When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
The brain activity of people who are easily injure is dissimilar from that of people who are n’t as prone to getting rag up , a new report hint .
Many multitude would consider a pretermit text from a good friend to be a harmless , inadvertent act . peradventure they ’re busy , or perhaps they read it and simply forgot to reply . However , some people are more probable to misunderstand this activity as strong-growing or uncongenial , reckon they ’re perhaps ignoring you on purpose . Scientists call this trend to get into the worst in people " hostile ascription preconception , " and it can make people more likelyto be strong-growing , experiencepoor genial healthand struggle tomaintain sizeable human relationship .

People with “hostile attribution bias” may interpret a friend not replying to a text as a hostile action, and this response is orchestrated by a specific part of their brain, a new study suggests.
A new study suggests that people with hostile ascription bias display a singular signature tune of brain activity in part of the brain called theventromedial prefrontal cortex(vmPFC ) when another person ’s action ensue in a disconfirming outcome for them . Among other function , the vmPFC is postulate in excited regulation , determination - fashioning and self - perception .
" The VmPFC is a high-pitched - order brain realm that integrates sensory information about the external world with internal state of matter and beliefs,“Yuan Chang Leong , co - older subject area writer and an associate professor of psychology at the University of Chicago , say Live Science in an email . In other words , the vmPFC helps control how we react to societal situation based on our already make bias .
concern : Neuralink crisp implant into human brain for the 1st time , Elon Musk says
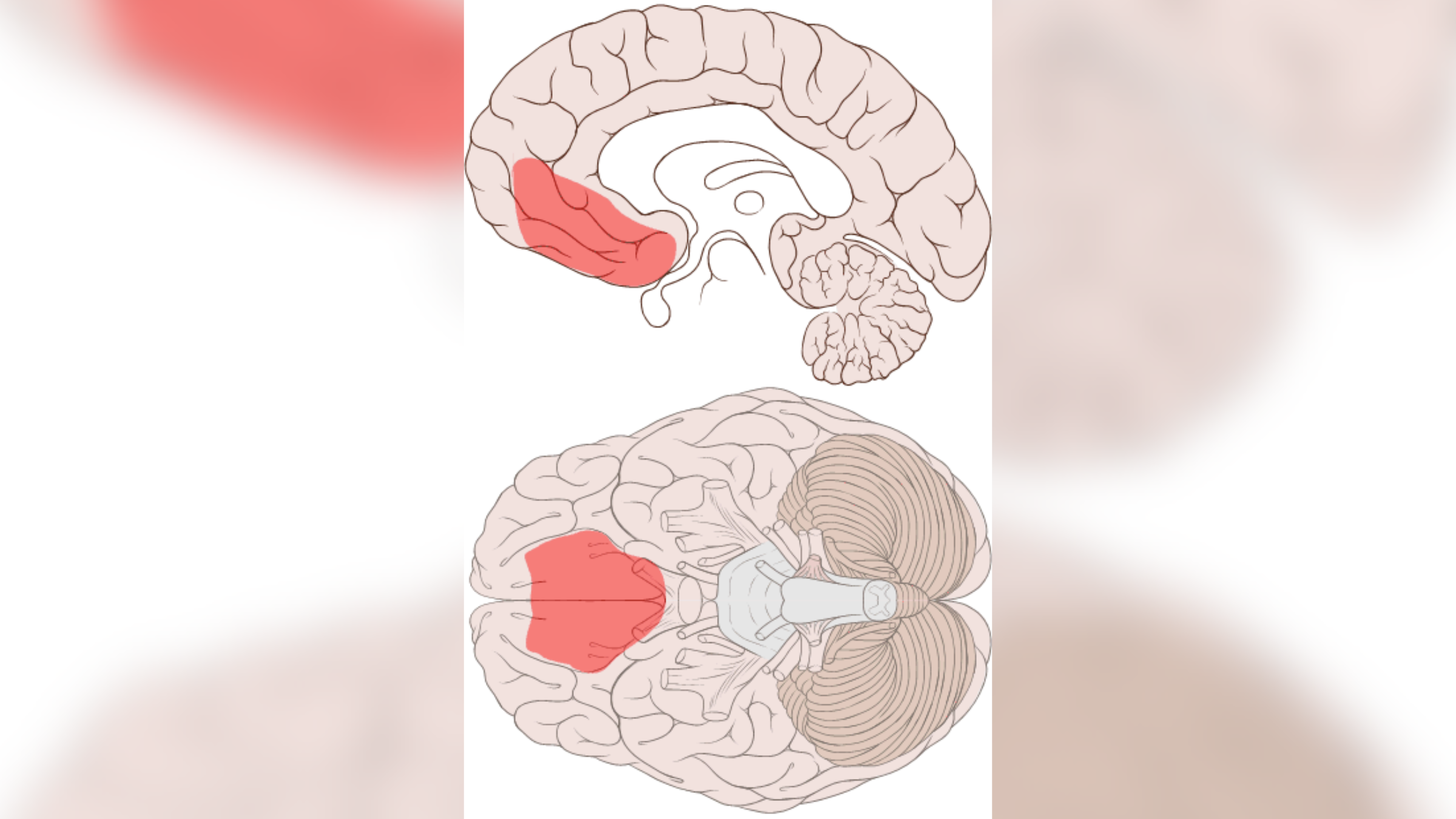
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex, illustrated in red above, is located in the frontal lobe of the brain.
The results of the new cogitation , put out Monday ( Feb. 5 ) inThe Journal of Neuroscience , suggest that the vmPFC plays a persona in govern a person ’s interpretation of a social billet by integrating information about the unfold scenario with their preconceived whimsey and memories , Leong say .
see the mentality mechanisms behind hostile ascription bias could fetch scientists a whole step nigher to developing ways of mitigating it — for example , through more targeted interventions to reduce aggressive conduct and promote levelheaded relationships , the writer indite in the paper .
In the bailiwick , 58 volunteer listened to audio recordings of mass describing 21 suppositional social scenario . On average , the miniskirt - podcasts were around 40 irregular long and involve a character executing action toward the listener — the study participant — that could have a negative issue on them . For instance , in one scenario , a professor forget to write a letter of testimonial for the player after they ’d agreed to do so .

