When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it form .
Around 4 billion class ago , an enormous asteroid that was at least 10 times large than the quad rock music that wiped out the dinosaur smash into Jupiter ’s monolithic icy moonshine , Ganymede . The cataclysmic collision was so devastating it created the with child impact volcanic crater in thesolar systemand knocked the supersized artificial satellite off its axis , new simulations show .
Ganymede isJupiter ’s third - closest major moon , orb the gaseous state giant or so once every seven solar day . It has a diameter of 3,270 miles ( 5,260 kilometers ) , consort toNASA , making it the most monumental ofthe solar system of rules ’s many moonsand larger than the planetMercury . Just like Earth ’s moon , Ganymede is tidally lock , meaning the same side constantly confront Jupiter ’s swirling , tempest - covered surface . Researchers believe the moon has a approximately 60 - mile - deep ( 100 km ) ocean hidden far below its icy surface .

A new study suggests that Jupiter’s moon Ganymede was knocked off its axis 4 billion years ago when a 90-mile-wide asteroid slammed into the planet.
In the 1980s , researcher discovered that large parts of the moon ’s control surface were covered with concentric ring of minute trench , or furrows , ring the remains of what looked like a declamatory impingement crater on Ganymede ’s far side ( the side facing aside from Jupiter ) . Photos from subsequent visit spacecraft , such asNASA ’s New Horizons probe , revealed the moon ’s scarred open is the potential resultant role of a massive asteroid collision that occurred around 600 million eld after the solar organization forge .
In the new study , publish Sept. 3 in the journalScientific Reports , researcherNaoyuki Hirata — an astronomer and planetary scientist at Kobe University in Japan — reconstructed Ganymede ’s ancient asteroid impact using calculator simulations based on the moon ’s furrows . This enable Hirata to incisively calculate the sizing of the rock that smashed into Ganymede for the first time . The simulation also showed how the impact in all probability knocked the lunar month off its original axis .
