When you purchase through links on our internet site , we may make an affiliate direction . Here ’s how it works .
Neanderthals , which melt from the archeological record some 40,000 years ago , have long been debate our closest evolutionary relative . But almost since the first uncovering of Neanderthal remains in the 1800s , scientists have been arguing over whether Neanderthals name their own mintage or if they ’re just a subset of our own species , Homo sapiens , that has since gone extinct .
So what does the science say ? In particular , what does the genetic evidence , which did n’t exist back when many early hominins were first chance on , show ?

Neanderthal skeletons look notably different from those of modern humans, and yet genetic evidence shows that the two interbred, indicating they could be members of the same species.
The question of whether Homo sapiens neanderthalensis can be take the same species as modern humans is complicated byour understanding of what a species is , Jeff Schwartz , a physical anthropologist and prof emeritus at the University of Pittsburgh , told Live Science . The most common definition , called the biological coinage construct , key a species as a group of individuals that can interbreed in nature and produce viable young . But even today , several odd hybridspoke holes in this definition .
" Horses and donkeys can breed , but the mules they give nascence to are sterile , and so the two are consider to be different coinage , " Schwartz said . But other combinations do produce executable offspring . These let in the liger ( a crown of thorns between a lion and a tiger ) and the beefalo ( a cross between a cow and an American bison ) .
For a retentive time , scientists did n’t know whether Neanderthals and modern homo interbred , so this definition was n’t particularly illuminating . Instead , early assessment were made based on Neanderthal material body , which is dissimilar enough fromH. sapiensthat specialists canoften distinguish bones from the two grouping . Neanderthals had a tenacious , humbled skull with a bonier forehead and a less - pronounced chin thanH. sapiens , for example , and their bodies were stockier .
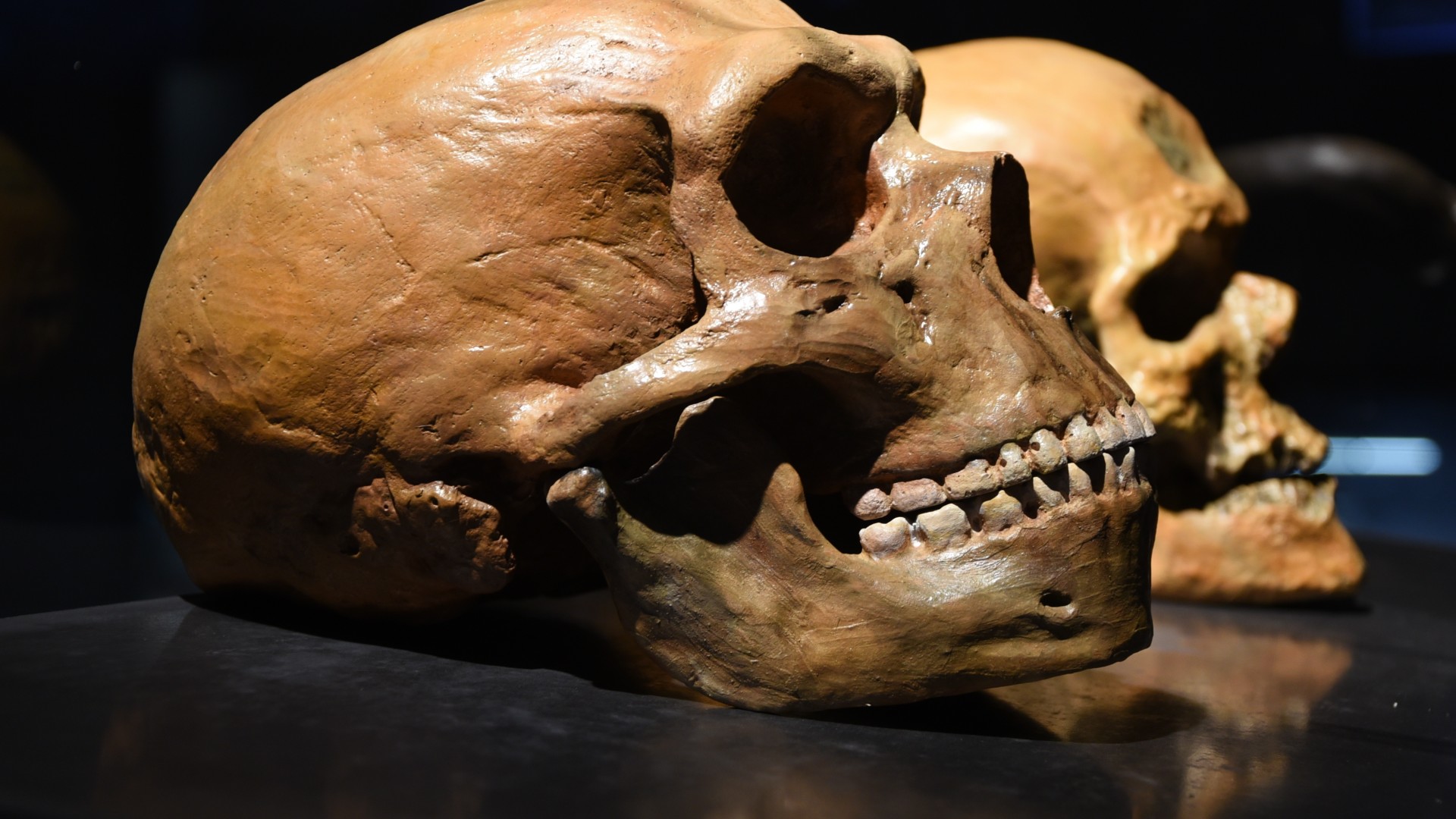
Neanderthal skeletons look notably different from those of modern humans, and yet genetic evidence shows that the two interbred, indicating they could be members of the same species.
Related : How fresh were the Neanderthals ?
