ? New hypothesis propose a cosmic ' off switch '
Then , in 2012 , stargazer spotted " cold straw man " in the clustering — immense , loose - eld - farseeing regions that likely form when galaxy clustering collide . These fronts tick the limit where hot gasolene from one bunch slams into coolheaded , denser gasoline from another . It was a strong clue that Perseus had been in a major cosmic clangor . But if that was true , a question remain : Where was the other bunch that caused it ?
‘Smoking gun’ evidence
In the new inquiry , astronomers based in the U.S. and South Korea opine they have set up the " smoke torpedo " in the showcase of the clandestine cosmic hit . In a new newspaper published in the journalNature Astronomy , the researchers excuse how they used a proficiency called weak gravitational lensing to blob the cadaver of a bunch that clash with the Perseus wandflower clustering long ago .
Albert Einsteinpredicted the phenomenon of gravitative lensing over 100 long time ago , whereby massive objects like galaxy would warpspace - time , deflect clear rays and amplify remote sources . The amount that an aim deflects light gives astronomers a handle on its mass , and scientists have since happen upon manyincredible examplesof gravitational lensing .
In weak gravitational lensing , the image of setting galaxies is only slenderly distort as it pass through the cluster on its way to us . Using the Subaru Telescope in Hawaii , the astronomer in the new study analyzed the aberration of light from beetleweed far behind the Perseus clump .
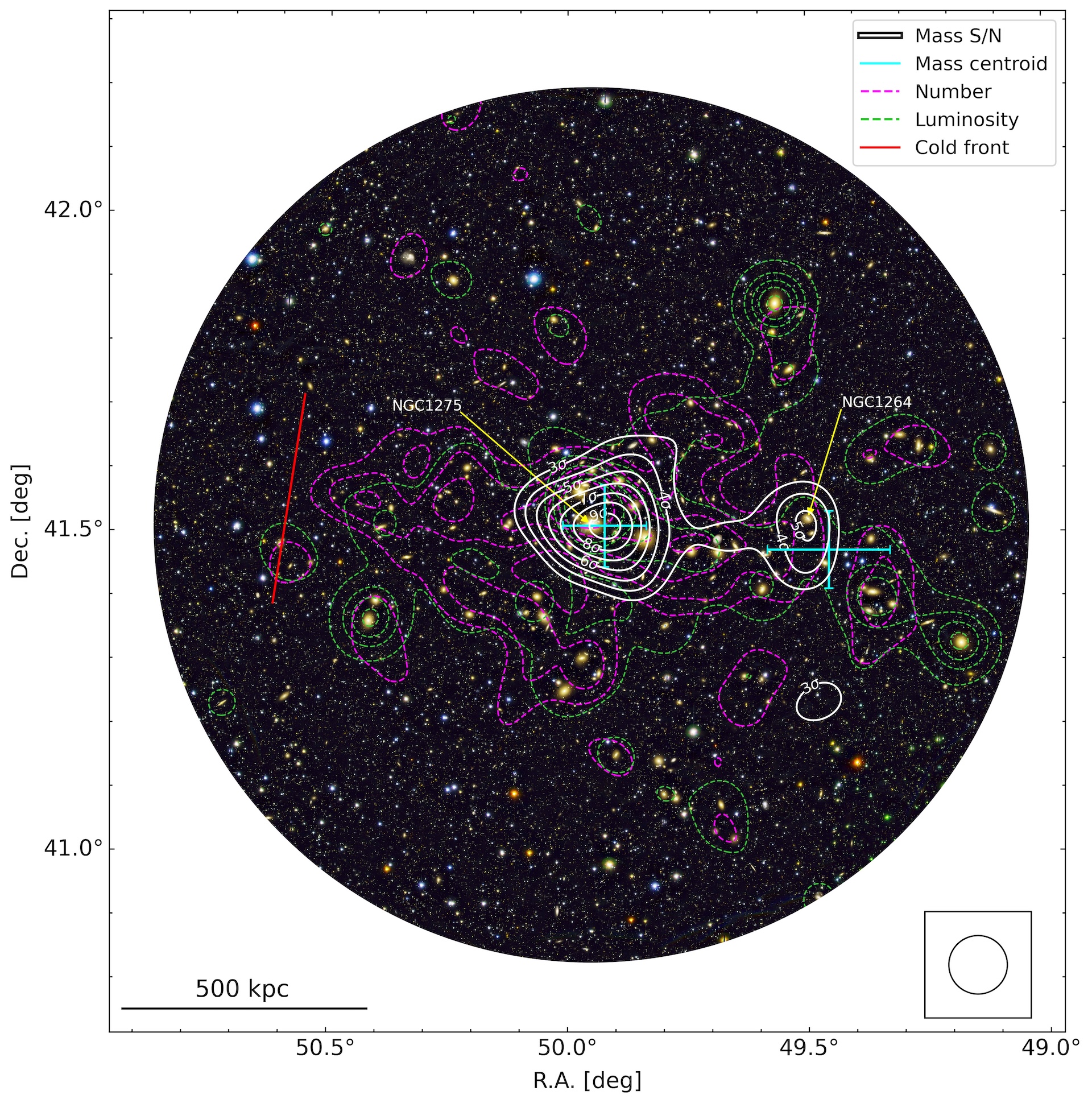
A figure from the paper showing the distribution of dark matter (white contours) and galaxies (green contours) in the Perseus cluster. The red line indicates the location of a large cold front.
" As we do not know the intrinsic conformation of each galaxy , we can not infer how much the image of the background galax are distorted,“HyeongHan Kim , a graduate student at Yonsei University in South Korea and first author of the composition , recount Live Science in an e-mail .
Yet , by consider lots of background galaxies , the team worked out the average distortion and used a computer pretending to figure out the amount of mass in the foreground cluster . They also pinpointed where the mass had to be in order of magnitude to produce the distortions they observed .
The astronomers find out a vast neighborhood of both visible and dark matter , called a subcluster halo , surrounding a smaller grouping of galaxies . This region was centered on galaxy NGC 1264 and imbed in the outskirts of the Perseus bunch . About 100 time the passel of the Milky Way , the subcluster is linked to the principal galaxy bunch by a " aggregate bridge " that is about 1.4 million loose - twelvemonth long and has almost the same muckle .