Related : The 10 weirdest Moon in the solar system
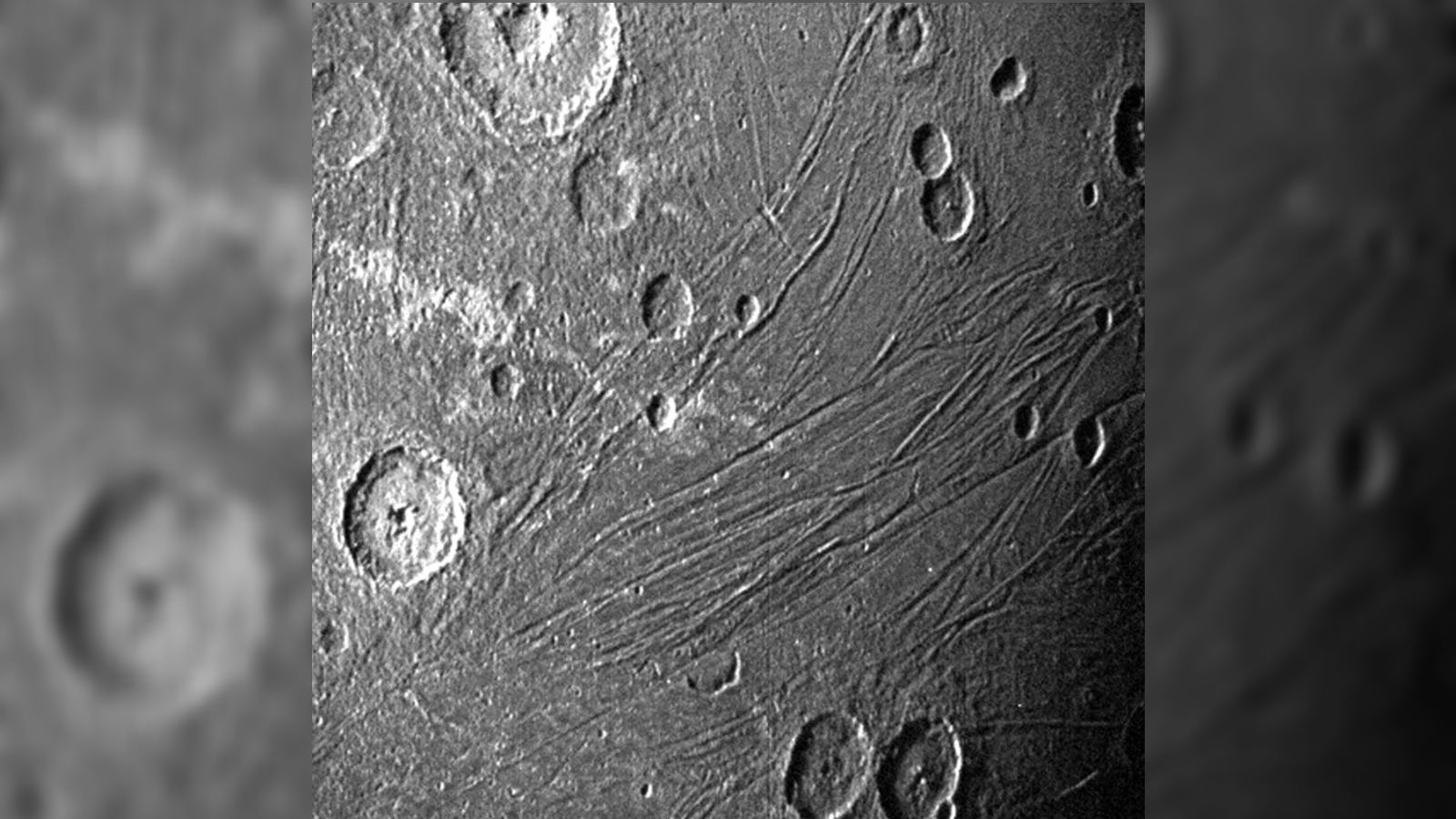
Photos of Ganymede’s far side show the concentric furrows etched into its surface by the ancient collision.
Hirata estimated that the initial encroachment volcanic crater was up to 1,000 sea mile ( 1,600 km ) wide , making it 10 time all-inclusive thanEarth ’s largest wallop construction — theVredefort Craterin South Africa . This means Ganymede ’s volcanic crater was the largest known impact crater in the solar system ’s history . However , it did not continue this size for long as debris from the event quickly fall back to the moonshine ’s surface and filled in most of the hole , Hirata write .
Based on the size of the crater , Hirata guess the asteroid creditworthy for have it would have been around 93 miles ( 150 kilometers astray ) — or about as long as the land of Delaware . That would make it somewhere between 10 and 15 multiplication large than the Chicxulub meteor , which slammed into what is now Mexico around 66 million year ago andwiped out up to 80 % of animal species on Earth , including all non - avian dinosaur .
Some medium outlets have quoted aKobe University news releasereporting that the asteroid was up to 20 times bombastic than the Chicxulub meteor . However , this does not array with the numbers share in the young study .
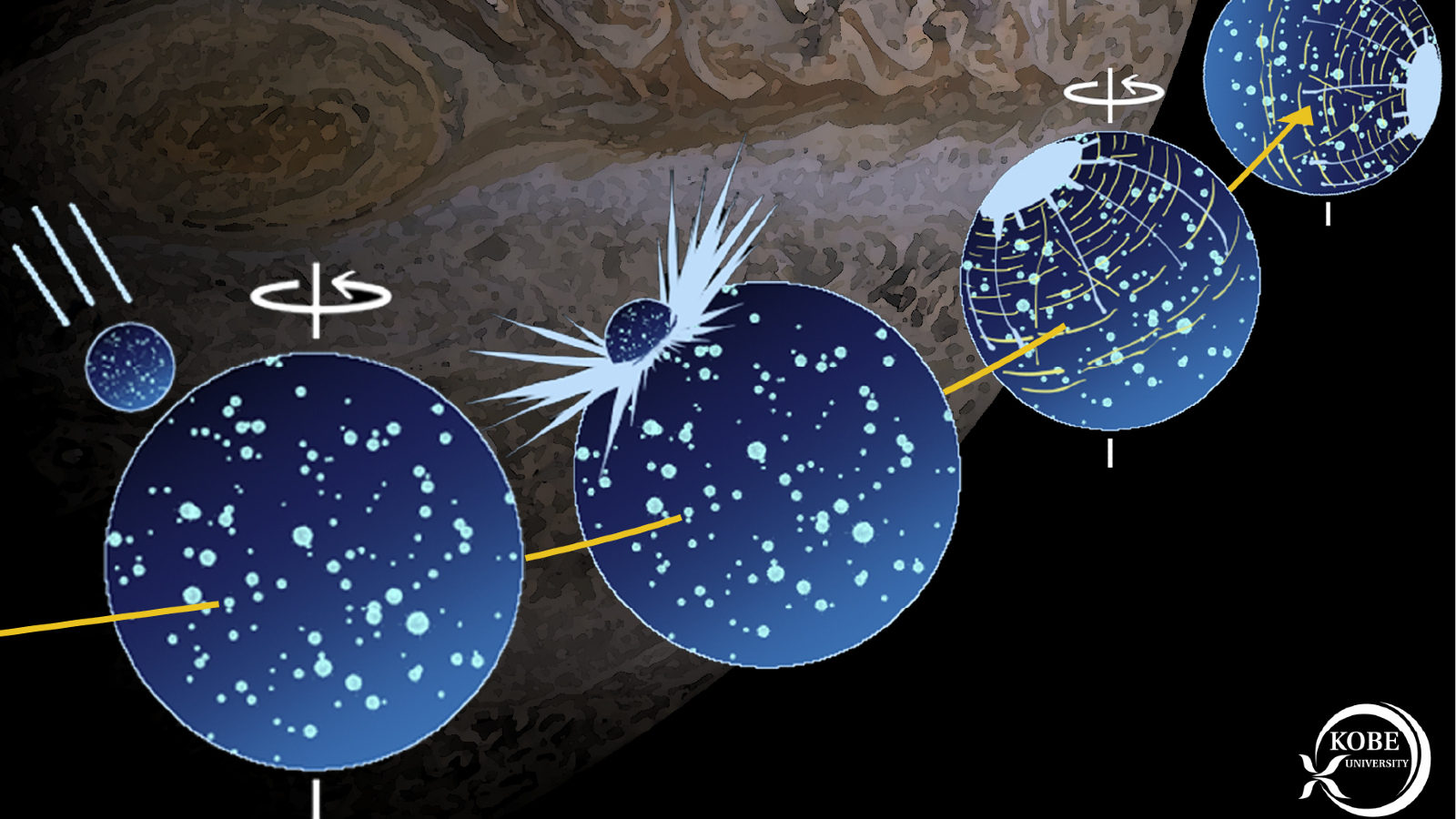
Simulations show that Ganymede was knocked off its axis by the asteroid strike.
The simulations also divulge how the encroachment reposition Ganymede ’s tidal axis vertebra away from its rotational axis , wee-wee it tilt relative to Juptier . Earth ’s arctic axis of rotation was cant in a similar room around 4.5 billion year ago when a Mars - sizing protoplanet , identify Theia , smashed into our major planet and created the Sun Myung Moon . This is why we have unlike season throughout the year .