Because of this , in 1864 , Neanderthals were first class as their own species , H. neanderthalensis . But as more other human relatives were observe — such asH. erectusin 1891,H. heidelbergensisin 1907 andH. habilisin 1960 — their relationship to one another became progressively complex . compare with other species , Neanderthals seemed much more " human , " Schwartz said . Recent research has suggest that both mathematical group hadsimilar auditory and vocal ability , and controversial finds trace that Neanderthals may haveburied their deadand madejewelryandart .
In 1962 , a group of anthropologists , geneticist and behaviorists met in Austria to draft and vote on an evolutionary account of human relation based on the species that had been discovered at the time . Their resulting manuscript , called " Classification and Human Evolution , " placed Neanderthals underH. sapiensas a race , orH. sapiens neanderthalensis . " And when I was in college , that ’s what I was taught , " Schwartz allege .
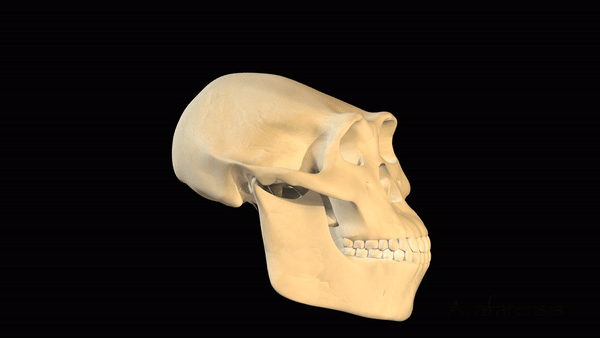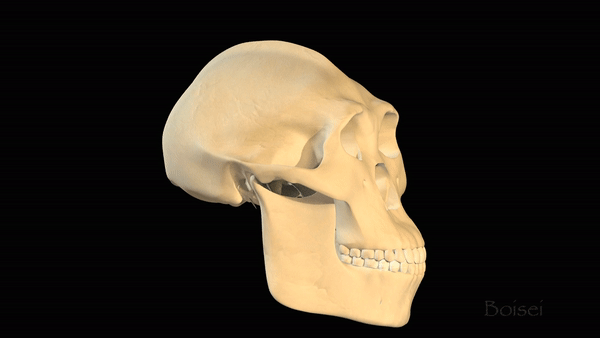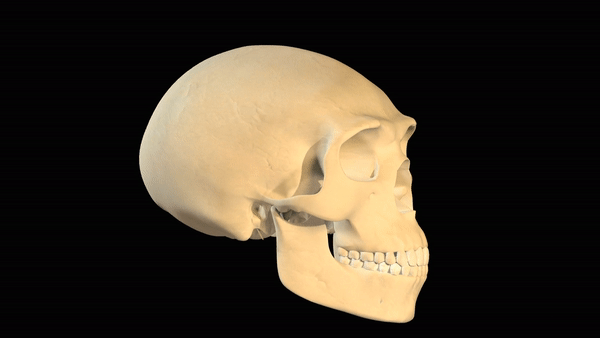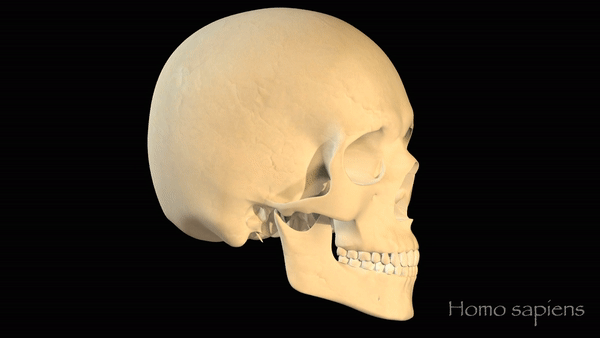
A series of morphing skulls, includingAustralopithecus afarensis,Australopithecus boisei(also known asParanthropus boisei),Homo erectus, Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) and modern humans (Homo sapiens).
It was only later , in the seventies and eighties , that Neanderthals were reclassified as their own species based on young analyses , and that continue the most mutual identification ascertain today .
But a 2010 discovery judder thing up yet again : An international team of lots of researcherspublished the first draught of the Neanderthalian genome , based on three individuals , and compared it with that of modern human being . The authors found hints of the Neanderthal signature tune in the human genome , suggesting that Neandertals mixed with modern human antecedent at least 120,000 twelvemonth ago . Dozens of papers have since sustain this and find that around 47,000 years ago , mix occur across multiple propagation for about 7,000 years.in time .
" The implication is clear : Neanderthals and humans were interbreeding,“Jaume Bertranpetit , an evolutionary life scientist at the Pompeu Fabra University in Barcelona , Spain , recite Live Science , tot up that Neanderthals andH. sapiensalso interbred with another grouping of former hominid , the Denisovans . It ’s possible , then , that all three could represent dissimilar versions of the same species , he said .