The computer model indicate that this nosepiece is direct evidence of a gravitational interaction between the two clusters , rather than a probability conjunction , and that it cooccur with the lopsided shape of the cluster . The team ’s electronic computer model also re - created the stale movement discovered in 2012 .
" The result surprised me , because I considered Perseus to be a relaxed cluster , " Kim said .
Their pretence starts around 7.5 billion days ago , when the meeting subcluster fell within the influence of the Perseus clustering . It take about 2 billion years for this subcluster to pass near the sum of the main cluster for the first time . Then , slowed down and pluck back by gravity , it guide through again 3 billion age afterward . This cosmic dance iterate , and near 2 billion age later , the subcluster passed through a third meter , roughly 750 million twelvemonth ago .

— Has the James Webb Space Telescope discovered a ' missing ' supermassive fateful hole ? ( picture )
— There ’s liquidness on Titan , Saturn ’s large moon . But something ’s overlook and scientist are confused
— Astronomers discover doomed satellite shedding a Mount Everest ’s Charles Frederick Worth of fabric every orbit , leaving behind a comet - alike tail

The findings are substantial because the realm is a prime mark for astronomers who are studying how wandflower clusters mould and evolve .
" The Perseus cluster , thanks to its propinquity , has been extensively inquire , " Kim say , " allow us to let on and examine many important astrophysical processes . " So even though this discipline focuses on a single clustering , it has broad significance for our savvy of the world , he added .
In addition , the result highlight the mightiness of weak gravitational lensing , particularly where traditional methods have failed to reveal the unseen universe . This approach not only aid to reveal blot out structures in the universe but also opens the door to key more galaxy - cluster mergers and to understanding how these massive systems take shape .

You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again , you will then be prompted to enter your display name .