Interestingly , the pretence showed that no matter of where the asteroid struck Ganymede ’s airfoil , the shock crater would always terminate up in the same patch on the moon ’s far side from Jupiter thanks to the gravitative effects of the debris ejected into outer space by the hit .
The new findings avail satisfy in details about an important chapter in Ganymede ’s account . However , they also raise new questions about how this wallop modify the evolution of the Jovian moon and its interior — especially its conjecture subsurface ocean .

— water system vaporisation notice on Brobdingnagian Jupiter ’s moon Ganymede for first time
— NASA finds constitutive compounds seeping up from hidden ocean on Jupiter ’s icy moon Ganymede
— Jupiter ’s largest moon reveal in arresting point in first close - up images in 20 yr

" The giant impact must have had a significant impact on the former evolution of Ganymede , but the thermal and structural effects of the impact on the inside of Ganymede have not yet been investigated at all , " Hirata said in astatement . Further research is needed to plow this , he added .
The answers to Hirata ’s questions could descend in 2034 when theEuropean Space Agency ’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer ( JUICE ) probe is due to carry out a closelipped flyby of Ganymede . The state - of - the - art probewas launch in April 2023and completed thefirst of three project slingshot manoeuvre around the Earth - moon systemon Aug. 21 . The spacecraft will arrive at Jupiter in 2031 .
Cloudy with a chance of mushballs : Jupiter ’s giant storms include softball game sizing hailstones made of ammonia water

Powerful solar flatus squish Jupiter ’s magnetic domain ' like a jumbo squash ball '
The constant surveillance of modernistic life could worsen our brain function in way we do n’t in full understand , disturb studies suggest






