When you buy through links on our land site , we may gain an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it work .
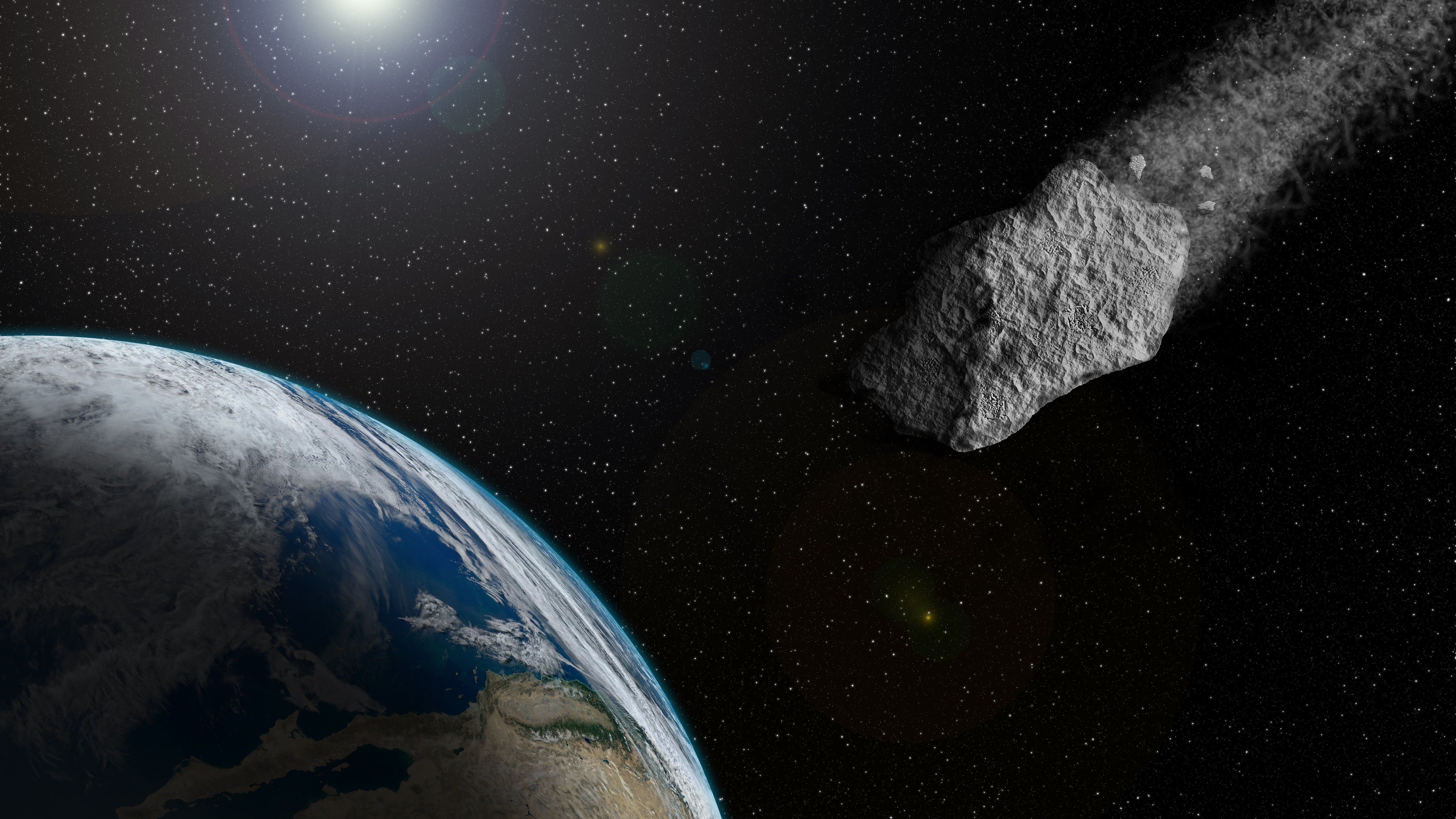
An asteroid that tore through the atmosphere over Germany in January was spinning quicker than any other cheeseparing - Earth target ever recorded , Modern research evoke .
The place rock , dub 2024 BX1 , sour into a fireball andexploded over Berlinin the other hours of Jan. 21 . Although small asteroids on hit form with Earth are typically detect only when they dash into the standard pressure , scientist spotted this one some three hours before impact .