Bertranpetit pointed to modern humans as an good example . People around the world have obtrusive differences in stature or cutis , hairsbreadth and eye color , but we ’re signally exchangeable from a transmissible standpoint . The amount of genetic variation between any two individualsis only about 0.1 % , meaning that only one base pair out of every 1,000 will be different . In comparison , the 2010 composition showed that the Neanderthal genome was 99.7 % identical to that of five present - day human race .
" To have big difference in morphology does not mean you need to have giving dispute ingenetics ; it just imply you ask some differences in specific cistron , " Bertranpetit said . " So this idea that they were dissimilar species does n’t make any sensation to me as a geneticist . "
Schwartz does n’t conceive the genetic grounds has necessarily settled the argumentation , but he has no misgiving about the rigor of the work the other groups have done . Moving forward , he advocates for an interdisciplinary approach that does n’t pose genetics as the final say . " We need a holistic approach , and we ca n’t keep pitting one field of study against another , " he order . " We have to get together and figure it out . "

— When did Homo sapiens first appear ?
— How many early human species existed on Earth ?
— How smart were Neanderthals ?

A2024 paper , meanwhile , reason thatH. sapiensand Neanderthals should be relegate as different species so we can better understand humans ' evolutionary chronicle . While the two add up from the same parent population in Africa , Neanderthals entered Eurasia at least 400,000 yr ago , sacrifice them sizeable sentence to evolve singly , including better ways to hold out in colder and less sunny climates that altered their genes and appearance , the authors publish .
When it come to deciding whetherH. sapiensand Neanderthals are a freestanding coinage , it ’s best to habituate a theoretical account that " meet speciation as an evolutionary physical process that starts in outer space , thereby involving a geographic dimension , and progresses in metre , " the authors write in the study . After all , " incremental assemblage of relevant characters " are steps in the evolutionary process as two related mathematical group diverge into two descendent species , they noted .