After listening , the participants range whether they thought these action were knowing and unfriendly — for representative , the prof was purposefully retaliating against them — or unintentional , meaning they simply forgot to write the letter .
Throughout the experiment , each participant wore a fitted crown on their headway that measured their brain activeness using a proficiency calledfunctional near - infrared spectroscopy(fNIRS ) . The researchers found that , during the recordings , fluctuations in brain jail cell activity in the vmPFC was similar among someone with standardised point of unfriendly attribution preconception and differ in those without the tendency .
This propose that this bias has steadily shaped how their brains react to such scenarios , drive the activity to look the same , Leong said . Using the brain - activity readouts , the authors could bode with 75 % accuracy whether someone had low or eminent hostile ascription bias , based on the pattern of activity in their vmPFC .

— Brain signature of desire reveal in lovesick rodents , and it may be in people , too
— Universal physical process that wires the brain is reproducible across species
— resiliency is a acquirement that can be train , a psychologist explains

The authors also regain that participant who exhibited less hostile attribution bias scored higher on a survey that assessed another psychological conception , calledattribution complexness . This measures how likely someone is to conceive that there may be many complex explanations for certain deportment .
As such , " fostering attributional complexness could be a potential strategy to mitigate uncongenial attribution preconception and at last raise healthier societal interactions , " the authors write in the paper .
Ever wonder whysome people make muscle more easy than othersorwhy freckle come out in the Dominicus ? Send us your questions about how the human soundbox works tocommunity@livescience.comwith the open line of reasoning " Health Desk Q , " and you may see your inquiry answered on the web site !