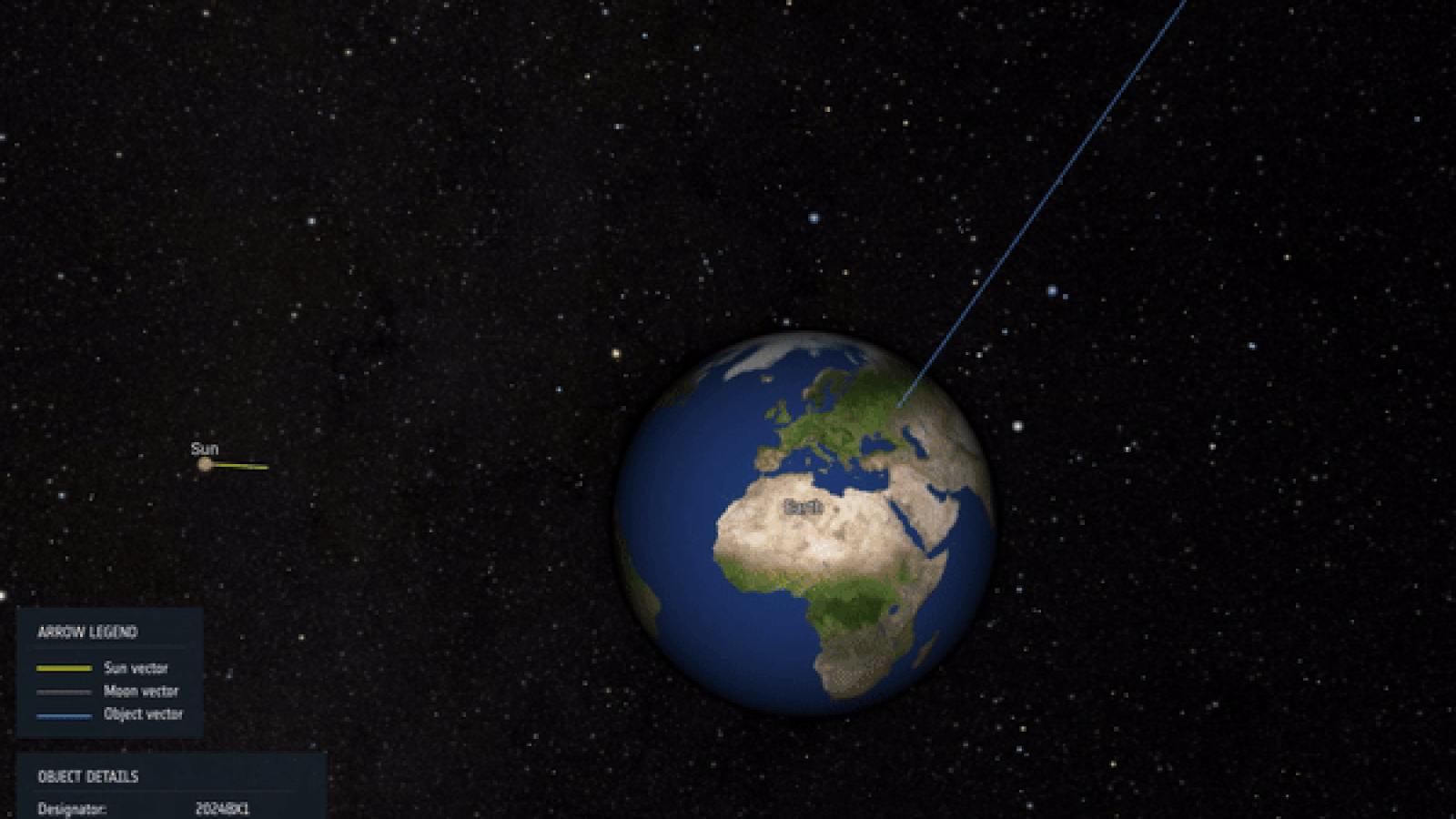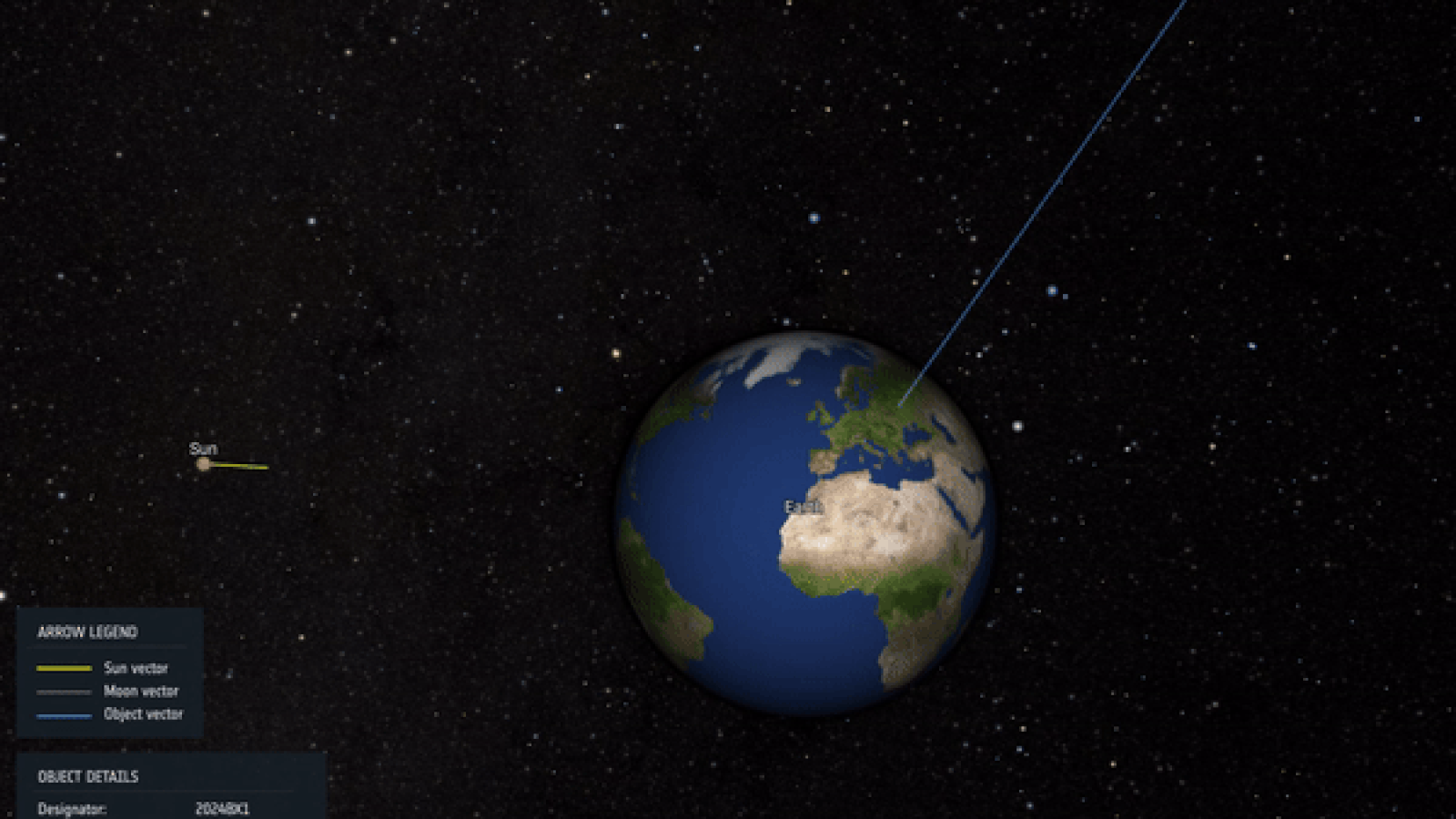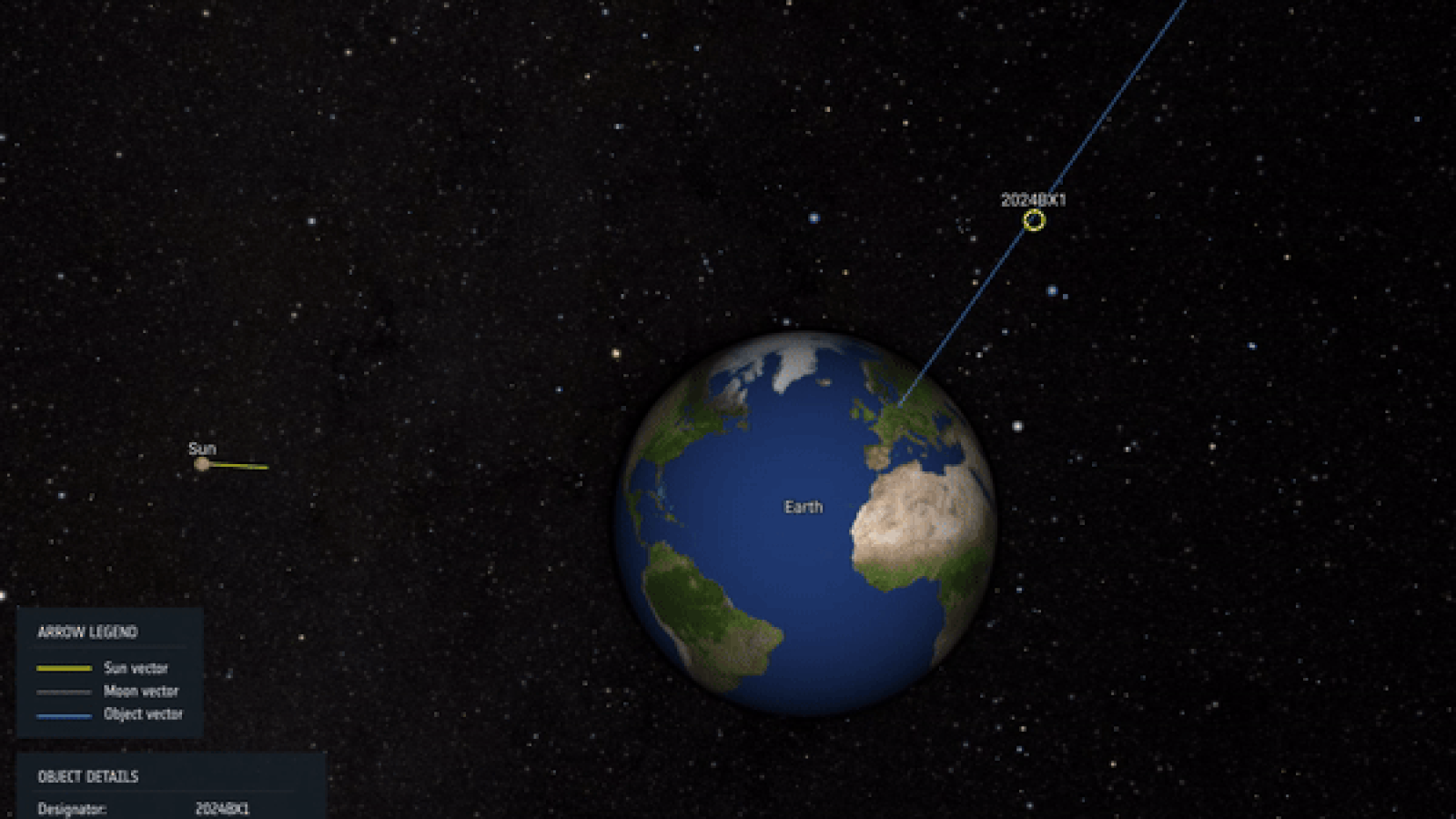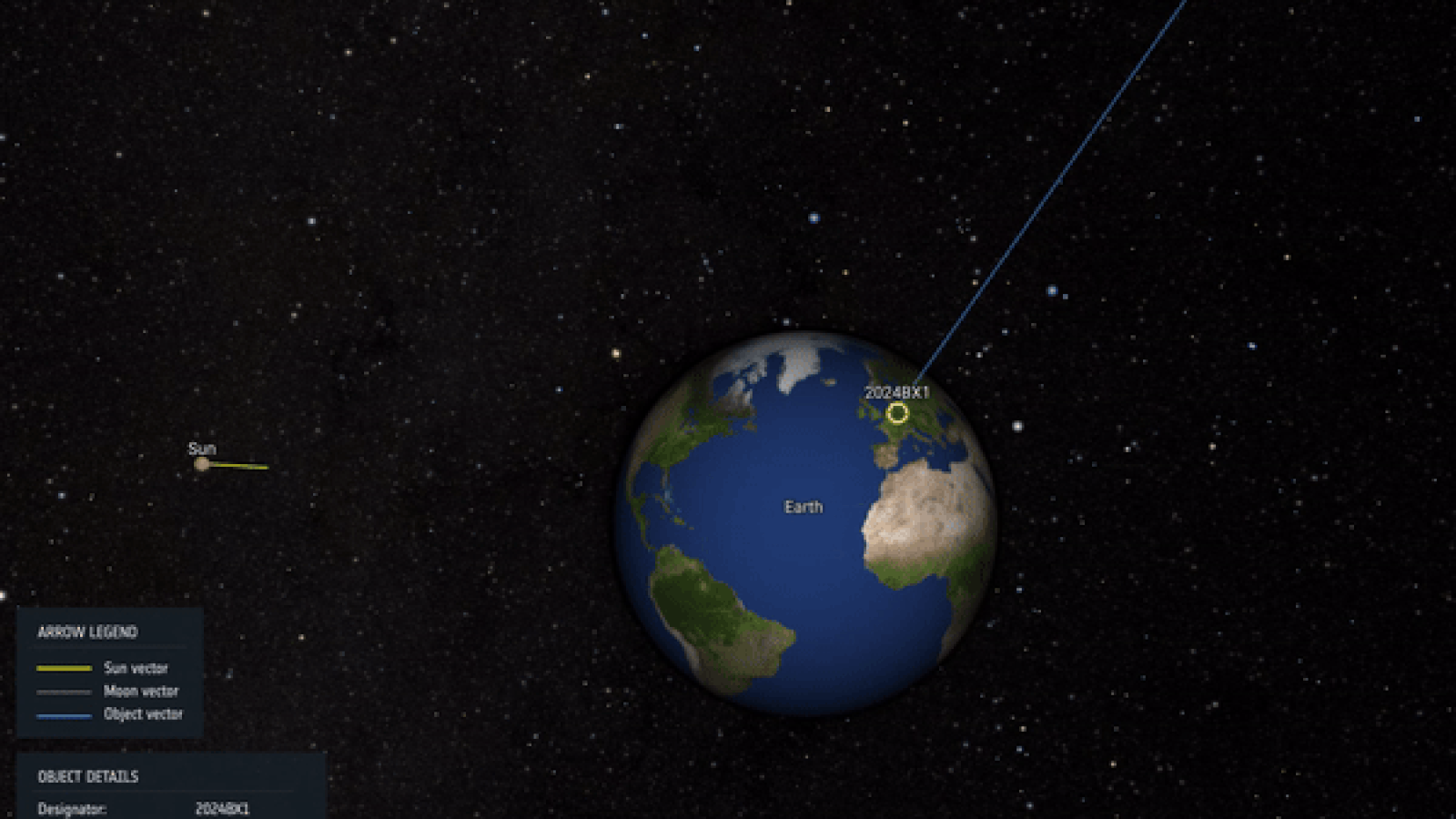
Visualization of the trajectory and impact of asteroid 2024 BX1, which exploded over Germany Jan. 21, 2024.
That ’s not the only way 2024 BX1 was strange , according to a report published to the preprint databasearXivon April 5 . Researchers imagine the asteroid , which was traveling 31,000 miles per hour ( 50,000 km / h ) , was rotating once every 2.6 seconds — the fast twist ever seen for an asteroid .
antecedently , the record for the fastest - spin asteroid belonged to a aviate rock called2020 HS7 , which showed arotation point of 2.99 minute . That asteroid measured between 13 and 24 feet ( 4 to 8 meters ) in diameter , which is slightly bigger than 2024 BX1 and may excuse why the latter spin faster .
Asteroidsspin for several reason , such as being propelled back into infinite after a collision . Because they are more compact , smaller asteroid tend to spin quicker than larger 1 . " They have internal strength , so they can rotate faster , " lead authorMaxime Devogèle , a physicist at the University of Central Florida who works with theEuropean Space Agency , toldNew Scientist .
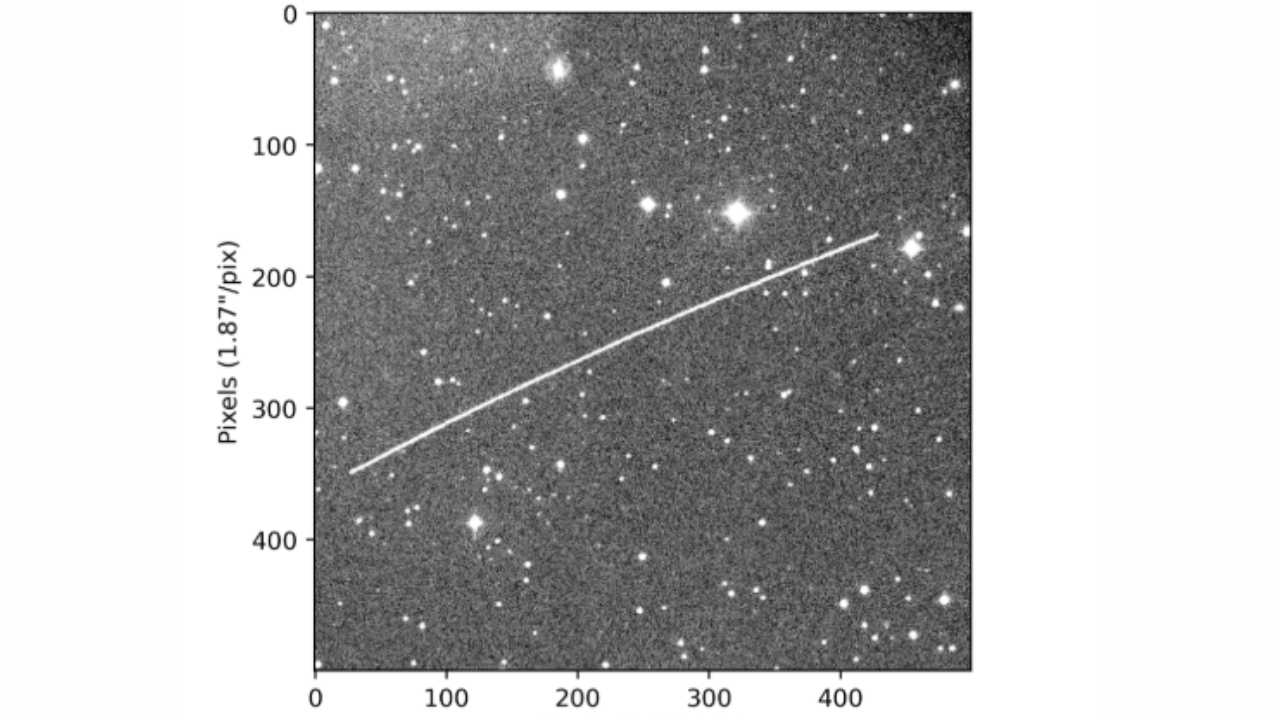
Observation of the asteroid 2023 CX1 nine minutes before impact from the Schiaparelli Observatory in Italy. The curvature of CX1’s trail is attributed to its very close proximity to the observer (approximately 4,350 miles, or 7,000 km) and the rapid variation of its relative motion in the sky.
interrelate : researcher just found more than 1,000 new solar organisation objective hiding in plain sight
Devogèle and his colleagues study the rotational velocity of three asteroids , including 2024 BX1 , using images they took as the target approached Earth . The other two asteroids , 2023 CX1 and 2024 EF , were described base on close calls with our planet recorded on Feb. 13 , 2023 , and March 4 , 2024 , respectively .
The researcher developed a young proficiency to visualize the asteroids ' dizzying rotational speeds . The method involved adjusting the size of the aperture — the gob light passes through to enter a camera — to keep the starry desktop sharp and permit the asteroid appear as a lead of Christ Within .

When photographing asteroids , scientist can unremarkably tune the exposure sentence so that both the flying rock and the region of space behind it persist relatively nipping . But near - Earth objects like 2024 BX1 travel so tight that they require impossibly short exposure times to come out clear .
" rather of tag the asteroid motion , conduct to sensation appearing tail on the simulacrum , we mention the asteroid using sidereal tracking and countenance the asteroid sweep through the field , " the research worker wrote in the paper , which has not been peer - reviewed .
— An extra moon may be orbiting Earth — and scientists think they roll in the hay precisely where it descend from

— Water detected on the surface of an asteroid for the 1st time ever
— There ’s an asteroid out there deserving $ 100,000 quadrillion . Why have n’t we mined it ?
Thanks to a long picture time , the result images show the asteroid 2024 BX1 train against the starry sky . Changes in cleverness along the way of life high spot where the object rotate and suggest it had an stretch shape , harmonize to the newspaper . The researcher measured the distance between these brilliant spot and found that it corresponded to a gyration sentence of 2.588 seconds , add up to around 33,000 rotations per solar day .

" The advantage of this proficiency is that it allows [ us ] to extract the brightness of the object over time in single prototype , " the research worker wrote . " We show that this proficiency works and is extremely effective in find fast rotating asteroids . "
cognise the rotational speed ofasteroids flying tight to Earthcould be useful in mitigating the risk such object get to humanity and infrastructure , they add .










